| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Quinolone
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
暴露于曲伐沙星(20 µM;24 小时)和肿瘤坏死因子(TNF;4 ng/mL)的 HepG2 细胞表现出乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)渗漏和细胞凋亡增加。将 HepG2 细胞与曲伐沙星(20 µM)和 TNF 孵育 24 小时后(4 ng/mL),早期 NF-κB 相关因子 A20 和 IκBα 的表达增加。在 HepG2 中,曲伐沙星延长 TNF 诱导的 MAPK 激活和 IKKα/β 激活[1]。
有效防止细胞凋亡吸收性 TO-PRO-3 是曲伐沙星。此外,曲伐沙星可防止凋亡细胞释放 ATP。曲伐沙星不会阻止细胞凋亡或 caspase 3/7 激活过程中 PANX1 的裂解[2]。 700 多个分离株的 MIC 为 0.06-0.25 mg/mL,曲伐沙星对青霉素敏感的肺炎球菌和对青霉素敏感的肺炎球菌同样有效。那些对其有抵抗力的人。 Trovafloxacin 对 90% 肺炎球菌分离株的最低抑菌浓度 (MIC) 为 0.125 μg/mL [3]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
用曲伐沙星(150 mg/kg;口服;雄性 C57BL/6 J 小鼠)治疗可防止 TNF 诱导的 p65 核易位。曲伐沙星治疗会增加早期 NF-κB 相关因子 IκBα 和 A20 的表达[1]。当曲伐沙星与脂多糖 (LPS) 或肿瘤坏死因子 (TNF) 一起给予小鼠时,会引起严重的肝毒性,并伴有肝脏大面积细胞凋亡、血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶 (ALT) 和促炎细胞因子水平升高[1]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal Model: Male C57BL/6 J mice (9-11-week-old) injected with recombinant murine TNF ion[1]
Dosage: 150 mg/kg Administration: Oral administration Result: revealed a higher proportion of cells in the liver with an elevated nuclear/cytoplasmic p65 ratio. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Well-absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration and does not depend on concomitant food intake. The absolute bioavailability is approximately 88%. Approximately 50% of an oral dose is excreted unchanged (43% in the feces and 6% in the urine). Metabolism / Metabolites Metabolism Trovafloxacin is metabolized by conjugation (the role of cytochrome P450 oxidative metabolism of trovafloxacin is minimal). The major metabolites include the ester glucuronide, which appears in the urine (13% of the administered dose); and the N -acetyl metabolite, which appears in the feces and serum (9% and 2.5% of the administered dose, respectively). Other minor metabolites include diacid, hydroxycarboxylic acid, and sulfamate, which have been identified in both the feces and the urine in small amounts (< 4% of the administered dose). Trovafloxacin has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[7-[(1R,5S)-6-amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-3-yl]-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carbonyl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. Biological Half-Life Following oral administration, half-life ranged from 9.1 hours to 12.2 hours over the dosage range of 100 to 200 mg tablets. Following intravenous infusion, half-life ranged from 9.4 to 12.7 hours over a dosage range of 100 to 300 mg. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of trovafloxacin during breastfeeding; however, amounts in breastmilk appear to be low. Fluoroquinolones have traditionally not been used in infants because of concern about adverse effects on the infants' developing joints. However, recent studies indicate little risk. The calcium in milk might prevent absorption of the small amounts of fluoroquinolones in milk, but insufficient data exist to prove or disprove this assertion. Use of trovafloxacin is acceptable in nursing mothers with monitoring of the infant for possible effects on the gastrointestinal flora, such as diarrhea or candidiasis (thrush, diaper rash). However, it is preferable to use an alternate drug for which safety information is available. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding The mean plasma protein bound fraction is approximately 76%, and is concentration-independent. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
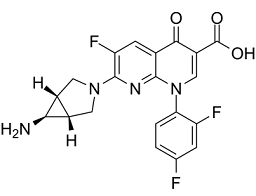
Trovafloxacin is a 1,8-naphthyridine derivative that is 4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid bearing additional 2,4-difluorophenyl, fluoro and 6-amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hex-3-yl substituents at positions 1, 6 and 7 respectively. A broad-spectrum antibiotic that was withdrawn from the market due to risk of liver failure. It has a role as an antimicrobial agent, a hepatotoxic agent, a topoisomerase IV inhibitor, a DNA synthesis inhibitor and an antibacterial drug. It is a 1,8-naphthyridine derivative, an amino acid, a monocarboxylic acid, an azabicycloalkane, a tertiary amino compound, a primary amino compound, a quinolone antibiotic, a fluoroquinolone antibiotic and a difluorobenzene. It is a conjugate base of a trovafloxacin(1+).
