| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Natural product
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
抗菌最小抑菌浓度测定及协同作用[1]
IVS/异戊酰紫草素是从常染色体梭菌中分离出来的,纯度为98.7%(补充图S1),对耐药试验菌株金黄色葡萄球菌RN4220显示出微弱的抗菌活性,MIC为16mg/L(表1;补充图S2)。作为阳性对照,抗生素万古霉素抑制菌株RN4220的生长,MIC为2mg/L。 生长动力学、溴化乙锭流出试验和异戊酰紫草素在转录水平上对msrA诱导的影响[1] 如补充图S3所示,用载体或0.25处理的细菌的生长曲线 × 异戊酰紫草素/IVS的MIC几乎重叠。0.25处理RN4220菌株的生长 × STM的MIC在12小时内几乎完全停止,此后迅速增长。与单独使用STM相比,用STM处理的菌株RN4220(0.25× MIC)与IVS(0.25× MIC)的增长速度较慢。因此,观察到STM和IVS对RN4220菌株的协同作用。 载体处理的细菌在1-60分钟内迅速将溴化乙锭消耗至<50%,随后减少速度较慢,最终荧光水平约为30%(图1)。IVS抑制了RN4220菌株的细菌外排(P<0.05),尽管这种抑制作用弱于阳性对照羰基氰化物间氯苯腙。 将载体处理的细菌中msrA mRNA的表达设定为诱导的参考水平(1倍)。菌株RN4220与STM(32mg/L,0.0125 × MIC)导致msrA mRNA的大量表达,当细菌与STM和异戊酰紫草素/IVS一起孵育时,msrA信使核糖核酸的表达显著降低(P<0.01)。然而,用STM联合IVS处理的细菌的mRNA表达水平高于用载体处理的细菌(补充图S4)。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
体内感染和急性毒性研究[1]
记录感染RN4220菌株的小鼠的7天存活曲线。载体组小鼠在感染后24小时内死亡,单独用异戊酰紫草素/IVS(40mg/kg)或单独用STM(10mg/kg)治疗的小鼠也是如此(图2)。大多数接受STM(10mg/kg)和IVS(10mg/kg的组合)治疗的小鼠在感染后24小时内死亡,存活率为20%,其余小鼠在接下来的24小时内去世。接受STM(10mg/kg)和IVS(20mg/kg)组合治疗的组合组小鼠中有8只在感染RN4220菌株后2天(48小时)内死亡,因此该组的最终7天存活率为10%。接受STM(10mg/kg)和高剂量IVS(40mg/kg)的联合组小鼠在感染后24小时内缓慢死亡,6只在感染后3天内死亡,最后7天的存活率为40%。注射万古霉素(110mg/kg)的阳性对照组小鼠在感染RN4220菌株7天后存活率为60%。异戊酰紫草素/IVS显著抑制了感染小鼠的细菌水平(补充图S6),增加了STM的体内抗菌活性。测量了IVS对小鼠的急性毒性,发现其50%致死剂量(LD50)为2.584 g/kg,表明IVS是一种低毒化合物(补充图S8)。 |
| 酶活实验 |
生长动力学、溴化乙锭流出试验、总RNA提取和实时PCR[1]
如前所述,对菌株RN4220的生长动力学进行了一些修改。如前所述,在细菌外排试验中评估了异戊酰紫草素/IVS。根据制造商的说明,使用TRIzol试剂从细菌中分离总RNA。使用RevertAidTM第一链cDNA合成试剂盒进行逆转录步骤以合成cDNA。使用ABI 7300实时荧光定量PCR系统进行PCR分析。详细方法见补充材料。 |
| 动物实验 |
In vivo infection and acute toxicity studies [1]
In vivo infection and acute toxicity studies were performed according to previously published methods, with some modifications. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Investigation of efficacy and safety in animal models is important in drug development. The synergistic effect between Isovalerylshikonin/IVS and STM against drug-resistant S. aureus infection was shown in vivo in a mouse model. The acute toxicity of IVS with a single exposure in mice was measured with an LD50 of 2.584 g/kg in present study (Supplementary material).[1]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Isovalerylshikonin has been reported in Onosma heterophylla with data available.
