| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 500μg |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
FAP (IC50 = 3.2 nM); PREP (IC50 = 1.8 μM)
In vitro activity: SP-13786 (formerly known as FAP-IN-1) is a novel, potent and highly selective inhibitor of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) with IC50 of 3.2 nM; it also inhibits prolyl oligopeptidase (PREP) with an IC50 of 1.8 μM. Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a serine protease related to dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV). It has been convincingly linked to multiple disease states involving remodeling of the extracellular matrix. FAP inhibition is investigated as a therapeutic option for several of these diseases, with most attention so far devoted to oncology applications. The log D values, plasma stabilities, and microsomal stabilities of SP-13786 were found to be highly satisfactory. Pharmacokinetic evaluation in mice of SP-13786 demonstrated high oral bioavailability, plasma half-life, and the potential to selectively and completely inhibit FAP in vivo. Kinase Assay: SP-13786 (formerly known as FAP-IN-1) is a novel, potent and highly selective inhibitor of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) with IC50 of 3.2 nM; it also inhibits prolyl oligopeptidase (PREP) with an IC50 of 1.8 μM. Cell Assay: FAP-IN-1 is also found to have better FAP/PREP selectivity and a very proficient ligand efficiency of 0.34. |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:SP-13786(以前称为 FAP-IN-1)是一种新型、有效、高选择性的成纤维细胞活化蛋白(FAP)抑制剂,IC50 为 3.2 nM;它还抑制脯氨酰寡肽酶 (PREP),IC50 为 1.8 μM。成纤维细胞激活蛋白 (FAP) 是一种与二肽基肽酶 IV (DPPIV) 相关的丝氨酸蛋白酶。它与涉及细胞外基质重塑的多种疾病状态有着令人信服的联系。 FAP 抑制作为其中几种疾病的治疗选择进行了研究,迄今为止,大多数注意力都集中在肿瘤学应用上。 SP-13786 的 log D 值、血浆稳定性和微粒体稳定性非常令人满意。 SP-13786 在小鼠中的药代动力学评估显示出较高的口服生物利用度、血浆半衰期以及体内选择性和完全抑制 FAP 的潜力。激酶测定:SP-13786(以前称为 FAP-IN-1)是一种新型、有效、高选择性的成纤维细胞活化蛋白(FAP)抑制剂,IC50 为 3.2 nM;它还抑制脯氨酰寡肽酶 (PREP),IC50 为 1.8 μM。细胞测定:还发现 FAP-IN-1 具有更好的 FAP/PREP 选择性和非常熟练的配体效率(0.34)。
UAMC1110 对 FAP 表现出强效抑制活性,IC₅₀ 为 3 nM,并且对相关的脯氨酸肽酶 PREP 具有高选择性(IC₅₀ > 1.8 µM,SI > 562.5)。在浓度高达 100 µM 时,对 DPPIV、DPP9 或 DPP2 没有显著抑制。 该化合物显示出高动力学溶解度(>200 µM)和 log D 值为 1.0。 它在小鼠(6 小时后 85% 未变化)和大鼠(6 小时后 95% 未变化)血浆中表现出良好的稳定性。 在大鼠肝微粒体中也显示出高稳定性(6 小时后 94% 未变化)。 在浓度高达 64 µM 时,未观察到对人胚胎肺成纤维细胞 MRC-5 的细胞毒性。[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 PK 研究中,FAP-IN-1 是 FAP 最广泛、持续时间最长的抑制剂。没有观察到紧密结合行为,并且该抑制剂证明可逆地与 FAP 结合。 FAP-IN-1 在小鼠中的药代动力学评估显示出较高的口服生物利用度、血浆半衰期以及体内选择性和完全抑制 FAP 的潜力
在雄性 Wistar 大鼠中单次口服给药(20 mg/kg)后,UAMC1110 在 0.33 小时达到最大血药浓度(Cₘₐₓ)14.6 µg/mL,消除半衰期(T₁/₂)为 3.4 小时,口服生物利用度为 74%。 对给药大鼠血浆样本的离体分析表明,单次口服剂量(20 mg/kg)的 UAMC1110 在所有测量时间点(5 分钟至 24 小时)均导致血浆 FAP 活性抑制超过 85%,表明在体内实现了完全或接近完全且持久的靶点占据。[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
基于透析实验的探针可逆性研究[2]
重组人FAP (rhFAP)在37°C下孵育15分钟,探针浓度预计可抑制约90%的FAP活性(5.1.08 nM;6: 2.50 nM;7: 1.35 nM;UAMC1110: 0.77 nM稀释于FAP测定缓冲液:50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 140 mM NaCl和1 mg/ml BSA)。用0.0002% DMSO孵育rhFAP作为溶剂对照。孵育15分钟后,测定FAP活性,如Bracke et al.(2019)发表的。随后,使用10 kDa截止Slide-A-Lyzer MINI透析装置,在4°C下对FAP测定缓冲液进行透析。在3小时、6小时、24小时、3天和7天后交换缓冲液(14ml),并在每个时间点后进行FAP活性测定。对于UAMC1110亲本化合物,仅在第3天和第7天测量FAP活性。 使用特定的显色底物,通过分光光度法测定化合物对 FAP、PREP、DPPIV、DPP9 和 DPP2 的抑制效力(IC₅₀)。 FAP 活性测定使用底物 Ala-Pro-对硝基苯胺(2 mM),在 50 mM Tris、1 M NaCl、1 mg/mL 牛血清白蛋白、pH 7.4 的缓冲液中进行。使用重组小鼠 FAP。 PREP 活性测定使用底物 Z-Gly-Pro-对硝基苯胺(0.25 mM),在 50 mM Tris、pH 7.5 的缓冲液中进行。使用重组人 PREP。 DPPIV 活性测定使用底物 Gly-Pro-对硝基苯胺(100 µM),在 50 mM Tris、pH 8.3 的缓冲液中进行。酶从人精浆中纯化获得。 DPPII 活性测定使用底物 Lys-Ala-对硝基苯胺(1 mM),在 50 mM 柠檬酸-磷酸盐、pH 5.5 的缓冲液中进行。酶从人精浆中纯化获得。 DPP9 活性测定使用底物 Ala-Pro-对硝基苯胺(300 µM),在 50 mM Tris、1 mg/mL 牛血清白蛋白、pH 7.4 的缓冲液中进行。酶从牛睾丸中纯化获得。 底物浓度选择在 Kₘ 值附近。在加入底物前,抑制剂与酶在 37°C 下预孵育 10 分钟。监测 405 nm 处吸光度的增加。根据剂量反应曲线计算 IC₅₀ 值。[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