Trovafloxacin is a broad spectrum antibiotic that has been commonly marketed under the brand name Trovan by Pfizer. It exerts its antibacterial activity by inhibiting the uncoiling of supercoiled DNA in various bacteria by blocking the activity of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. It was shown to be more effective against Gram-positive bacteria than Gram-negative bacteria when compared to previous fluoroquinolones. Due to its hepatotoxic potential, trovafloxacin was withdrawn from the market. Drug Indication For treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in uncomplicated urethral gonorrhea in males and endocervical and rectal gonorrhea in females caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae as well as non gonoccocal urethritis and cervicitis due to Chlamydia trachomatis. Trovafloxacin is a synthetic broad spectrum quinolone antibacterial agent indicated for the treatment of the following infections in adults: Pneumonia: Community Acquired Pneumonia and Nosocomial Pneumonia (mild, moderate, and severe). Note: Efficacy in patients with very severe nosocomial pneumonia and in particular infections due to less susceptible pathogens e. g. P. aeruginosa, has not been established. See also section 4. 2. Acute Exacerbations of Chronic BronchitisAcute SinusitisComplicated Intra-abdominal Infections and Acute Pelvic InfectionsSalpingitisUncomplicated Gonococcal Urethritis and CervicitisChlamydial CervicitisComplicated Skin and Soft Tissue InfectionsConsideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents. Trovafloxacin is a synthetic broad spectrum quinolone antibacterial agent indicated for the treatment of the following infections in adults: Pneumonia: Community Acquired Pneumonia and Nosocomial Pneumonia (mild, moderate, and severe). Note: Efficacy in patients with very severe nosocomial pneumonia and in particular infections due to less susceptible pathogens e. g. P. aeruginosa, has not been established. See also section 4. 2. Acute Exacerbations of Chronic BronchitisAcute SinusitisComplicated Intra-abdominal Infections and Acute Pelvic InfectionsSalpingitisUncomplicated Gonococcal Urethritis and CervicitisChlamydial CervicitisComplicated Skin and Soft Tissue InfectionsConsideration should be given to official guidance on the appropriate use of antibacterial agents. Mechanism of Action Trovafloxacin is a fluoronaphthyridone related to the fluoroquinolones with in vitro activity against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms. The bactericidal action of trovafloxacin results from inhibition of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. DNA gyrase is an essential enzyme that is involved in the replication, transcription, and repair of bacterial DNA. Topoisomerase IV is an enzyme known to play a key role in the partitioning of the chromosomal DNA during bacterial cell division. Pharmacodynamics Trovafloxacin is a broad spectrum antibiotic that inhibits DNA supercoiling in various bacteria by blocking the activity of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. It is not used widely due to the risk of hepatotoxicity. It tends to have better gram-positive bacterial coverage and less gram-negative coverage than the previous fluoroquinolones. Mechanism of action of fluoroquinolones including trovafloxacin is different from that of penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, macrolides, and tetracyclines. Therefore fluoroquinolones may be active against pathogens that are resistant to these antibiotics. There is no cross-resistance between trovafloxacin and the mentioned classes of antibiotics. The overall results obtained from in vitro synergy studies, testing combinations of trovafloxacin with beta-lactams and aminoglycosides, indicate that synergy is strain specific and not commonly encountered. This agrees with results obtained previously with other fluoroquinolones. Resistance to trovafloxacin in vitro develops slowly via multiple-step mutation in a manner similar to other fluoroquinolones. Resistance to trovafloxacin in vitro occurs at a general frequency of between 1x10-7 to 10-10. Although cross-resistance has been observed between trovafloxacin and some other fluoroquinolones, some microorganisms resistant to other fluoroquinolones may be susceptible to trovafloxacin. |
| 分子式 |
C20H15F3N4O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
416.35
|
| 精确质量 |
416.11
|
| CAS号 |
147059-72-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Trovafloxacin mesylate;147059-75-4
|
| PubChem CID |
62959
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.612g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
630.5ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
246ºC
|
| 闪点 |
335.1ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
9.21E-17mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.672
|
| LogP |
2.659
|
| tPSA |
101.45
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
770
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C1[C@@H]2[C@@H](C2N)CN1C3=C(C=C4C(=O)C(=CN(C4=N3)C5=C(C=C(C=C5)F)F)C(=O)O)F
|
| InChi Key |
WVPSKSLAZQPAKQ-SOSAQKQKSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H15F3N4O3/c21-8-1-2-15(13(22)3-8)27-7-12(20(29)30)17(28)9-4-14(23)19(25-18(9)27)26-5-10-11(6-26)16(10)24/h1-4,7,10-11,16H,5-6,24H2,(H,29,30)/t10-,11+,16
|
| 化学名 |
7-[(1R,5S)-6-amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-3-yl]-1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~9.09 mg/mL (~21.83 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4018 mL | 12.0091 mL | 24.0183 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4804 mL | 2.4018 mL | 4.8037 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2402 mL | 1.2009 mL | 2.4018 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|