| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PI3Ka
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
基于构象动力学的设计驱动H1047R对WT和其他同工异构体的选择性[1]
为了提高[1]的效价和PI3Kα H1047R选择性,我们利用自由能微扰计算和结合WT和H1047R的化合物的x射线结构来鉴定类似物。我们最初对双氨基吡啶核心和周围的甲苯和甲酰胺基团进行了修饰。用氨基异吲哚代替双氨基吡啶(补充案文)导致PI3Kα H1047R的IC50提高9倍,H1047R的选择性提高2倍(表1)。进一步用2-氯-5-氟苯基和[1,2,4]三唑[1,5-a]吡啶-5-碳腈基分别取代[3]的甲苯和甲酰胺基团,得到RLY-2608,对PI3Kα H1047R的效价进一步提高,选择性进一步提高(表1)。氨基异吲哚核的这些亲和性改善可能源于更有效的空间填充,包括与Y1021更广泛的相互作用,以及与D1018主链更强的氢键([3]中的1.9 Å与[2]中的2.5 Å)。最终化合物中的5-氟取代RLY-2608,同样导致苯基所在的疏水袋的填充改善,而2-氯取代引入了与E1012的主羰基的卤素键(图3E)。 [1] < br > RLY-2608对异构体具有高度选择性(补充图S5),并且不能检测到抑制其他激酶(补充表S1)。此外,我们观察到螺旋突变体E542K和E545K在RLY-2608预孵育后具有相当水平的生化选择性。此外,值得注意的是,无论使用脂质体还是可溶性脂质底物dic8-PIP2, RLY-2608的泛突变选择性谱都是相似的(补充表S3)。这种新开发的变构抑制剂应该能够抑制突变激酶的致癌活性,同时避免抑制WT和其他亚型所带来的负信号后果。 RLY-2608在细胞中抗尾和螺旋结构域突变[1] 为了评估RLY-2608的选择性,我们使用了等基因MCF10A细胞系模型系统,其中单个突变等位基因的表达负责信号传导。正位分子抑制AKT的磷酸化,AKT是PI3K激活的下游标记物,在不同细胞系之间具有相同的抑制作用。然而,RLY-2608优先调节突变细胞系中的信号传导(图4A)。此外,我们观察到,当内源性突变癌细胞系(T47D)与WT,但pi3k依赖性细胞系(SKB3)一起处理时,突变选择性,而alpelisib同样抑制两者(图4B)。这些发现被扩展到一组癌细胞系,其中包含PIK3CA中三个热点残基的突变,并代表各种适应症(补充图S6A和S6B)。RLY-2608导致信号传导和增殖抑制,这与固有的PI3Kα细胞依赖性相关,通过alpelisib(一种正位抑制剂)的活性来评估。RLY-2608在多种PIK3CA突变细胞模型中抑制激酶结构域和螺旋突变体的能力表明,这些变异在p85α解离和隐口袋打开之间表现出类似的耦合。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
RLY-2608抑制动物模型中胰岛素水平的影响[1]
为了评估RLY-2608在体内的活性,我们将激素受体阳性(HR+)的乳腺癌细胞(T47D)植入小鼠体内,这些细胞是激酶结构域突变体(H1047R;图4 c)。当肿瘤生长达到200 mm3后,我们口服矫形抑制剂alpelisib或RLY-2608。在两种模型中,RLY-2608 (100mg /kg b.i.d)均能显著抑制肿瘤生长,导致与alpelisib治疗相似的停滞或消退。RLY-2608对螺旋结构域突变体(E545K;图4 d)。RLY-2608单独以100 mg/kg剂量给药小鼠,肿瘤消退明显。当RLY-2608与临床相关剂量的氟维司汀(雌激素受体降降剂)联合使用,以及与氟维司汀和ribociclib(一种细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4/6抑制剂)三联使用时,肿瘤消退进一步增强。此外,在ER+/HER2−患者来源的异种移植物中观察到类似的肿瘤退化,激酶突变(ST1056: H1047R)或螺旋结构域突变(ST986: E542K)单独使用 ry -2608 100 mg/kg。与氟维司汀联合使用也观察到疗效的提高(图4E)。值得注意的是,这些结果表明,RLY-2608在体内具有活性,可以以耐受的方式抑制依赖于多种pi3k α激活突变的肿瘤的生长(Supplementary Fig. S7)。由于alpelisib临床观察到的主要并发症是剂量限制性高血糖和高胰岛素血症(17),我们监测胰岛素和胰岛素c肽水平作为葡萄糖的替代标志物,这在荷瘤动物中可以可靠地测量(图4F)。尽管alpelisib在治疗后数小时内显示出两种标记物的显著增加,但即使在最高剂量RLY-2608时,这些标记物仍低于alpelisib治疗,水平更接近基线。综上所述,这些研究表明RLY-2608可以最大限度地抑制由影响PI3Kα调控的突变驱动的肿瘤,同时减轻抑制WT蛋白导致的高血糖不良反应。 在ReDiscover的首次人体研究(NCT05216432)的剂量递增部分中,在PIK3CA激酶和螺旋结构域突变型乳腺癌患者中观察到活性,没有与WT PI3Kα抑制相关的不良事件。 案例研究1 [1] 患者A是一名58岁女性,患有转移性(肝、肺、骨、LN) ER+/PR+、HER2低乳腺癌,在既往12次治疗(内分泌、化疗和靶向治疗,包括曲妥珠单抗德鲁西替康)后进展。组织和循环肿瘤DNA (ctDNA)的基因组分析显示激活了PIK3CA H1047R和E453K突变。该患者符合该研究单一治疗组的入组资格标准,并被分配接受RLY-2608 400mg p.o. b.i.d。在治疗4周内,患者骨痛明显改善。此外,与基线相比,第4周肿瘤标志物评估显示CA15-3(1598至933 U/mL)和CEA(68至24 U/mL)降低。8周后的影像学评估(C3D1)显示部分缓解,多个肝、肺和软组织靶病变减少[靶病变(TL)与RECIST 1.1基线相比- 36%]。 案例研究2 [1] 临床活动也证明了患者的螺旋突变。患者B是一名66岁的女性,患有转移性(骨,软组织)ER+/PR+/HER2 -乳腺癌,在氟维司汀和帕博西尼联合治疗的标准护理下进展。她被转介进行临床试验评估。基因组分析显示PIK3CA E542K突变。该患者符合该研究联合组的入组资格标准,并被分配接受RLY-2608 600 mg p.o. b.i.d.加氟维司汀。与基线相比,4周肿瘤标志物评估显示CA15-3(192至119 U/mL)和CEA(22至12 U/mL)降低。8周后(C3D1)放射学评估显示部分缓解,软组织靶病变消失(与RECIST 1.1基线相比,TL为- 100%)。[1] 综上所述,这些病例证明了RLY-2608是PI3Kα的同类同种异构体和突变选择性变构抑制剂,它可以在单一治疗或与氟维西汀联合治疗具有激酶或螺旋突变的乳腺癌时诱导临床反应,对葡萄糖稳态的影响最小。 |
