| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Prostaglandin I2 synthase inhibitor 9α[2]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
U-51605 (3 μM) 可抑制乙酰胆碱诱导的内皮依赖性收缩[1]。U-51605 (0.5、1、3、10 μM) 可增加乙酰胆碱诱导的 PGE2 和 PGF2α 释放[1]。U-51605同时抑制血栓素合成和血小板悬液聚集。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
前列腺素IP受体拮抗剂4,5-二氢-N-[4-[[4-(1-甲基乙氧基)苯基]甲基]苯基]-1H-咪唑-2-胺(CAY10441)和前列腺素I2合酶抑制剂9α,11α-偶氮前列腺素-5Z,13E-二烯-1-酸(U-51605)对NOR3诱导的视网膜血管舒张反应显示出类似的预防作用。CAY10441和U-51605均未对NOR3的降压反应产生任何显著影响。NOR3增强了培养的人视网膜微血管内皮细胞释放前列腺素I2,环氧化酶-1抑制剂SC-560几乎完全消除了NOR3诱导的前列腺素I2释放,但环氧化酶-2抑制剂NS-398没有完全消除。然而,NOR3并没有增加人肠微血管内皮细胞释放前列腺素I2。这些结果表明,NO通过视网膜血管系统中的环氧化酶-1/前列腺素I2/前列腺素IP受体信号机制发挥其舒张作用[2]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Stock solutions of U-51605 in methyl acetate (5 mg/ml) and CAY10441 in dimethyl sulfoxide (20 mg/ml) were diluted in saline, separately. The final concentrations of methyl acetate and dimethyl sulfoxide in these solutions were 12% and 45%, respectively. [2]
Indomethacin (5 mg/kg), U-51605 (0.6 mg/kg) or CAY10441 (6 mg/kg) was administered i.v., and the methoxamine infusion was started 45 min later (15 min for indomethacin). The timing of administration and dose of each compound were selected based on previous reports (Ogawa et al., 2007, Ogawa et al., 2009, Gohin et al., 2011). After hemodynamic parameters had reached a stable level (~15 min later), NOR3 (0.5–10 μg/kg/min) or prostaglandin I2 (0.005–0.3 μg/kg/min) was injected into the femoral vein, using a syringe pump. [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
The comparative effects of three so called “thromboxane-synthetase- inhibitors” (imisazole, N-0.164, and U-51065) on arachidonate metabolism and on platelet aggregation were studied. All three compounds blocked platelet microsomal thromboxane synthesis from prostaglandin endoperoxides without affecting platelet adenyl cyclase. Imidazole, blocked thromboxane synthesis in intact platelets either from arachidonic acid or PGH2, without affecting aggregation. U-51605 simultaneously inhibited thromboxane synthesis and platelet suspension aggregation. N-0164 inhibited aggregation probably at extracellular sites, at concentrations that did not alter arachidonate or PGH2 metabolism. High concentrations of N-0164 simultaneously inhibited PG cyclo-oxygenase and thromboxane synthetase. The lack of specificity of these compounds requires that other actions of these compound must be considered when they are used as pharmacological tools to inhibit thromboxane synthetase. [2]
The soluble guanylyl cyclase/cGMP system plays an important role in the vasodilator response to nitric oxide (NO) in various vascular beds. However, in rat retinal arterioles, the cyclooxygenase-1/cAMP-mediated pathway contributes to the vasodilator effects of NO, although the specific prostanoid involved remains to be elucidated. In the present study, we investigated the role of prostaglandin I2 and its receptor (prostanoid IP receptor) system in NO-induced vasodilation of rat retinal arterioles in vivo. Fundus images were captured using a digital camera that was equipped with a special objective lens. Changes in diameter of retinal arterioles were assessed. The NO donor (±)-(E)-4-ethyl-2-[(E)-hydroxyimino]-5-nitro-3-hexenamide (NOR3) increased the diameter of retinal arterioles but decreased systemic blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment of rats with indomethacin, a non-selective cyclooxygenase inhibitor, markedly attenuated the retinal vasodilator, but not depressor responses to NOR3. The prostanoid IP receptor antagonist 4,5-dihydro-N-[4-[[4-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl]methyl]phenyl]-1H-imadazol-2-amine (CAY10441), and the prostaglandin I2 synthase inhibitor 9α,11α-azoprosta-5Z,13E-dien-1-oic acid (U-51605), both showed similar preventive effects against the NOR3-induced retinal vasodilator response. Neither CAY10441 nor U-51605 showed any significant effects on the depressor response to NOR3. NOR3 enhanced the release of prostaglandin I2 from cultured human retinal microvascular endothelial cells and the NOR3-induced prostaglandin I2 release was almost completely abolished by the cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitor SC-560, but not by the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor NS-398. However, NOR3 did not increase the release of prostaglandin I2 from human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells. These results suggest that NO exerts its dilatory effect via cyclooxygenase-1/prostaglandin I2/prostanoid IP receptor signaling mechanisms in the retinal vasculature. [2] In the present study, we used U-51605 as an inhibitor of prostaglandin I2 synthase. However, the compound can inhibit thromboxane synthase (Gorman et al., 1977) and act on prostanoid TP receptors as a partial agonist (Gluais et al., 2005). The results clearly indicated that U-51605 reduced the NOR3-induced vasodilation of retinal arterioles to a similar degree as the prostanoid IP receptor antagonist CAY10441. However, we cannot exclude the possibility that effects of U-51605 on the thromboxane A2/prostanoid TP receptor system could also contribute to its inhibitory effect on NOR3-induced responses. Unfortunately, selective inhibitors for prostaglandin I2 synthase are not currently available. In the future, when highly selective inhibitors for this enzyme are developed, these issues should be addressed. |
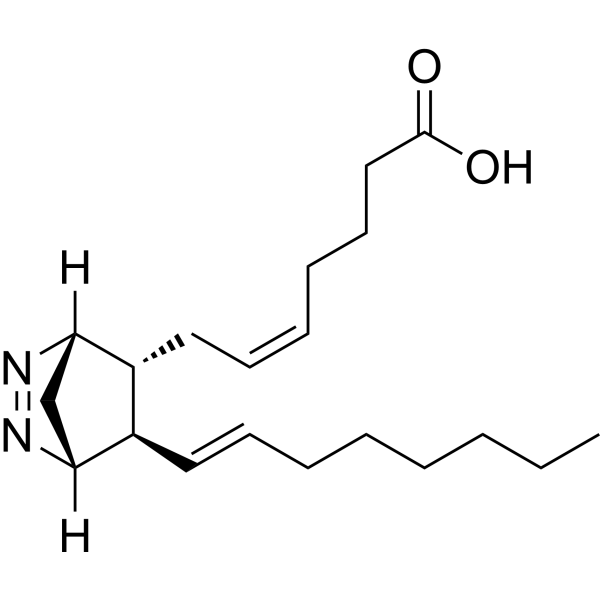
| 分子式 |
C20H32N2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
332.48
|
| CAS号 |
64192-56-9
|
| PubChem CID |
6438575
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solids at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
463.1±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
233.8±25.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.56
|
| LogP |
4.68
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
484
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
3
|
| SMILES |
C(O)(=O)CCC/C=C\C[C@@H]1[C@@H](/C=C/CCCCCC)[C@@]2([H])C[C@]1([H])N=N2
|
| 别名 |
9,11-Azoprosta-5,13-dienoic acid; U 51605; 64192-56-9; (Z)-7-[(1R,4S,5R)-1-[(E)-Oct-6-enyl]-2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-en-5-yl]hept-5-enoic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0077 mL | 15.0385 mL | 30.0770 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6015 mL | 3.0077 mL | 6.0154 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3008 mL | 1.5038 mL | 3.0077 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。