| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| 100g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Glycine transporter type 1 (GlyT1) inhibitor; Positive allosteric modulator of NMDA receptors [1][2]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Sarcosine 增强大鼠海马切片中NMDA受体介导的兴奋性突触后场电位(fEPSPs)。该增强作用可被NMDA拮抗剂AP5阻断,证实其NMDA受体依赖性 [2]
Sarcosine(100–300 μM)以浓度依赖性方式增加fEPSPs的振幅和斜率,且不影响非NMDA受体介导的反应 [2] 商业麦角补充剂是由氨基酸及其衍生物制成的。它们影响合成代谢激素的释放、活动燃料的可用性、在压力下清晰思考的能力以及防止劳累引起的肌肉损伤。它们被认为是有利的协同食品成分[1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在戊四氮(PTZ)诱导的小鼠癫痫模型中,腹腔注射Sarcosine(600 mg/kg)显著延迟癫痫发作潜伏期(延长48%),并将死亡率从100%降至30% [1]
在最大电休克(MES)模型中,Sarcosine(600 mg/kg,腹腔注射)使强直性后肢伸展持续时间缩短35%,并在40%小鼠中阻止该症状发生 [1] Sarcosine (400–800 mg/kg; ip) 显着提高电惊厥阈值 [2]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Albino Swiss mouse body weight (25-30 g)[2]
Doses: 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg, 400 mg/kg, 800 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection Experimental Results: in mice MEST In trials, epilepsy thresholds were elevated at doses of 400 mg/kg and 800 mg/kg. For PTZ seizures: Mice received PTZ (85 mg/kg, s.c.) 30 min after Sarcosine (300 or 600 mg/kg, i.p.) dissolved in saline. Seizure latency and mortality were monitored for 30 min [1] For MES seizures: Mice were pretreated with Sarcosine (600 mg/kg i.p.) 30 min before electrical stimulation (50 mA, 0.2 sec). Tonic extension duration and protection rates were recorded [1] For hippocampal slice studies: Rats were sacrificed, and brain slices (400 μm) were perfused with artificial CSF. fEPSPs were evoked by Schaffer collateral stimulation [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Metabolism / Metabolites
Sarcosine is metabolized to glycine by the enzyme sarcosine dehydrogenase, while glycine-N-methyl transferase generates sarcosine from glycine. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Sarcosine is an oncometabolite. Sarcosine appears to upregulate the expression of the potent oncoprotein called human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/neu) in androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells upon exposure to exogenous sarcosine. Thus, sarcosine may induce prostate cancer progression by increased HER2/neu expression. Toxicity Data NA No mortality or behavioral toxicity (e.g., ataxia, sedation) observed at anticonvulsant doses (≤600 mg/kg) in mice [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Deliquescent crystals or powder. Has a sweetish taste. (NTP, 1992)
Sarcosine is a N-alkylglycine that is the N-methyl derivative of glycine. It is an intermediate in the metabolic pathway of glycine. It has a role as a glycine transporter 1 inhibitor, a glycine receptor agonist, a human metabolite, an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a N-alkylglycine, a N-methyl-amino acid and a member of N-methylglycines. It is a conjugate base of a sarcosinium. It is a conjugate acid of a sarcosinate. It is a tautomer of a sarcosine zwitterion. Sarcosine has been investigated for the treatment of Schizophrenia. Sarcosine is a metabolite found in or produced by Escherichia coli (strain K12, MG1655). Sarcosine has been reported in Sarcococca saligna, Drosophila melanogaster, and other organisms with data available. Sarcosine is an amino acid that is an intermediate and byproduct in glycine synthesis and degradation with potential anti-depressant and anti-schizophrenic activities. Sarcosine is a product of dietary consumption of choline and creatine and is rapidly converted into glycine. Oral administration of sarcosine with certain antipsychotics may cause increased