| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
H1 Receptor
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Readily absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract. H1 antagonists are eliminated more rapidly by children than by adults and more slowly in those with severe liver disease. /H1 Receptor Antagonists/ The H1 antagonists are well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Following oral administration, peak plasma concentrations are achieved in 2 to 3 hours ... . /H1 Receptor Antagonists/ Elimination and metabolic profiles of the glucuronide products of doxylamine and its N-demethylated metabolites were determined after the oral admin of (14)C-doxylamine succinate (13.3 and 133 mg/kg doses) to male and female Fischer 344 rats. The cumulative urinary and fecal eliminations of these conjugated doxylamine metaboites at the 13.3 mg/kg dose were 44.4 + or - 4.2% and 47.3 + or - 8.1% of the total recoverd dose for male and female rats, respectively. The cumulative urinary and fecal eliminations of conjugated doxylamine metabolites at the 133 mg/kg dose were 55.2 + or - 2.6% and 47.9 + or - 2.5% of the total recovered dose for male and female rats, respectively. The conjugated doxylamine metabolites that were isolated, quantitiated, and identified are doxylamine O-glucuronide, N-desmethyl-doxylamine O-glucuronide, and N,N-didesmethyldoxylamine O-glucuronide. The elimination of doxylamine and metabolites was determined after iv admin of (14)C-doxylamine succinate at 0.7 and 13.3 mg/kg to the adult female rhesus monkey. Although the total recovery of radioactivity was the same for the low- and high-dose studies (90.2%), the rate of plasma elimination of doxylamine and its demethylated metabolite (desmethyldoxylamine) was slower for the high dose group. The 24 hr urinary excretion of doxylamine metabolites, desmethyl- and didesmethyldoxylamine, was significantly incr and the polar doxylamine metabolites were significantly decr as the iv doxylamine succinate dose was incr. The plasma elimination of GC-detected doxylamine was determined after po admin of Bendectin (doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride) /also contains dicyclomine hydrochloride/ at 7, 13.3, and 27 mg/kg to adult female rhesus monkeys. As the dose incr, the clearance of doxylamine decr. A statistically evaluated fit of the po data to a single-compartment, parallel first-order elimination model and a single-compartment, parallel first- and second-order (Michaelis-Menten) elimination model indicated that the more complex model containing the second-order process was most consistent with the observed elimination data. /Doxylamine succinate/ Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. The conjugated doxylamine metabolites that were isolated, quantitiated, and identified are doxylamine O-glucuronide, N-desmethyl-doxylamine O-glucuronide, and N,N-didesmethyldoxylamine O-glucuronide. Analysis of doxylamine N-oxide and pyrilamine N-oxide as synthetic standards and biologically derived metabolites by thermospray mass spectrometry (TSP/MS) provided (M + H) + ions for each metabolite. ... In addition, TSP/MS and TSP/MS/MS analysis of ring-hydroxylated N-desmethyldoxylamine ... is also reported. Hepatic. Half Life: 10 hours Biological Half-Life 10 hours The drug has an elimination half-life of about 10 hours in healthy adults. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Like other antihistamines, doxylamine acts by competitively inhibiting histamine at H1 receptors. It also has substantial sedative and anticholinergic effects. Hepatotoxicity Despite widespread use over many decades, doxylamine has not been linked to liver test abnormalities or to clinically apparent liver injury. The reason for its safety may relate its short half-life and limited duration of use. Likelihood score: E (unlikely to be a cause of clinically apparent liver injury). References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of antihistamines are given together after the Overview section on Antihistamines. Drug Class: Antihistamines Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Small occasional doses of doxylamine would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. Larger doses or more prolonged use may cause drowsiness and other effects in the infant or decrease the milk supply, particularly in combination with a sympathomimetic such as pseudoephedrine or before lactation is well established. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information on doxylamine was not found as of the revision date. In one telephone follow-up study, mothers reported irritability and colicky symptoms 10% of infants exposed to various antihistamines and drowsiness was reported in 1.6% of infants. None of the reactions required medical attention. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Antihistamines in relatively high doses given by injection can decrease basal serum prolactin in nonlactating women and in early postpartum women. However, suckling-induced prolactin secretion is not affected by antihistamine pretreatment of postpartum mothers. Whether lower oral doses of antihistamines have the same effect on serum prolactin or whether the effects on prolactin have any consequences on breastfeeding success have not been studied. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Interactions Concurrent use may potentiate the CNS depressant effects of either these medications /alcohol or other CNS depression-producing medications/ or antihistamines; also, concurrent use of maprotiline or tricyclic antidepressants may potentiate the anticholinergic effects of either antihistamines or these medications. /Antihistamines/ Anticholinergic effects may be potentiated when these medications /anticholinergics or other medications with anticholinergic activity/ are used concurrently with antihistamines; patients should be advised to report occurrence of gastrointestinal problems promptly since paralytic ileus may occur with concurrent therapy. /Antihistamines/ Concurrent use of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors with antihistamines may prolong the intensify the anticholinergic and CNS depressant effects of antihistamines; concurrent use is not recommended. /Antihistamines/ Concurrent use /of ototoxic medications/ with antihistamines may mask the symptoms of ototoxicity such as tinnitus, dizziness, or vertigo. /Antihistamines/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for DOXYLAMINE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Doxylamine is a clear colorless liquid. (NTP, 1992)
Doxylamine is a member of pyridines and a tertiary amine. It has a role as a histamine antagonist, a cholinergic antagonist, a sedative, an antiemetic, a H1-receptor antagonist, an anti-allergic agent and an antitussive. Histamine H1 antagonist with pronounced sedative properties. It is used in allergies and as an antitussive, antiemetic, and hypnotic. Doxylamine has also been administered in veterinary applications and was formerly used in parkinsonism. Doxylamine is an Antihistamine. The mechanism of action of doxylamine is as a Histamine Receptor Antagonist. Doxylamine is a first generation antihistamine that is used for symptoms of allergic rhinitis and the common cold and as a short acting sedative. Doxylamine has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Doxylamine is a first generation ethanolamine with antiinflammatory, sedative and antihistamine properties. Doxylamine competitively inhibits the histamine 1 (H1) receptor, thereby preventing the action of endogenous histamine as well as the subsequent release of pro-inflammatory mediators from basophils and mast cells. This agent acts as an inverse agonist that combines with, and stabilizes the inactive form of the H1-receptor, shifting the H1 receptor equilibrium toward the inactive state. This results in downregulation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and NF-kappaB dependent antigen presentation, chemotaxis, as well as expression of cell-adhesion molecules and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Histamine H1 antagonist with pronounced sedative properties. It is used in allergies and as an antitussive, antiemetic, and hypnotic. Doxylamine has also been administered in veterinary applications and was formerly used in parkinsonism. [PubChem] Histamine H1 antagonist with pronounced sedative properties. It is used in allergies and as an antitussive, antiemetic, and hypnotic. Doxylamine has also been administered in veterinary applications and was formerly used in PARKINSONISM. See also: Doxylamine Succinate (has salt form). Drug Indication Used alone as a short-term sleep aid, in combination with other drugs as a night-time cold and allergy relief drug. Also used in combination with Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) to prevent morning sickness in pregnant women. Mechanism of Action Like other antihistamines, doxylamine acts by competitively inhibiting histamine at H1 receptors. It also has substantial sedative and