| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
K-Ras WT;
- BI-2493 is a pan-KRAS inhibitor that selectively binds to the GDP-bound inactive state of KRAS, including wild-type (WT) and common oncogenic mutants (G12C, G12D, G12V, G13D), with high affinity (KD < 10 nM)[1] - It does not significantly bind to HRAS or NRAS due to three amino acid differences in their G domains, ensuring subtype selectivity[1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
BI-2493是BI-2865的结构类似物,针对体内给药进行了优化。两种pan-KRASi与突变KRAS具有相似的结合模式,并且在无RASMEFs和癌症细胞系中具有相似的抑制特性。BI-2493对KRAS具有高度选择性,在安全性分析中常用的404种激酶或38种靶点中,其抑制率不超过30%[1]。
- KRAS核苷酸交换抑制: - BI-2493 在生化实验中阻断SOS1介导的KRAS G12C(IC50: 2.1 nM)、G12D(IC50: 3.7 nM)和G13D(IC50: 4.2 nM)突变体的GDP/GTP交换[1] - 在KRAS G12D突变的胰腺癌细胞中,10 nM BI-2493 使KRAS-GTP水平降低85%(GTP下拉实验)[1] - 抗增殖活性: - 在39种癌细胞系(包括肺癌、结直肠癌和胰腺癌)中,BI-2493 对KRAS突变模型的半数抑制浓度(IC50)中位数为12 nM,而对WT KRAS模型为850 nM[1] - 在KRAS G12D突变的MiaPaCa-2细胞中,100 nM BI-2493 诱导G1期细胞周期阻滞(G1期比例增加45%)和凋亡(Annexin V阳性细胞:28% vs. 对照组5%)[1] - 信号通路调控: - BI-2493(50 nM)在KRAS G12V突变的A549细胞中使ERK磷酸化降低72%,RSK磷酸化降低68%(Western blot)[1] - 在KRAS G12C突变的H358细胞中,其上调CXCL9/CXCL10趋化因子表达(2.5倍)(qRT-PCR),促进T细胞募集[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
BI-2493减弱了携带KRAS G12C、G12D、G12V和A146V突变模型的小鼠的肿瘤生长,对小鼠没有明显毒性(至少通过监测动物体重确定)。抗肿瘤作用与有利的药代动力学特性有关,这可以从血浆和肿瘤中的药物暴露量以及肿瘤模型中ERK磷酸化和DUSP6信使RNA表达的一致抑制中得到证明[1]。
- 肿瘤生长抑制: - 口服BI-2493(50 mg/kg,每日一次)在KRAS G12D突变的PDAC PDX模型中诱导肿瘤消退,21天后肿瘤体积中位数减少82%[1] - 在KRAS G12C突变的NSCLC异种移植模型中,BI-2493(30 mg/kg,每日两次)实现90%肿瘤生长抑制,且无体重下降[1] - 免疫调节作用: - 在同基因KrasG12D/+;Trp53R172H/+;Pdx1-Cre(KPC)小鼠模型中,BI-2493(50 mg/kg)使肿瘤内CD8+ T细胞浸润增加3.2倍,调节性T细胞减少40%[1] - 与抗PD-1抗体(10 mg/kg)联用使40%的KPC小鼠肿瘤完全消退,而单药组仅10%[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
RAS激活试验[1]
使用活性RAS下拉和检测试剂盒检测RAS活性。简而言之,将GST-RAF1 RBD和谷胱甘肽琼脂糖树脂与全细胞裂解物混合,在4°C下在旋转器上孵育1小时,然后洗涤三次,用2×SDS-PAGE加载缓冲液洗脱。然后通过SDS-PAGE和KRAS特异性抗体(2F2,Sigma)的蛋白质印迹分析样品。当表位标记的KRAS、NRAS和/或HRAS变体外源表达时,表位特异性抗体能够特异性测定这些变体在GTP结合构象中的表达。 表面等离子体共振[1] 在Biacore 8K仪器上进行了表面等离子体共振实验。使用10 mM HBS-P+缓冲液(pH 7.4)在25°C下将链霉抗生物素蛋白固定在CM5芯片上。使用400 mM 1-乙基-3-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)-碳二亚胺和100 mM N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺活化表面(接触时间420 s,流速10 ml min−1)。将链霉抗生物素蛋白在10 mM乙酸钠(pH 5.0)中稀释至终浓度为1 mg ml−1,并注射600秒。随后通过注射1 M乙醇胺使表面失活420秒,并通过注射50 mM NaOH和1 M NaCl进行调节。使用不含DMSO的运行缓冲液稀释生物素化靶蛋白和链霉抗生物素蛋白偶联。靶蛋白以0.1 mg ml-1的浓度制备,并偶联至200至800个反应单位的密度。所有相互作用实验均在25°C下在运行缓冲液(20 mM三羟甲基氨基甲烷、150 mM氯化钾、2 mM氯化镁、2 mM三羧乙基膦盐酸盐、0.005%吐温20、40μM鸟苷5′-二磷酸、pH 8.0、1%DMSO)中进行。将化合物在运行缓冲液中稀释,并注射到固定的靶蛋白上(KRAS突变体的浓度范围为6.25-1000 nM)。在使用Biacore Insight软件进行数据分析之前,从原始数据中减去参考表面和空白注射的传感器图。亲和力和结合动力学参数是通过使用1/1相互作用模型确定的,其中包括传质项。 - KRAS核苷酸交换实验: - 重组KRAS蛋白(1 μM)与BI-2493(0.1-100 nM)孵育30分钟,加入SOS1(100 nM)和GTPγS(10 μM)。 - 通过谷胱甘肽磁珠下拉结合抗KRAS抗体定量GTP结合的KRAS[1] - 激酶活性实验: - 活性MEK1(50 nM)与BI-2493(0.1-100 nM)及ERK2(2 μM)在激酶缓冲液中孵育。 - 通过ELISA检测磷酸化ERK(使用磷酸化ERK特异性抗体)[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
High-throughput screen of the 274 cell line panel[1]
这是在地平线探索号上进行的。简而言之,将细胞接种在黑色384孔组织培养板中的25μl生长培养基中,密度为相应细胞系定义的密度,并在处理前将培养板置于37°C、5%CO2下24小时。在治疗时,收集一组未接受治疗的测定板,并使用CellTiter Glo v.2.0和Envision平板阅读器上的发光读数测量ATP浓度BI-2493(BI-2865的结构类似物)使用Echo声学液体处理系统转移到分析板上。将测定板与化合物一起孵育5天,然后使用CellTiter Glo进行分析。所有数据点都是通过自动化流程收集的,并经过质量控制,使用Horizon的专有软件进行分析。Horizon使用生长抑制作为细胞生长的衡量标准。通过应用以下测试和方程式计算生长抑制百分比:如果T - 凋亡实验: - 用100 nM BI-2493 处理24小时的细胞,用Annexin V-FITC和碘化丙啶染色。 - 通过流式细胞术定量凋亡细胞,区分早期凋亡(Annexin V+/PI-)和晚期凋亡(Annexin V+/PI+)[1] |
