| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Vannicline diHClide(1 μM,24 小时)可抑制 RAW 264.7 巨噬细胞 LPS 诱导的细胞因子分泌(IL-1β、IL-6 和 TNFα)和细胞增殖率 [1]。当暴露于 250 nM vannicline diHClide 时,从男性和女性器官捐献者分离的人肾上腺嗜铬细胞在没有 ACh 刺激的情况下表现出动作电位 (Aps) 刺激 [3]。通过降低 VE-钙粘蛋白表达,vannicline diHClide(100 μM,4 小时)刺激 HUVEC 迁移 [4]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在尼古丁(0.5 mg/kg 皮下注射)之前 10 分钟给药时,万尼克林 disalk(0.01-1 mg/kg 皮下注射,3 天)可抑制尼古丁条件性位置偏好 (CPP) [5]。由vannicline diHClide(皮下注射,2.5 mg/kg,3天)引起的位置厌恶依赖于α5 nAChR,但不依赖于β2 nAChR [5]。皮下注射vannicline diHClide(0.1和0.5 mg/kg,3天)以剂量相关的方式逆转与尼古丁戒断相关的躯体症状和痛觉过敏以及戒断引起的厌恶[5]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定 [1]
细胞类型: RAW 264.7 小鼠巨噬细胞(用 4 μg/mL LPS 处理 24 小时) 测试浓度: 1 μM 孵育时间:0-48小时 实验结果:LPS诱导的细胞增殖率减弱。 蛋白质印迹分析[4] 细胞类型: HUVEC 测试浓度: 1、10、100 μM 孵育持续时间:24 小时或 30 分钟 实验结果:VE-钙粘蛋白表达减少,ERK1/2、p38 和 JNK 信号传导激活。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: ICR male mice [5]
Doses: 0.01-1 mg/kg, 3 days Route of Administration: subcutaneous injection Experimental Results: Inhibited nicotine conditioned place preference (CPP) in a dose-dependent manner. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Varenicline undergoes minimal metabolism, with 92% excreted unchanged in the urine. Renal elimination of varenicline is primarily through glomerular filtration along with active tubular secretion possibly via the organic cation transporter, OCT2. Maximum plasma concentrations of varenicline occur typically within 3-4 hours after oral administration. Following administration of multiple oral doses of varenicline, steady-state conditions were reached within 4 days. Over the recommended dosing range, varenicline exhibits linear pharmacokinetics after single or repeated doses. In a mass balance study, absorption of varenicline was virtually complete after oral administration and systemic availability was ~90%. Oral bioavailability of varenicline is unaffected by food or time-of-day dosing. Plasma protein binding of varenicline is low (Varenicline is eliminated principally in urine as unchanged drug. Renal elimination of the drug occurs primarily through glomerular filtration along with active tubular secretion. Varenicline is distributed into milk in animals. Not known whether varenicline is distributed into human milk. Metabolism / Metabolites Metabolism is limited (<10%). Most of the active compound is excreted by the kidneys (81%). A minor amount of varenicline is glucuronidated, oxidated, N-formylated, as well as conjugated to form a hexose. Varenicline undergoes minimal metabolism, with 92% excreted unchanged in the urine. Varenicline undergoes minimal metabolism with 92% excreted unchanged in the urine and less than 10% excreted as metabolites. Minor metabolites in urine include varenicline N-carbamoylglucuronide and hydroxyvarenicline. In circulation, varenicline comprises 91% of drug related material. Minor circulating metabolites include varenicline N-carbamoylglucuronide and N-glucosylvarenicline. Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life of varenicline is approximately 24 hours The elimination half-life of varenicline is approximately 24 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Varenicline has not been associated with rates of serum enzyme elevations during therapy greater than occurs with placebo therapy, but information on these abnormalities is limited and occasional instances of asymptomatic ALT elevations leading to drug discontinuation have been reported. In prelicensure pivotal registration trials in several thousand patients, varenicline was not associated with cases of jaundice or hepatitis. Since licensure, rare case reports of serum enzyme elevations without jaundice arising within 4 weeks of starting varenicline have been published, but largely in patients with other causes of liver injury (alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis C). The injury was self-limited in course and not associated with immunoallergic or autoimmune features. In Iceland, a single case of varenicline hepatotoxicity has been reported (Case 1), there having been an estimated 20,000 persons treated with the drug in the country since its introduction. Likelihood score: C (probable rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Varenicline is a partial nicotine agonist used orally to assist smoking cessation and by nasal spray for dry eyes. One researcher points out that based on animal data on nicotine, varenicline might interfere with normal infant lung development and recommends against its use in nursing mothers. Because no information is available on the use of varenicline during breastfeeding, an alternate drug is preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. However, maternal drug exposure after the nasal spray is only about 7.5% that of the oral drug, so the spray is much less likely to affect the infant. If a mother chooses to breastfeed while taking varenicline, she should monitor her infant for seizures and excessive vomiting. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Less than 20%. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Elif Baris, et al. Varenicline Prevents LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response via Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Oct 12;8:721533.