| 酶活实验 |
PI3Kα酶活性及抑制试验[1]
用Echo555从384孔低死体积板中分取合适体积的10 mmol/L DMSO抑制剂至1536孔板,加入2 nmol/L酶(50 mmol/L HEPES pH 7.4, 50 mmol/L NaCl, 6 mmol/L MgCl2, 5 mmol/L DTT, 0.03% CHAPS蒸馏水),在室温下与抑制剂孵育2小时。然后,将含有20 μmol/L PI(4,5)P2 diC8和200 μmol/L ATP的底物溶液(50 mmol/L HEPES pH 7.4, 50 mmol/L NaCl, 5 mmol/L DTT,蒸馏水中0.03% CHAPS) 1:1加入酶溶液中,室温下使PIP2磷酸化1小时。然后根据制造商的说明,使用ADP- glo激酶测定法测量所得ADP产物浓度,使用0.1秒超灵敏发光方案的Envision板读取器定量发光。使用以下公式将每板的发光值归一化为中性和完全抑制对照: 其中,x为样品孔的发光值,m−为中性对照孔(实验缓冲液中的DMSO载体)的平均发光值,m+为抑制剂对照孔(GDC-0032,浓度为100 nmol/L)的平均发光值。最后,使用GraphPad Prism将归一化浓度-响应数据拟合为s型(四参数逻辑)线性回归方程,计算抑制剂的IC50值。 脂质体制备及PI3Kα抑制测定[1] 将以下三种脂质体:18:1 (Δ9-Cis) PE (DOPE, Avanti 850725)、18:1 PS (DOPS, Avanti 840035)和18:1 PI(4,5)P2 (PIP2, Avanti 850155)按75:23:2的摩尔比组合,根据制造商推荐通过物理挤出制备直径为100nm的脂质体。在Zetasizer上用动态光散射法测定了脂质体的大小和多分散性。如前所述,用ADP-Glo测定PI3Kα酶的抑制作用,在酶反应中用含有PIP2浓度为25 μmol/L的脂质体溶液取代PIP2底物。 结构确定[1] 所有晶体学数据都是在100 K下在以下波长下收集的:WT 1–1053 apo:0.979Å,WT 1–1052+[2]:1.000Å,H1047R 1–1053apo:1.033Å,H1047R 1–1053+[1]:1.116Å,H047R 1-1053+[2]:1.116 Ao,H1047 R 1–1043+[3]:1.033Å,WT 1–1053+RLY-2608:1.116Å。使用autoPROC(全局相位)对数据进行索引、整合和缩放。使用PDBID 2RD0作为搜索模型,通过分子置换求解初始结构。后续结构通过使用本文提出的结构进行分子置换来解决。对于所有病例,均使用Phenix中实施的Phaser-MR4)进行分子置换。最终模型是通过Coot和ISOLDE中的迭代手动构建生成的,并使用phenix.refine进行了细化。CryoEM模型从本文提出的WT 1-1053 X射线结构开始,同样是通过Coot和ISOLDE中的迭代手动细化以及Phenix的真实空间细化生成的。 细化信息[1] Ramachandran、侧链和碎屑岩统计数据如下。WT 1–1053载脂蛋白:96.6%有利,3.2%允许,0.16%异常值,0.86%旋转异构体异常值,全原子分类核心:1.87。WT 1–1053+[2]:96.1%赞成,3.8%允许,0.1%异常值,1.3%旋转异构体异常值,所有原子分类分数:1.43。WT 1–1053+RLY-2608:95.4%赞成,4.66%允许,0%异常值,0.94%旋转异构体异常值,所有原子分类分数:1.85。H1047R 1–1053载脂蛋白:96.6%有利,3.2%允许,0.2%异常值,0.95%旋转异构体异常值,全原子分类核心:2.08。H1047R 1–1053+[1]:97.0%赞成,2.9%允许,0.1%异常值,1.36%旋转异构体异常值,所有原子分类分数:1.38。H1047R 1–1053+[2]:96.0%赞成,4.0%允许,0%异常值,1.02%旋转异构体异常值,所有原子分类分数:1.56。H1047R 1–1053+[3]:95.6%赞成,4.3%允许,0%异常值,1.79%旋转异构体异常值,所有原子分类分数:1.66。 DNA编码文库选择和富集评分[1] 在所有选择中,使用Ni-NTA琼脂糖固定带有N端8xHis标签的全长PI3Kα(WT、H1047R、E542K和E545K)。如前所述,获得了数据分析和富集值。 表面等离子体共振光谱[1] 表面等离子体共振实验在25°C下在Biacore S200仪器上进行,使用由20 mmol/L HEPES pH 7.5、150 mmol/L NaCl、0.005%吐温20(v/v)、1 mmol/L MgCl2、1 mmol/L TCEP和2%二甲基亚砜组成的分析缓冲液。CM5芯片用100 mmol/L HCl、50 mmol/L NaOH和0.5%(v/v)SDS以100μL/min的流量进行2×6秒的脉冲预处理。使用胺偶联化学将大约6000个响应单位(RU)的PI3Kα固定在生物传感器表面上。10μL/分钟流量下的固定化步骤:7分钟400 mmol/L 1-乙基-3-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐/100 mmol/L N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺活化,1-2分钟20μg/mL PI3Kα在10 mmol/L MES pH 6.0中,含0.03%CHAPS,7分钟1 M乙醇胺HCl,pH 8.5。使用单循环动力学,以50μL/分钟的流速将浓度逐渐增加的化合物(最高浓度20μmol/L,3倍稀释系列,5个浓度)注入PI3Kα表面。将关联设置为180秒,然后分离4分钟。使用Biacore S200评估软件v1.1处理原始数据,并将数据动力学拟合到包含传质限制的1:1结合模型中。进行2次结合测量以计算标准偏差。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞培养[1]