成纤维细胞活化蛋白(FAP)是一种脯氨酸选择性蛋白酶,属于丝氨酸蛋白酶S9家族。它通常在肿瘤微环境(TME)中高度表达,特别是在肿瘤基质的主要细胞成分——癌症相关成纤维细胞中。其酶活性在TME中的确切作用在很大程度上仍然未知。因此,能够在TME中对FAP进行选择性的、基于活动的可视化的工具可以帮助揭示FAP的功能。我们描述了基于FAP抑制剂UAMC1110的三种不同活性探针(生物素-,Cy3-和cy5标记)的合成,生化表征和应用。UAMC1110是一种内部开发的分子,被认为是最有效和选择性的FAP抑制剂。我们证明这三种探针对相关的S9家族成员具有亚纳摩尔的FAP亲和力和明显的选择性。此外,我们报道了荧光Cy3-和cy5标记探针能够选择性地检测细胞背景下的FAP,使这些化学探针非常适合进一步的生物学研究。此外,在患者来源的尿路上皮肿瘤冷冻切片中,提供了原位FAP活性染色的概念证明。前沿化学。Reference: Front Chem. 2021 Apr 14;9:640566.
在 MRC-5SV2 人胚胎二倍体成纤维细胞上评估细胞毒性。细胞在补充有 L-谷氨酰胺、NaHCO₃ 和 5% 灭活胎牛血清的 MEM 培养基中,于 37°C、5% CO₂ 条件下培养。 细胞暴露于测试化合物特定时间。使用 MTT 法评估细胞活力。测试的最高浓度为 64 µM。[1] |
| 动物实验 |
20 mg/kg; p.o.; 5 mg/kg. i.v. Rats: The PK parameters are determined for inhibitors 4, 5, 60 (FAP-IN-1), and 61 in rats. Six male rats are treated for each inhibitor tested, three of which received the compound via a single intravenous (iv) administration at 5 mg/kg. The other three animals are dosed per os (po) at 20 mg/kg. Blood samples are collected at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h after administration. Inhibitor concentrations are determined using UPLC MS/MS, and pharmacokinetic parameters are calculated using standard algorithms For pharmacokinetic studies, male Wistar rats (~250 g) were used. For each compound, six rats were divided into two groups (n=3 per group). One group received a single intravenous (iv) administration of the compound formulated in PEG₂₀₀ at a dose of 5 mg/kg. The other group received a single oral (po) administration (gavage) of the compound formulated in PEG₂₀₀ at a dose of 20 mg/kg. Blood samples were collected via tail vein or cardiac puncture at time points: 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 24 h after administration. Plasma was separated and stored at -20°C until analysis. Plasma concentrations of the inhibitor were determined using UPLC-MS/MS. Pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated using standard non-compartmental analysis.[1] For ex vivo FAP inhibition assessment, residual FAP activity was measured in the plasma samples collected during the PK study, using the substrate Z-Gly-Pro-AMC under conditions excluding soluble PREP activity. Activity was compared to vehicle-treated controls.[1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Oral bioavailalbility in rats = 51%
T1/2 = 3.2 hrs UAMC1110 showed high kinetic solubility (>200 µM). The measured log D value was 1.0. It exhibited good stability in mouse plasma (85% unchanged after 6 h) and rat plasma (95% unchanged after 6 h). It demonstrated high stability in rat hepatic microsomes (94% unchanged after 6 h). In rats, after a single iv dose (5 mg/kg), it had a Cₘₐₓ of 11.8 µg/mL, an AUC of 23.4 µg·h/mL, a clearance (Cl) of 2.83 mL/min, a volume of distribution (Vz) of 0.43 L, and a half-life (T₁/₂) of 1.74 h. After a single oral dose (20 mg/kg), it had a Tₘₐₓ of 0.33 h, a Cₘₐₓ of 14.6 µg/mL, an AUC of 76.7 µg·h/mL, a Cl of 1.55 mL/min, a Vz of 0.34 L, a T₁/₂ of 3.4 h, and a relative oral bioavailability of 74%.[1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
No signs of cellular toxicity were observed on MRC-5 cells at the highest concentration tested (64 µM).[1]
In the in vivo rat PK study, all animals treated with UAMC1110 (iv and po) showed no signs of toxicity during the observation period or upon autopsy, in contrast to the related compound 4 which caused mortality.[1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a serine protease related to dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV). It has been convincingly linked to multiple disease states involving remodeling of the extracellular matrix. FAP inhibition is investigated as a therapeutic option for several of these diseases, with most attention so far devoted to oncology applications. We previously discovered the N-4-quinolinoyl-Gly-(2S)-cyanoPro scaffold as a possible entry to highly potent and selective FAP inhibitors. In the present study, we explore in detail the structure-activity relationship around this core scaffold. We report extensively optimized compounds that display low nanomolar inhibitory potency and high selectivity against the related dipeptidyl peptidases (DPPs) DPPIV, DPP9, DPPII, and prolyl oligopeptidase (PREP). The log D values, plasma stabilities, and microsomal stabilities of selected compounds were found to be highly satisfactory. Pharmacokinetic evaluation in mice of selected inhibitors demonstrated high oral bioavailability, plasma half-life, and the potential to selectively and completely inhibit FAP in vivo.[1]
Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a proline-selective protease that belongs to the S9 family of serine proteases. It is typically highly expressed in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and especially in cancer-associated fibroblasts, the main cell components of the tumor stroma. The exact role of its enzymatic activity in the TME remains largely unknown. Hence, tools that enable selective, activity-based visualization of FAP within the TME can help to unravel FAP's function. We describe the synthesis, biochemical characterization, and application of three different activity-based probes (biotin-, Cy3-, and Cy5-labeled) based on the FAP-inhibitor UAMC1110, an in-house developed molecule considered to be the most potent and selective FAP inhibitor available. We demonstrate that the three probes have subnanomolar FAP affinity and pronounced selectivity with respect to the related S9 family members. Furthermore, we report that the fluorescent Cy3- and Cy5-labeled probes are capable of selectively detecting FAP in a cellular context, making these chemical probes highly suitable for further biological studies. Moreover, proof of concept is provided for in situ FAP activity staining in patient-derived cryosections of urothelial tumors.[2] UAMC1110 is a (4-quinolinoyl)glycyl-2-cyanopyrrolidine derivative, specifically the compound with a 4,4-difluorinated pyrrolidine ring at the P1 position. It is identified as one of the most potent and selective FAP inhibitors reported in this study. The compound binds reversibly to FAP and does not exhibit slow, tight-binding kinetics. The prolonged ex vivo FAP inhibition observed is attributed mainly to its favorable pharmacokinetic half-life. The authors highlight the structural similarity of this compound series and note an unexpected in vivo toxicity observed with the parent compound 4 in rats, the cause of which remains unclear and is not observed with UAMC1110.[1] |
| 分子式 |
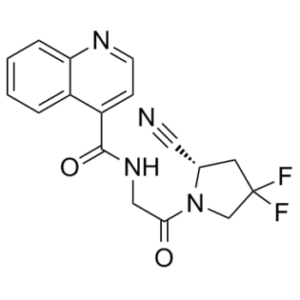
C₁₇H₁₄F₂N₄O₂
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
344.32
|
|
| 精确质量 |
344.108
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.30; H, 4.10; F, 11.04; N, 16.27; O, 9.29
|
|
| CAS号 |
1448440-52-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1448440-52-5;
|
|
| PubChem CID |
71621488
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as White to off-white solid at room temperature
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
676.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
362.9±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.621
|
|
| LogP |
0.22
|
|
| tPSA |
86.1
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
588
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1(CN(C(CNC(C2C=CN=C3C=CC=CC=23)=O)=O)[C@H](C#N)C1)F
|
|
| InChi Key |
PUOOCZVRHBHJRS-NSHDSACASA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H14F2N4O2/c18-17(19)7-11(8-20)23(10-17)15(24)9-22-16(25)13-5-6-21-14-4-2-1-3-12(13)14/h1-6,11H,7,9-10H2,(H,22,25)/t11-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
N-[2-[(2S)-2-cyano-4,4-difluoropyrrolidin-1-yl]-2-oxoethyl]quinoline-4-carboxamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9043 mL | 14.5214 mL | 29.0428 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5809 mL | 2.9043 mL | 5.8086 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2904 mL | 1.4521 mL | 2.9043 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 J Med Chem.2014 Apr 10;57(7):3053-74. |