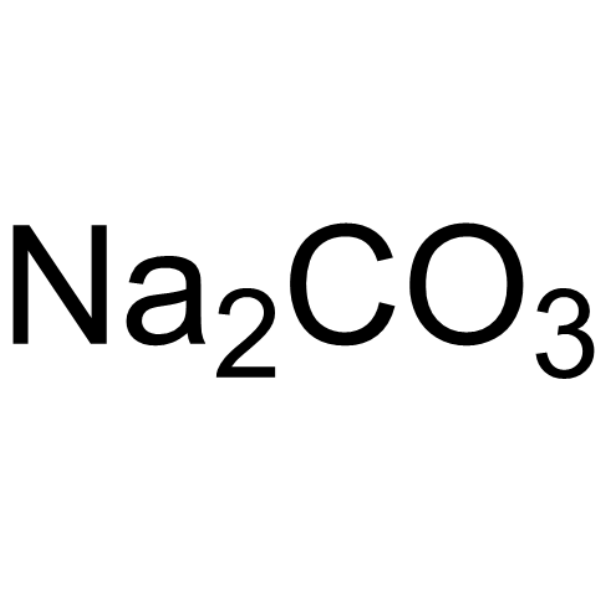
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
可用于去除外周膜蛋白的缓冲液的一种成分是碳酸钠。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The uptake of sodium, via exposure to sodium carbonate, is much less than the uptake of sodium via food. Therefore, sodium carbonate is not expected to be systemically available in the body. Furthermore, an oral uptake of sodium carbonate will result in a neutralization in the stomach due to the gastric acid. Filtered and reabsorbed by the kidney; less than 1% of filtered bicarbonate is excreted. Distribution occurs naturally and is confined to the systemic circulation. The major extracellular buffer in the blood and the interstitial fluid of vertebrates is the bicarbonate buffer system ... . Carbon dioxide from the tissues diffuses rapidly into red blood cells, where it is hydrated with water to form carbonic acid. This reaction is accelerated by carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme present in high concentrations in red blood cells. The carbonic acid formed dissociates into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. Most of the bicarbonate ions diffuse into the plasma. Since the ratio of H2CO3 to dissolved CO2 is constant at equilibrium, pH may be expressed in terms of bicarbonate ion concentration and partial pressure of CO2 by means of the Henderson-Hasselbach equation: pH = pk + log [HCO3-]/aPCO2. The blood plasma of /humans/ normally has a pH of 7.40. Should the pH fall below 7.0 or rise above 7.8, irreversible damage may occur. Compensatory mechanisms for acid-base disturbances function to alter the ratio of HCO3 - to PCO2 , returning the pH of the blood to normal. ... The uptake of sodium, via exposure to sodium carbonate, is much less than the uptake of sodium via food. Therefore, sodium carbonate is not expected to be systemically available in the body. Furthermore ... an oral uptake of sodium carbonate will result in a neutralization in the stomach due to the gastric acid. Metabolism / Metabolites None. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Sodium carbonate is a grayish-white powder of lumps containing up to 99% sodium carbonate. Sodium carbonate is used for the production of glass, soaps and detergents and other chemicals and it also used by the 'metals and mining' industry and the 'pulp and paper' industry. Sodium carbonate is not only used by industry but is also used by consumers. It may be used directly in solutions of sodium carbonate for soaking of clothes, dishwashing, floor washing and for degreasing operations but it is also present in a large number of consumer products like cosmetics, soaps, scouring powders, soaking and washing powders. Sodium carbonate is also a food additive. HUMAN STUDIES: Aqueous solutions are strongly alkaline, concentrated solutions tend to produce local necrosis of mucous membranes. An aqueous solution, 50% weight/volume, of sodium carbonate was applied to the intact and abraded skin of human volunteers. The sites were examined at 4, 24, and 48 hr and scored for erythema, edema, and corrosion. The solution produced no erythema and edema. The human skin showed tissue destruction at the abraded sites. Ingestion of large quantities may produce corrosion of GI tract, vomiting, diarrhea, circulatory collapse, death. Dusts of vapors of sodium carbonate may cause irritation of mucous membranes with subsequent coughing and shortness of breath. It is a primary irritant at concentrations below 15% and caustic at concentrations above approximately 15% depending on contact time, areas of exposure, and other factors. ANIMAL STUDIES: An aqueous solution, 50% weight/volume, of sodium carbonate was applied to the intact and abraded skins of rabbits, guinea pigs. The sites were examined at 4, 24, and 48 hr and scored for erythema, edema, and corrosion. The solution produced no erythema and edema. The rabbit skin showed tissue destruction at the abraded sites. Dry, powdered sodium carbonate, as 25% to 75% of a mixture with dry sodium sulfate, applied to eyes of rabbits and monkeys in a systematic study was judged "corrosive" or "harmful" to both species, whether or not followed by irrigation at two minutes after application. However, most monkey eyes exposed to 50% mixture showed little or no persistent injury 21 days after exposure. A repeated dose inhalation study was conducted in male rats exposed to a 2% aqueous sodium carbonate aerosol for 4 hr/day, 5 days/week for 3.5 months. Pulmonary ascorbic acid levels were decreased. Deviations in lungs were found in control and experimental animals but only experimental animals displayed hyperplasia and desquamination of bronchiolar epithelium, and perivascular edema. Other pulmonary changes included thickening of alveolar walls, hyperemia and lymphoid infiltration but these changes were also observed in about 50% of the controls. Aqueous solutions of sodium carbonate were administered daily via oral intubation to pregnant mice at doses ranging from 3.4 to 340 mg/kg bw during days 6-15 of gestation. The test substance produced no unwanted effects. Similar negative results were reported for rats and rabbits for daily doses from 2.45-245 mg/kg bw and 1.79-179 mg/kg bw, respectively. An in vitro mutagenicity test with bacteria was negative. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: Sodium carbonate at 10 mg/L, reduced oxygen consumption in Caspian Sea shrimp in all of the observation periods, except days 3 and 10, when it was higher than the control. At 100 mg/L, oxygen consumption was higher during 1st 5 days and thereafter reduced gradually. Sodium carbonate is naturally occurring and commonly found in soil and water in the environment suggesting that releasing low levels of sodium carbonate would not be expected to adversely effect wildlife or water resources. Toxicity Data LC50 (rat) = 2,300 mg/m3/2hr Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 2.8 g/kg LD50 Rat oral 4090 mg/kg LC50 Rat inhalation 2300 mg/cu m/2 hr LD50 Rat (Wistar) oral (gavage) 2800 mg/kg bw /Sodium carbonate monohydrate/ For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for Sodium carbonate (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Sodium carbonate is an organic sodium salt and a carbonate salt.