突变半合子系在永生化、胰岛素生长因子反应性乳腺上皮细胞系MCF10A杂合背景中进行工程改造。通过在一轮靶向中通过Cas9核酸酶介导的双链DNA断裂的非同源末端连接修复靶向PIK3CA位点进行细胞系生成,导致转录本PIK3CA-201(ENST000000263967.4)的外显子9中2 bp缺失,导致WT等位基因的过早终止密码子,如cDNA和gDNA分析所证实。 T47D、NCIH1048、SKBR3、MCF7、ME180、MCF7,EFM19、CAL33、CAL51(DSMZ)、GP2D、OAW42、MFE280和OVISE是从商业供应商处购买的。细胞系通过细胞系库的短串联重复DNA分析进行鉴定。它们都是在检测无支原体后提供的,并在培养过程中进行常规检测。所有细胞系在解冻后培养不到1个月,并在收到后10代内使用。细胞系在供应商推荐的培养基中,在37°C的5%CO2加湿空气中培养。 药效学测定[1] 将细胞接种在384孔板中的12μL培养基中。在37°C、5%CO2下孵育24小时后,用DMSO或12.5 nL的测试化合物在37°℃、5%CO2条件下处理细胞2小时。按照制造商的说明进行磷酸化AKT(Ser473)细胞HTRF测定。将数据拟合到S形四参数曲线以确定IC50。 增殖[1] 将细胞接种在40μL培养基中,放入384孔、透明的底板中,包括24小时后读取的第0天未处理的平板。在37°C、5%CO2下孵育24小时后,用DMSO或额外40 nL的测试化合物在37°℃、5%CO2条件下处理细胞120小时。孵育后,将平板和CellTiter Glo 2.0平衡至室温30分钟。向所有孔中加入30μL CellTiter Glo 2.0。将平板在室温下放置在摇床上(避光)30分钟,并在EnVision平板阅读器上读取。通过从所有处理过的样品测量值中减去第0天的值来对数据进行归一化,然后归一化为DMSO对照并转换为存活率百分比。使用S形四参数曲线来确定IC50。 |
| 动物实验 |
Xenograft Studies [1]
Female Balb/c nude mice at 6–8 weeks of age were inoculated subcutaneously on the flank with 2 × 107 T47D or 1.5 × 107 MCF cells in 0.1 mL of 1:1 mixture of 1640 RPMI: BD Matrigel. For MCF7-inoculated animals, a 17-beta Estradiol tablet (0.5 mg, 90-day release) was implanted subcutaneously in the left flank. Patient-derived xenograft studies were conducted at START. Tumor fragments (∼70 mg) were implanted subcutaneously in athymic nude mice. Animals were supplemented with exogenous estradiol ad libitum via drinking water throughout the study duration. Treatment was initiated when tumors reached a volume of about 200 mm3. Tumors were measured twice weekly in two dimensions using a caliper. Tumor volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula: V = 0.5 a × b2, where a and b are the long and short diameters of the tumor, respectively. ReDiscover Phase I/II Study [1] ReDiscover is a global, open-label, phase I/II, first-in-human study (NCT05216432) of RLY-2608 in advanced cancer patients. Key objectives of phase I are to define the maximum tolerated dose and recommended phase II dose in monotherapy and in combination with fulvestrant, as well as the safety profile, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and preliminary antitumor activity in patients with PIK3CA mutations and unresectable or metastatic solid tumors (monotherapy) or metastatic breast cancer (combination). The key objectives of phase II are to define the overall response rate and duration of response per RECIST 1.1 for patients with advanced PIK3CA mutated solid tumors (monotherapy) or breast cancer (combination). Additional phase II objectives are to assess the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of RLY-2608 at the RP2D. The study was initiated in December 2021 and phase I dose escalation is ongoing concurrently with phase II dose expansion at the first selected RP2D of RLY-2608 600 mg b.i.d. with fulvestrant. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was reviewed and approved by the institutional review board of each clinical site. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients before study entry. Patients eligible for study participation were ≥18 years old; had Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0–1; no prior treatment with PI3Ka inhibitors; no type 1 or 2 diabetes; no uncontrolled CNS metastases and adequate cardiac function. Additional enrollment criteria are provided in Supplementary Appendix S1. RLY-2608 was administered orally, twice daily, in 4-week cycles. Adverse events were graded per Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) 5.0. The response was evaluated per RECIST version 1.1. Levels of ctDNA in plasma were assessed by next-generation sequencing, using 74-gene Guardant360 CDx. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
PIK3CA (PI3Kα) is a lipid kinase commonly mutated in cancer, including ∼40% of hormone receptor–positive breast cancer. The most frequently observed mutants occur in the kinase and helical domains. Orthosteric PI3Kα inhibitors suffer from poor selectivity leading to undesirable side effects, most prominently hyperglycemia due to inhibition of wild-type (WT) PI3Kα. Here, we used molecular dynamics simulations and cryo-electron microscopy to identify an allosteric network that provides an explanation for how mutations favor PI3Kα activation. A DNA-encoded library screen leveraging electron microscopy-optimized constructs, differential enrichment, and an orthosteric-blocking compound led to the identification of RLY-2608, a first-in-class allosteric mutant-selective inhibitor of PI3Kα. RLY-2608 inhibited tumor growth in PIK3CA-mutant xenograft models with minimal impact on insulin, a marker of dysregulated glucose homeostasis. RLY-2608 elicited objective tumor responses in two patients diagnosed with advanced hormone receptor–positive breast cancer with kinase or helical domain PIK3CA mutations, with no observed WT PI3Kα-related toxicities.
Significance:
Treatments for PIK3CA-mutant cancers are limited by toxicities associated with the inhibition of WT PI3Kα. Molecular dynamics, cryo-electron microscopy, and DNA-encoded libraries were used to develop RLY-2608, a first-in-class inhibitor that demonstrates mutant selectivity in patients. This marks the advance of clinical mutant-selective inhibition that overcomes limitations of orthosteric PI3Kα inhibitors. [1]