anticholinergic effects. Therapeutic Uses Anti-Allergic Agents; Antiemetics; Antitussive Agents; Histamine H1 Antagonists; Sedatives, Nonbarbiturate ANTIHISTAMINIC AGENT PROBABLY EFFECTIVE FOR SYMPTOMATIC TREATMENT OF... ALLERGIC RHINITIS, VASOMOTOR RHINITIS, ALLERGIC CONJUNCTIVITIS DUE TO INHALANT ALLERGENS & FOODS, MILD, UNCOMPLICATED ALLERGIC SKIN MANIFESTATIONS OF URTICARIA & ANGIOEDEMA, AMELIORATION & PREVENTION OF...REACTIONS TO BLOOD OR PLASMA... /SUCCINATE/ VET USE: AS ARE OTHER ANTIHISTAMINES IN STOMATITIS, LAMINITIS, URTICARIA, RESPIRATORY DISORDERS, BLOAT, & INDIGESTION IN CATTLE; IN URTICARIA & LAMINITIS IN HORSES; IN DERMATITIS, URTICARIA, MOTION SICKNESS, & IN PREVENTION OF DEPIGMENTATION IN BLUE NOSED DOGS. /SUCCINATE/ Antihistamines are indicated in the prophylactic and symptomatic treatment of perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis, vasomotor rhinitis, and allergic conjunctivitis due to inhalant allergens and foods. /Antihistamines; Included in US product labeling/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for DOXYLAMINE (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings PERSONS TAKING ANTIHISTAMINES SHOULD BE ALERTED TO THEIR SEDATIVE EFFECTS & SHOULD BE CAUTIONED NOT TO DRIVE AUTOMOBILE, FLY AIRPLANE, OR OPERATE HAZARDOUS MACHINERY... /ANTIHISTAMINES/ VET: USE OF ANTIHISTAMINES IN STOMATITIS, GANGRENOUS MASTITIS, METRITIS, & TOXIC ENGORGEMENTS HAVE BEEN QUESTIONED. /SUCCINATE/ Like other antihistamines, doxylamine should not be used in premature or full-term neonates. Safety and efficacy of doxylamine as a nighttime sleep aid in children younger than 12 years of age have not been established. In addition, children may be more prone than adults to paradoxically experience CNS stimulation rather than sedation when antihistamines are used as nighttime sleep aids. Because doxylamine may cause marked drowsiness that may be potentiated by other CNS depressants (e.g., sedatives, tranquilizers), the antihistamine should be used in children receiving one of these drugs only under the direction of a physician. As an antihistamine, doxylamine should be used in children 2 to younger than 6 years of age only under the direction of a physician; use of the drug in children younger than 2 years of age is not recommended. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions to antihistamines in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or doxylamine, taking into account the importance of the drug to the woman. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for DOXYLAMINE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Doxylamine is an antihistamine commonly used as a sleep aid. This drug is also used to relieve symptoms of hay fever (allergic rhinitis), hives (rash or itching), and other allergic reactions. Doxylamine is a member of the ethanolamine class of antihistamines and has anti-allergy power far superior to virtually every other antihistamine on the market, with the exception of diphenhydramine (Benadryl). It is also the most powerful over-the-counter sedative available in the United States, and more sedating than many prescription hypnotics. In a study, it was found to be superior to even the barbiturate, phenobarbital for use as a sedative. Doxylamine is also a potent anticholinergic. |
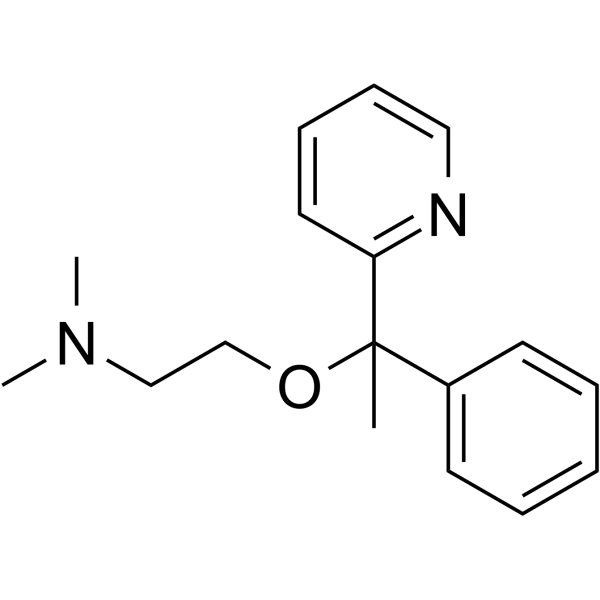
| 分子式 |
C17H22N2O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
270.3695
|
| 精确质量 |
270.173
|
| CAS号 |
469-21-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Doxylamine succinate;562-10-7;Doxylamine-d5 succinate;1216840-94-6
|
| PubChem CID |
3162
|
| 外观&性状 |
LIQ
|
| 密度 |
1.043 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
364.9ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
25°C
|
| 闪点 |
174.5ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.5486 (estimate)
|
| LogP |
2.923
|
| tPSA |
25.36
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
276
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
CC(C1=CC=CC=C1)(C2=CC=CC=N2)OCCN(C)C
|
| InChi Key |
HCFDWZZGGLSKEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H22N2O/c1-17(20-14-13-19(2)3,15-9-5-4-6-10-15)16-11-7-8-12-18-16/h4-12H,13-14H2,1-3H3
|
| 化学名 |
N,N-dimethyl-2-(1-phenyl-1-pyridin-2-ylethoxy)ethanamine
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6986 mL | 18.4932 mL | 36.9864 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7397 mL | 3.6986 mL | 7.3973 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3699 mL | 1.8493 mL | 3.6986 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。