Antimicrobial resistance is the greatest threat to the treatment of bacterial infectious diseases. The development of resistance-modifying agents (RMAs) represents a promising strategy to mitigate the spread of bacterial antimicrobial resistance. In this study, a natural product, isovalerylshikonin (IVS), was isolated from Arnebia euchroma, a traditional Chinese medicine herb, that exhibited marginal antibacterial activity against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus RN4220, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 16 mg/L. In addition, a synergistic effect between IVS and streptomycin (STM) was detected by the microdilution antimicrobial chequerboard assay, with a reduction in the MIC of STM by up to 16-fold against strain RN4220. A bacterial ethidium bromide efflux assay and reverse transcription PCR were performed to investigate the synergistic mechanism. IVS significantly inhibited bacterial efflux and expression of msrA mRNA in vitro. A murine peritonitis/sepsis model was employed to test the in vivo synergistic activity of IVS and STM. IVS synergistically decreased bacterial counts with STM in peritoneal, spleen and liver tissue and increased mouse survival with STM in 7 days. The acute toxicity of IVS was tested and the 50% lethal dose (LD50) of IVS with a single exposure was 2.584 g/kg in mice. Overall, IVS, a low-toxicity RMA, exhibited synergistic antibacterial activities in vitro and in vivo against drug-resistant S. aureus. The effects were mediated by suppression of msrA mRNA expression and reduced bacterial efflux. In addition, these data support that IVS is a potential RMA against microbial resistance caused by the MsrA efflux pump.[1] This study focused on the discovery of a new RMA against the MsrA efflux pump. IVS isolated from A. euchroma was shown to be an effective RMA against microbial resistance caused by the MsrA efflux pump, exhibiting in vitro and in vivo synergistic activities against S. aureus RN4220. The effects were mediated by suppression of msrA expression at the mRNA level and by a reduction of bacterial efflux. In addition, IVS is a low toxicity agent with an LD50 of 2.584 g/kg in mice and may serve as a potential agent for therapeutic use in infections.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C21H24O6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
372.41
|
| 精确质量 |
372.157
|
| CAS号 |
76549-35-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
52387-14-1
|
| PubChem CID |
335426
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 沸点 |
570.1±50.0 °C(Predicted)
|
| LogP |
3.105
|
| tPSA |
111.9
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
656
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
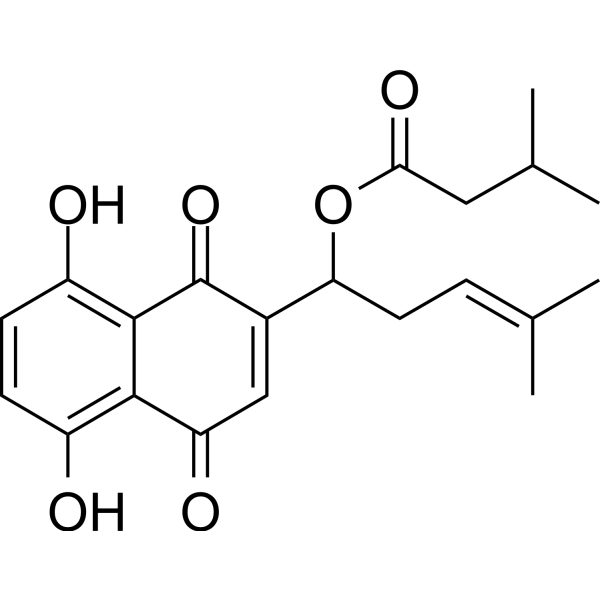
CC(C)CC(=O)OC(CC=C(C)C)C1=CC(=O)C2=C(C=CC(=C2C1=O)O)O
|
| InChi Key |
UTOUNDHZJFIVPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H24O6/c1-11(2)5-8-17(27-18(25)9-12(3)4)13-10-16(24)19-14(22)6-7-15(23)20(19)21(13)26/h5-7,10,12,17,22-23H,8-9H2,1-4H3
|
| 化学名 |
[1-(5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-dioxonaphthalen-2-yl)-4-methylpent-3-enyl] 3-methylbutanoate
|
| 别名 |
Isovalerylshikonin; 76549-35-4; [1-(5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-dioxonaphthalen-2-yl)-4-methylpent-3-enyl] 3-methylbutanoate; NSC344556; 52387-14-1; Butanoic acid, 3-methyl-, 1-(1,4-dihydro-5,8-dihydroxy-1,4-dioxo-2-naphthalenyl)-4-methyl-3-pentenyl ester; Alkannin isovalerate; SCHEMBL13389448;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
Typically soluble in DMSO (e.g. 10 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6852 mL | 13.4261 mL | 26.8521 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5370 mL | 2.6852 mL | 5.3704 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2685 mL | 1.3426 mL | 2.6852 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。