Pan-mutant-selective PI3K-alpha Inhibitor RLY-2608 is an orally bioavailable, pan-mutant selective inhibitor of the class I phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PI3K) catalytic subunit alpha (phosphoinositide 3-kinase alpha; PIK3CA; PI3K p110alpha), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, pan-mutant selective PI3K-alpha inhibitor RLY-2608 selectively targets and allosterically binds to PIK3CA mutated forms, thereby preventing the activity of PIK3CA mutants. This prevents mutant PIK3CA-mediated activation of the PI3K/Akt (protein kinase B)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. This results in both apoptosis and growth inhibition in PIK3CA-mutant expressing tumor cells. By specifically targeting PIK3CA mutants, RLY-2608 may be more efficacious and less toxic than PI3K-alpha inhibitors that also inhibit the wild-type (WT) form. Dysregulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway is often found in solid tumors and results in the promotion of tumor cell growth, survival, and resistance to chemo- and radio-therapy. PIK3CA, one of the most frequently mutated oncogenes, encodes the p110-alpha catalytic subunit of the class I PI3K. [1] The two patient vignettes described here demonstrate clinical proof of concept in metastatic HR+ HER2− breast cancer and the potential to have improved tolerability and efficacy with pan-mutant- and isoform-selective PI3Kα inhibition with the allosteric inhibitor RLY-2608. These two examples highlight patients who achieved confirmed responses with RLY-2608 treatment without adverse events that are associated with WT PI3Kα inhibition. These examples also demonstrate activity in a variety of contexts: in kinase and helical mutations, in earlier and later lines of therapy, and in monotherapy and combination with fulvestrant. Two decades after the discovery of oncogenic PIK3CA mutations, our collective understating of optimal PI3Kα targeting continues to evolve. Allosteric mutant-selective agents provide a novel advantage of a broader therapeutic index over older generation PI3Kα inhibitors. To this end, the past few years have seen intensifying research activities in developing mutant-selective PI3Kα inhibitors. RLY-2608 is a first-in-class PI3Kα inhibitor that demonstrates mutant-selective efficacy in the clinic. These features have the potential to improve outcomes in patients with PIK3CA-mutant tumors, in monotherapy, and in combination with other targeted therapies. The ongoing phase I/II ReDiscover trial (NCT05216432), studying RLY-2608 in monotherapy, in doublet with fulvestrant, and in triplet with CDK4/6 inhibitor and fulvestrant, will further define the potential benefit of RLY-2608 in patients with advanced PIK3CA-mutant solid tumors and breast cancer. More broadly, the problem of isoform and mutant selectivity is common across many targets in oncology. Here, we have developed an approach to overcoming this problem via allosteric, rather than orthosteric, inhibitor discovery. In our study, it was essential to use cryoEM and molecular dynamics to discover differences in the