glycine concentration in the brain, which may lead to increased NMDA receptor activation and a reduction in symptoms. Sarcosine is the N-methyl derivative of glycine. Sarcosine is metabolized to glycine by the enzyme sarcosine dehydrogenase, while glycine-N-methyl transferase generates sarcosine from glycine. Sarcosine is a natural amino acid found in muscles and other body tissues. In the laboratory it may be synthesized from chloroacetic acid and methylamine. Sarcosine is naturally found in the metabolism of choline to glycine. Sarcosine is sweet to the taste and dissolves in water. It is used in manufacturing biodegradable surfactants and toothpastes as well as in other applications. Sarcosine is ubiquitous in biological materials and is present in such foods as egg yolks, turkey, ham, vegetables, legumes, etc. Sarcosine is formed from dietary intake of choline and from the metabolism of methionine, and is rapidly degraded to glycine. Sarcosine has no known toxicity, as evidenced by the lack of phenotypic manifestations of sarcosinemia, an inborn error of sarcosine metabolism. Sarcosinemia can result from severe folate deficiency because of the folate requirement for the conversion of sarcosine to glycine (Wikipedia). Sarcosine has recently been identified as a biomarker for invasive prostate cancer. It was found to be greatly increased during prostate cancer progression to metastasis and could be detected in urine. Sarcosine levels were also increased in invasive prostate cancer cell lines relative to benign prostate epithelial cells (A3519). An amino acid intermediate in the metabolism of choline. Sarcosine (N-methylglycine) is an endogenous glycine derivative that inhibits GlyT1, increasing synaptic glycine levels to potentiate NMDA receptor function [1][2] Demonstrates anticonvulsant effects in PTZ and MES models, supporting potential therapeutic use in epilepsy [1] NMDA receptor potentiation suggests applications in neurological disorders involving NMDA hypofunction (e.g., schizophrenia) [2] An amino acid intermediate in the metabolism of choline. |
| 分子式 |
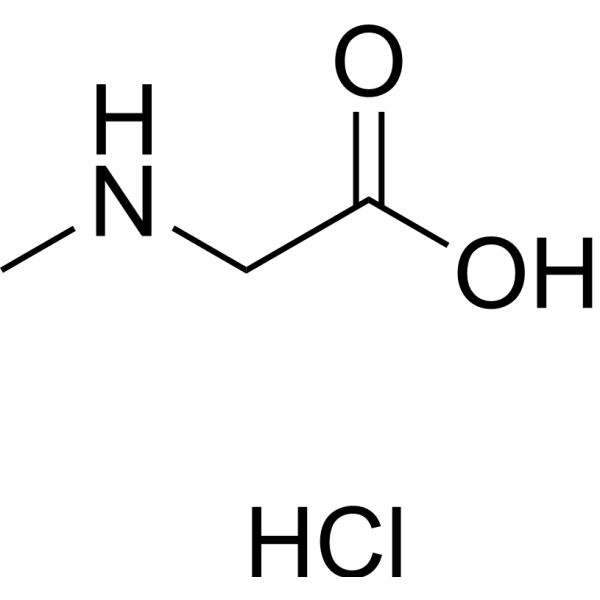
C3H8CLNO2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
125.55
|
| 精确质量 |
125.024
|
| CAS号 |
637-96-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
107-97-1; 2-(Methylamino)acetic acid-d3 hydrochloride;347840-04-4;2-(Methylamino)acetic acid-d5 hydrochloride;1219794-62-3
|
| PubChem CID |
69483
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.48 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
195.1ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
173-175 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
71.8ºC
|
| LogP |
0.483
|
| tPSA |
49.33
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
7
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
52.8
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
Cl[H].O([H])C(C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O
|
| InChi Key |
WVKIFIROCHIWAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C3H7NO2.ClH/c1-4-2-3(5)6;/h4H,2H2,1H3,(H,5,6);1H
|
| 化学名 |
2-(methylamino)acetic acid;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
Sarcosine hydrochloride; Glycine, N-methyl-, hydrochloride; n-methylglycine hydrochloride; CCRIS 3353; Sarcosine, hydrochloride; EINECS 211-310-2; UNII-W50V8R1ZE9; ...; 637-96-7;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.9650 mL | 39.8248 mL | 79.6495 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.5930 mL | 7.9650 mL | 15.9299 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.7965 mL | 3.9825 mL | 7.9650 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。