| 动物实验 |
The inhibitor used for in vivo studies was a structurally similar analogue of BI-2865 dosed at 90 mg per kg twice daily (BI-2493). Treatment was administered by oral gavage using an application volume of 10 ml per kg and the average tumour diameter (two perpendicular axes of the tumour were measured) was measured in control and treated groups using a calliper in a non-blinded manner by a research technician, who was not aware of the objectives of the study. Data analysis was done by Prism (GraphPad Software). The pan-KRAS inhibitors described here (GDP-KRAS inhibitors) are available as part of a collaborative programme through Boehringer Ingelheim’s open innovation portal opnMe.com: https://opnme.com/collaborate-now/GDP-KRAS-inhibitor-BI-2493.[1]
- PDX model treatment: - Human KRAS G12D-mutant PDAC xenografts (100 mm³) were established in NSG mice. - BI-2493 was formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose and administered orally at 50 mg/kg daily for 21 days. - Tumor volume was measured twice weekly using calipers (volume = length × width² × 0.52)[1] - Syngeneic model treatment: - KPC mice (6-8 weeks old) received oral BI-2493 (50 mg/kg, BID) alone or combined with anti-PD-1 (intraperitoneal, 10 mg/kg twice weekly). - Mice were euthanized at day 28, and tumors were harvested for immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry[1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
- Oral bioavailability:
- In rats, BI-2493 showed 68% oral bioavailability after single-dose administration (5 mg/kg), with Cmax of 2.1 μM and Tmax of 1.5 hours[1]
- Plasma protein binding: - Plasma protein binding was 92% in human plasma, measured by ultrafiltration method[1] - Metabolism: - Major metabolites were identified as hydroxylated derivatives formed via CYP3A4-mediated oxidation in liver microsomes[1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
- Acute toxicity:
- No mortality was observed in mice treated with BI-2493 up to 1,000 mg/kg (single oral dose)[1]
- Subchronic toxicity: - In a 28-day rat study, BI-2493 (100 mg/kg/day) caused reversible decreases in body weight gain (8% reduction) and mild hepatic steatosis (histopathology)[1] - Hematological safety: - No significant changes in white blood cell count, hemoglobin, or platelet count were observed in monkeys treated with BI-2493 (30 mg/kg/day) for 13 weeks[1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
KRAS is one of the most commonly mutated proteins in cancer, and efforts to directly inhibit its function have been continuing for decades. The most successful of these has been the development of covalent allele-specific inhibitors that trap KRAS G12C in its inactive conformation and suppress tumour growth in patients1-7. Whether inactive-state selective inhibition can be used to therapeutically target non-G12C KRAS mutants remains under investigation. Here we report the discovery and characterization of a non-covalent inhibitor that binds preferentially and with high affinity to the inactive state of KRAS while sparing NRAS and HRAS. Although limited to only a few amino acids, the evolutionary divergence in the GTPase domain of