conformational dynamics of mutant and WT. Next, we identified inhibitors that impinge on the discovered allosteric network using a DEL screen. Importantly, the conditions of the DEL screen must be biased to magnify the differences between mutant and WT protein. In our case, blocking the orthosteric site was essential to avoid molecules that target the active site, and using full-length protein was essential because the tail plays a key role in the equilibrium governing cryptic pocket opening. Due to the favorable properties of allosteric inhibitors for gaining specificity, we expect the integrated use of cryoEM, MD, and DEL screening that we have leveraged here can help attack many other important targets in the future. [1] |
| 分子式 |
C29H14CLF5N6O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
608.905481815338
|
| 精确质量 |
608.078
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 57.20; H, 2.32; Cl, 5.82; F, 15.60; N, 13.80; O, 5.25
|
| CAS号 |
2733573-94-7
|
| PubChem CID |
166822065
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
5.5
|
| tPSA |
112
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
43
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1120
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
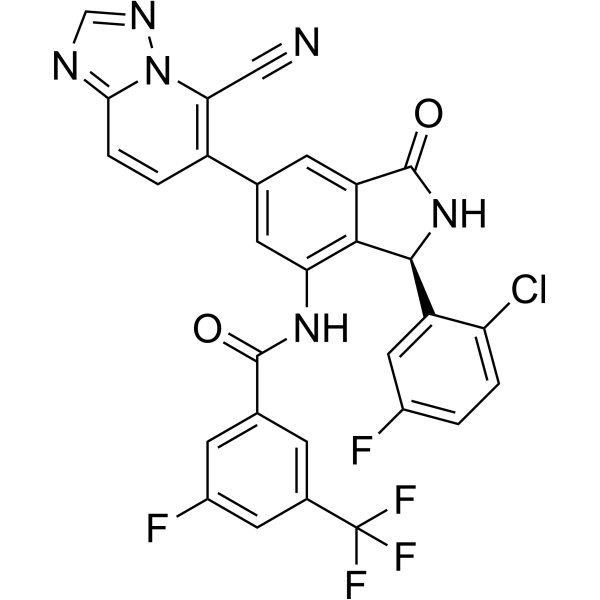
C1=CC(=C(C=C1F)[C@H]2C3=C(C=C(C=C3NC(=O)C4=CC(=CC(=C4)F)C(F)(F)F)C5=C(N6C(=NC=N6)C=C5)C#N)C(=O)N2)Cl
|
| InChi Key |
VYWRYBZVVSPTQN-SANMLTNESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C29H14ClF5N6O2/c30-21-3-1-16(31)10-19(21)26-25-20(28(43)40-26)7-13(18-2-4-24-37-12-38-41(24)23(18)11-36)8-22(25)39-27(42)14-5-15(29(33,34)35)9-17(32)6-14/h1-10,12,26H,(H,39,42)(H,40,43)/t26-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
N-[(3R)-3-(2-chloro-5-fluorophenyl)-6-(5-cyano-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-6-yl)-1-oxo-2,3-dihydroisoindol-4-yl]-3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide
|
| 别名 |
RLY-2608; N-[(3R)-3-(2-chloro-5-fluorophenyl)-6-(5-cyano-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-6-yl)-1-oxo-2,3-dihydroisoindol-4-yl]-3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide; N-((3R)-3-(2-chloro-5-fluorophenyl)-6-(5-cyano-(1,2,4)triazolo(1,5-a)pyridin-6-yl)-1-oxo-2,3-dihydroisoindol-4-yl)-3-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide; PI3Ka Inhibitor RLY-2608; RLY 2608; Pan-mutant PI3Ka Inhibitor RLY-2608; Mutant-selective PI3Ka Inhibitor RLY-2608; ...; 2733573-94-7;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~164 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6423 mL | 8.2114 mL | 16.4228 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3285 mL | 1.6423 mL | 3.2846 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1642 mL | 0.8211 mL | 1.6423 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。