Sodium Carbonate is the disodium salt of carbonic acid with alkalinizing property. When dissolved in water, sodium carbonate forms carbonic acid and sodium hydroxide. As a strong base, sodium hydroxide neutralizes gastric acid thereby acting as an antacid. Sodium Carbonate is the disodium salt of carbonic acid with alkalinizing property. When dissolved in water, sodium carbonate forms carbonic acid and sodium hydroxide. As a strong base, sodium hydroxide neutralizes gastric acid thereby acting as an antacid. Soda is a beverage consisting of carbonated water and a flavoring. See also: Carbonate Ion (has active moiety); Citric acid; magnesium oxide; sodium carbonate (component of); Sodium carbonate; sulfur; tellurium (component of) ... View More ... Drug Indication Used topically for dermatitides, mouthwash, vaginal douche; veterinary use as emergency emetic.Occasionally, for dermatitides topically as a lotion. Medication (Vet): In solution to cleanse skin, in eczema, to soften scabs of ringworm. Mechanism of Action Carbon dioxide from the tissues diffuses rapidly into red blood cells, where it is hydrated with water to form carbonic acid. This reaction is accelerated by carbonic anhydrase, an enzyme present in high concentrations in red blood cells. The carbonic acid formed dissociates into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. Most of the bicarbonate ions diffuse into the plasma. Since the ratio of H2CO3 to dissolved CO2 is constant at equilibrium, pH may be expressed in terms of bicarbonate ion concentration and partial pressure of CO2 by means of the Henderson-Hasselbach equation: pH = pk + log [HCO3-]/aPCO2 Therapeutic Uses Used topically for dermatitides, mouthwash, vaginal douche; veterinary use as emergency emetic. Occasionally, for dermatitides topically as a lotion. Medication (Vet): Has been used as an emetic. In solution to cleanse skin, in eczema, to soften scabs of ringworm. Sodium bicarbonate infusion is widely recommended ... for patients who present with self-poisoning from tricyclic antidepressives. Cardiac conduction disorders could also be treated or prevented by means of such an infusion. The scientific basis for these recommendations was investigated by using Medline to search for publications about clinical studies that supported the use of sodium carbonate; 111 articles were scrutinized. Observational studies and case reports mention a rapid improvement in hypotension and cardiac arrhythmias following the administration of sodium bicarbonate. Results from animal experiments are contentious; it is not clear whether alkalinization or the administration of extra sodium causes the effect. Randomized studies in patients have not been carried out. As the toxicity of sodium bicarbonate is low, and its potential benefit appears to be high, /the authors/ recommend its use, despite the lack of scientific evidence. No recommendations concerning dosing, concentration and the length of the therapy can be provided on the basis of the literature. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Sodium carbonate (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Alkalizing buffering action: Sodium bicarbonate is an alkalinizing agent that dissociates to provide bicarbonate ion. Bicarbonate in excess of that needed to buffer hydrogen ions causes systemic alkalinization and, when excreted, urine alkalinization as well. Oral antacid action: Taken orally, sodium bicarbonate neutralizes stomach acid by the above mechanism. |
| 分子式 |
NA2CO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
105.99
|
| 精确质量 |
105.964
|
| CAS号 |
497-19-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
144-55-8 (Parent)
|
| PubChem CID |
10340
|
| 外观&性状 |
Grayish-white powder or lumps containing up to 99% sodium carbonate
White hygroscopic powder White ... small crystals or monoclinic powder |
| 密度 |
2.53
|
| 沸点 |
1600°C
|
| 熔点 |
851 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
169.8ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.535
|
| tPSA |
63.19
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
0
|
| 重原子数目 |
6
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
18.8
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)[O-]
|
| InChi Key |
CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/CH2O3.2Na/c2-1(3)4;;/h(H2,2,3,4);;/q;2*+1/p-2
|
| 化学名 |
disodium;carbonate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 9.4349 mL | 47.1743 mL | 94.3485 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.8870 mL | 9.4349 mL | 18.8697 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.9435 mL | 4.7174 mL | 9.4349 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。