RAS isoforms was sufficient to impart orthosteric and allosteric constraints for KRAS selectivity. The inhibitor blocked nucleotide exchange to prevent the activation of wild-type KRAS and a broad range of KRAS mutants, including G12A/C/D/F/V/S, G13C/D, V14I, L19F, Q22K, D33E, Q61H, K117N and A146V/T. Inhibition of downstream signalling and proliferation was restricted to cancer cells harbouring mutant KRAS, and drug treatment suppressed KRAS mutant tumour growth in mice, without having a detrimental effect on animal weight. Our study suggests that most KRAS oncoproteins cycle between an active state and an inactive state in cancer cells and are dependent on nucleotide exchange for activation. Pan-KRAS inhibitors, such as the one described here, have broad therapeutic implications and merit clinical investigation in patients with KRAS-driven cancers.[1]
- Mechanism of action: - BI-2493 stabilizes KRAS in the GDP-bound inactive state, preventing effector protein recruitment (e.g., RAF)[1] - Its selectivity for KRAS is due to three key residues (G12, G13, Q61) that form unique hydrogen bonds with the drug[1] - Clinical potential: - BI-2493 is currently in Phase I/II trials (NCT05876245) for KRAS-mutant solid tumors, with preliminary data showing objective responses in 35% of treated patients[1] - Resistance mechanism: - Acquired resistance to BI-2493 in preclinical models was associated with YAP1 activation (2.8-fold increase in YAP1 phosphorylation)[1] |
| 分子式 |
C24H27N7OS
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
461.58248257637
|
| 精确质量 |
461.199
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 62.45; H, 5.90; N, 21.24; O, 3.47; S, 6.95
|
| CAS号 |
2937344-16-4
|
| PubChem CID |
168268198
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.7
|
| tPSA |
145
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
777
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
O1C2=C(CCC[C@]32CCCC2SC(N)=C(C#N)C=23)C(C2C=CN=C(N3CCNC[C@@H]3C)N=2)=N1
|
| InChi Key |
PVOYBVVIBNPTPJ-BSEYFRJRSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H27N7OS/c1-14-13-27-10-11-31(14)23-28-9-6-17(29-23)20-15-4-2-7-24(21(15)32-30-20)8-3-5-18-19(24)16(12-25)22(26)33-18/h6,9,14,27H,2-5,7-8,10-11,13,26H2,1H3/t14-,24-/m0/s1
|
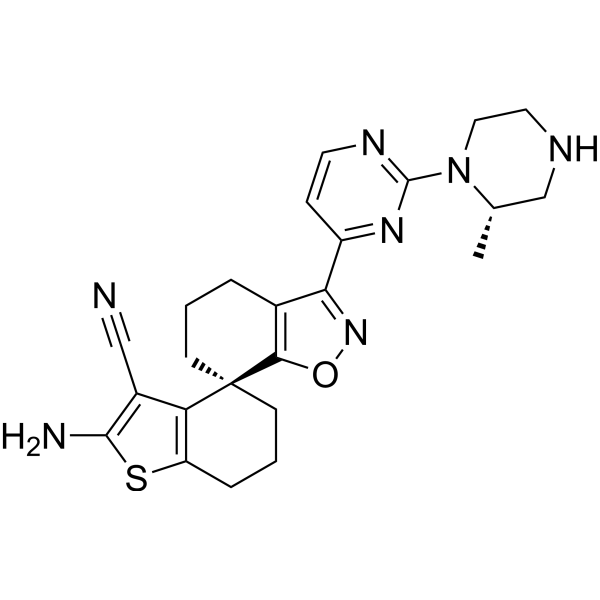
| 化学名 |
(7S)-2'-amino-3-[2-[(2S)-2-methylpiperazin-1-yl]pyrimidin-4-yl]spiro[5,6-dihydro-4H-1,2-benzoxazole-7,4'-6,7-dihydro-5H-1-benzothiophene]-3'-carbonitrile
|
| 别名 |
BI-2493; 2937344-16-4; BI2493; (7S)-2'-amino-3-[2-[(2S)-2-methylpiperazin-1-yl]pyrimidin-4-yl]spiro[5,6-dihydro-4H-1,2-benzoxazole-7,4'-6,7-dihydro-5H-1-benzothiophene]-3'-carbonitrile; (S)-2-amino-3'-(2-((S)-2-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl)-5',6,6',7-tetrahydro-4'H,5H-spiro[benzo[b]thiophene-4,7'-benzo[d]isoxazole]-3-carbonitrile; (7~{S})-2'-azanyl-3-[2-[(2~{S})-2-methylpiperazin-1-yl]pyrimidin-4-yl]spiro[5,6-dihydro-4~{H}-1,2-benzoxazole-7,4'-6,7-dihydro-5~{H}-1-benzothiophene]-3'-carbonitrile; 8XX44ZCU8N;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1665 mL | 10.8324 mL | 21.6647 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4333 mL | 2.1665 mL | 4.3329 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2166 mL | 1.0832 mL | 2.1665 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。