[2]. Mihalak KB, et al. Varenicline is a partial agonist at alpha4beta2 and a full agonist at alpha7 neuronal nicotinic receptors.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;70(3):801-5. Epub 2006 Jun 9. [3]. Jin H, et al. Therapeutic concentrations of varenicline in the presence of nicotine increase action potential firing in human adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 2017 Jan;140(1):37-52. [4]. Mitsuhisa Koga, et al. Varenicline promotes endothelial cell migration by lowering vascular endothelial-cadherin levels via the activated α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mitogen activated protein kinase axis. Toxicology. 2017 Sep 1;390:1-9. [5]. Bagdas D, et al. New insights on the effects of varenicline on nicotine reward, withdrawal and hyperalgesia in mice.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Aug;138:72-79. |
| 其他信息 |
Varenicline is a prescription medication used to treat smoking addiction. This medication is the first approved nicotinic receptor partial agonist. Specifically, varenicline is a partial agonist of the alpha4/beta2 subtype of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. In addition it acts on alpha3/beta4 and weakly on alpha3beta2 and alpha6-containing receptors. A full agonism was displayed on alpha7-receptors. On March 9, 2015, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration warned that Varenicline, in the form of Pfizer Inc's quit-smoking drug, Chantix, has been associated with seizures and that some patients who drink while taking the drug may become aggressive or black out. Pfizer is conducting an additional safety study of the drug, results of which are expected in late 2015. The FDA said it is keeping the black box in place at least until the results of the trial are announced.
Varenicline is a partial agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and is used to help in smoking cessation. Varenicline has been associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations during therapy and, since approval and its widescale use, with rare instances of clinically apparent mild liver injury. Varenicline is a partial agonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subtype alpha4beta2. Nicotine stimulation of central alpha4beta2 nAChRs located at presynaptic terminals in the nucleus accumbens causes the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which may be associated with the experience of pleasure; nicotine addiction constitutes a physiologic dependence related to this dopaminergic reward system. As an AChR partial agonist, varenicline attenuates the craving and withdrawal symptoms that occur with abstinence from nicotine but is not habit-forming itself. A benzazepine derivative that functions as an ALPHA4-BETA2 NICOTINIC RECEPTOR partial agonist. It is used for SMOKING CESSATION. See also: Varenicline dihydrochloride (annotation moved to). Drug Indication For use as an aid in smoking cessation. Varenicline as a nasal spray is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of dry eye disease. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Varenicline is an alpha-4 beta-2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist. The drug shows high selectivity for this receptor subclass, relative to other nicotinic receptors (>500-fold alpha-3 beta-4, >3500-fold alpha-7, >20,000-fold alpha-1 beta gamma delta) or non-nicotinic receptors and transporters (>2000-fold). The drug competitively inhibits the ability of nicotine to bind to and activate the alpha-4 beta-2 receptor. The drug exerts mild agonistic activity at this site, though at a level much lower than nicotine; it is presumed that this activation eases withdrawal symptoms. Varenicline is a selective alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist. The drug binds with high affinity and selectivity to alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors located in the brain and stimulates receptor-mediated activity, but at a substantially lower level than nicotine;1 6 this low-level receptor stimulation and subsequent moderate, sustained release of mesolimbic dopamine are thought to reduce craving and withdrawal symptoms associated with smoking cessation. Varenicline also blocks the ability of nicotine to activate alpha4beta2 receptors, preventing nicotine-induced stimulation of the mesolimbic dopaminergic system and thereby reducing the reinforcement and reward effects of cigarette smoking. ... The rationale for and the design of alpha(4)beta(2) neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) partial agonists as novel treatments for tobacco addiction. Such agents are expected to exhibit a dual action by sufficiently stimulating alpha(4)beta(2)-nAChR-mediated dopamine release to reduce craving when quitting and by inhibiting nicotine reinforcement when smoking. Potent and selective alpha(4)beta(2) nAChR partial agonists that exhibit dual agonist and antagonist activity in preclinical models can be identified. The validity of this approach is demonstrated by the clinical efficacy of the alpha(4)beta(2) nAChR partial agonist varenicline, which has significantly better quit rates than do other treatments and offers a new option for smoking cessation pharmacotherapy. ... Varenicline has been shown to be a partial agonist of alpha4beta2 receptors, and in equilibrium binding assays, it is highly selective for the alpha4beta2 receptor. ... The functional activity of varenicline at a variety of rat neuronal nicotinic receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes and assayed under two-electrode voltage clamp /was examined/ . Varenicline is a potent, partial agonist at alpha4beta2 receptors, with an EC50 of 2.3 +/- 0.3 microM and an efficacy (relative to acetylcholine) of 13.4 +/- 0.4%. Varenicline has lower potency and higher efficacy at alpha3beta4 receptors, with an EC50 of 55 +/- 8 microM and an efficacy of 75 +/- 6%. Varenicline also seems to be a weak partial agonist at alpha3beta2 and alpha6-containing receptors, with an efficacy <10%. It is remarkable that varenicline is a potent, full agonist at alpha7 receptors with an EC50 of 18 +/- 6 microM and an efficacy of 93 +/- 7% (relative to acetylcholine). Thus, whereas varenicline is a partial agonist at some heteromeric neuronal nicotinic receptors, it is a full agonist at the homomeric alpha7 receptor. Some combination of these actions may be involved in the mechanism of varenicline as a smoking cessation aid. |
| 分子式 |
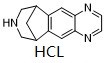
C13H15CL2N3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
284.1843
|
| 精确质量 |
247.088
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 54.94; H, 5.32; Cl, 24.95; N, 14.79
|
| CAS号 |
866823-63-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Varenicline;249296-44-4;Varenicline-d4 hydrochloride;Varenicline-d4 dihydrochloride
|
| PubChem CID |
45263226
|
| 外观&性状 |
Brown to dark brown solid powder
|
| LogP |
2.934
|
| tPSA |
37.81
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
0
|
| 重原子数目 |
18
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
254
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
Cl.N1C2C(=CC3C4CC(CNC4)C=3C=2)N=CC=1
|
| 别名 |
Varenicline dihydrochloride; HSDB7591; HSDB-7591; HSDB 7591; CP 526555; CP-526555; CP526555;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~62.5 mg/mL (~219.93 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5189 mL | 17.5945 mL | 35.1890 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7038 mL | 3.5189 mL | 7.0378 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3519 mL | 1.7594 mL | 3.5189 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Botswana Smoking and Abstinence Reinforcement Trial
CTID: NCT05694637
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Enrolling by invitation
Date: 2024-11-13