| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Topoisomerase II[4]
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
aldoxorubicin salted (INNO-206)(0.27 至 2.16 μM)以 pH 依赖性方式减少多发性骨髓瘤细胞的增殖并防止血管形成[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
盐酸醛柔比星 (INNO-206) (10.8 mg/kg,静脉注射) 耐受性良好; 90% 的 LAGκ-1A 肿瘤小鼠存活到研究得出结论[1]。第 28 天时,肿瘤尺寸和 IgG 水平明显降低。在一项 I 期研究中,盐酸醛柔比星 (INNO-206) 可导致乳腺癌、小细胞肺癌和肉瘤的肿瘤消退 [2]。在剂量高达 260 mg/mL 阿霉素当量时,它还表现出出色的安全性。在小鼠肾细胞癌和乳腺癌异种移植模型中,盐酸醛柔比星(INNO-206)表现出比阿霉素更好的疗效[3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
在含有FBS的RPMI-1640培养基中,以1×105个细胞/100μL/孔的密度将细胞接种在96孔板上24小时,然后进行处理。细胞在培养基、INNO-206或阿霉素存在下培养48小时。接下来,使用CellTiter 96 AQueous非放射性细胞增殖试验(Promega)定量细胞存活率。每个孔用MTS处理1至4小时,之后使用96孔板读数器记录490nm处的吸光度。甲赞产物的测量量与活细胞的数量成正比。绘制的数据为平均值±SEM,每个数据点使用3个重复。 通过MTS法测定不同pH水平的INNO-206对多发性骨髓瘤细胞系增殖的抗多发性髓瘤作用,并通过绒毛尿囊膜/羽毛芽法测定其抗血管生成活性。使用我们的多发性骨髓瘤异种移植物模型,还将INNO-206的抗多发性髓瘤作用和毒性与常规阿霉素和聚乙二醇化脂质体阿霉素(PLD)单独使用以及与硼替佐米联合使用进行了比较[1]。 |
| 动物实验 |
INNO-206 stock solutions (5.4 mg/mL) were prepared using 50% ethanol and 50% water and further diluted in sterile water. [1]
For the LAGκ-1A experiment, INNO-206 was administered to SCID mice at 10.8 mg/kg (doxorubicin equivalent dose of 8.0 mg/kg) once weekly. Mice were treated with conventional doxorubicin at 4.0 and 8.0 mg/kg once weekly. For the LAGκ-2 experiment, INNO-206 was administered once weekly (W) at doses of 2.7 and 5.4 mg/kg, or on 3 consecutive days (W-F) weekly at doses of 0.9 and 1.8 mg/kg. Bortezomib was administered twice weekly (W, F) at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg. Doxorubicin was administered to SCID mice at 2, 4, and 8 mg/kg, and PLD was administered to SCID mice at 2 mg/kg once weekly. Each drug was administered i.v. in a volume of 100 μL.[1] The (6-maleimidocaproyl)hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin (INNO-206) is an albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin with acid-sensitive properties that is being assessed clinically. The prodrug binds rapidly to circulating serum albumin and releases doxorubicin selectively at the tumor site. This novel mechanism may provide enhanced antitumor activity of doxorubicin while improving the overall toxicity profile. Preclinically, INNO-206 has shown superior activity over doxorubicin in a murine renal cell carcinoma model and in breast carcinoma xenograft models. In this work, we compared the antitumor activity of INNO-206 and doxorubicin at their respective maximum tolerated doses in three additional xenograft models (breast carcinoma 3366, ovarian carcinoma A2780, and small cell lung cancer H209) as well as in an orthotopic pancreas carcinoma model (AsPC-1). INNO-206 showed more potent antitumor efficacy than free doxorubicin in all tumor models and is thus a promising clinical candidate for treating a broad range of solid tumors[3]. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Aldoxorubicin, an antineoplastic agents, is an albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin.
Aldoxorubicin is a 6-maleimidocaproyl hydrazone derivative prodrug of the anthracycline antibiotic doxorubicin (DOXO-EMCH) with antineoplastic activity. Following intravenous administration, aldoxorubicin binds selectively to the cysteine-34 position of albumin via its maleimide moiety. Doxorubicin is released from the albumin carrier after cleavage of the acid-sensitive hydrazone linker within the acidic environment of tumors and, once located intracellularly, intercalates DNA, inhibits DNA synthesis, and induces apoptosis. Albumin tends to accumulate in solid tumors as a result of high metabolic turnover, rapid angiogenesis, hypervasculature, and impaired lymphatic drainage. Because of passive accumulation within tumors, this agent may improve the therapeutic effects of doxorubicin while minimizing systemic toxicity.
Mechanism of Action INNO-206 is the (6-Maleimidocaproyl) hydrazone of doxorubicin. INNO-206 is a prodrug of doxorubicin that binds endogenous albumin after administration. The bound doxorubicin is released in the acidic environment of the tumor cell through cleavage of an acid sensitive linker. In preclinical models, INNO-206 was superior to doxorubicin with regard to antitumor efficacy and toxicity. Doxorubicin has shown efficacy especially in combination treatment for the treatment of multiple myeloma; however, its side effects limit its use. INNO-206 is an albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin, which is released from albumin under acidic conditions. Because INNO-206 has not been previously evaluated in any hematologic malignancy, we determined its anti–multiple myeloma effects. Experimental Design: The anti–multiple myeloma effect of INNO-206 at different pH levels on multiple myeloma cell proliferation using multiple myeloma cell lines with the MTS assay and antiangiogenic activity using the chorioallantoic membrane/feather bud assay were determined. The anti–multiple myeloma effects and toxicity of INNO-206 were also compared with conventional doxorubicin and PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) alone, and in combination with bortezomib, using our multiple myeloma xenograft models. Results: INNO-206 inhibited blood vessel formation and reduced multiple myeloma cell growth in a pH-dependent fashion. INNO-206 alone produced marked anti–multiple myeloma effects in vivo at doses that doxorubicin was toxic, and the combination of INNO-206 plus bortezomib produced increased anti–multiple myeloma effects compared with either agent alone. In contrast, all mice receiving bortezomib with doxorubicin or PLD died. Conclusions: These findings show that INNO-206 produces anti–multiple myeloma effects in vitro and in vivo. It also enhances the antitumor effects of bortezomib. These results suggest that INNO-206 may provide patients with multiple myeloma with an anthracycline that may be administered safely at higher doses compared with free doxorubicin, resulting in superior efficacy compared with the currently available anthracyclines to treat this B-cell malignancy.[1] Clin Cancer Res; 18(14); 3856–67. ©2012 AACR. The (6-maleimidocaproyl)hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin (INNO-206, formerly DOXO-EMCH) is a prodrug of the anticancer agent doxorubicin which is selectively bound to the cysteine-34 position of endogenous albumin within a few minutes after intravenous administration planned for 2011. Preclinically as well as clinically, the albuminbound form of INNO-206 has a large AUC, a small volume of distribution and low clearance compared to doxorubicin, uptake in solid tumors being mediated by the pathophysiology of tumor tissue, characterized by angiogenesis, hypervasculature, a defective vascular architecture, and an impaired lymphatic drainage. The prodrug contains an acid-sensitive hydrazone linker allowing doxorubicin to be released either extracellularly in the slightly acidic environment often present in tumor tissue or intracellularly in acidic endosomal or lysosomal compartments after cellular uptake of the albumin conjugate by the tumor cell. INNO-206 shows significantly superior antitumor efficacy over free doxorubicin in a spectrum of preclinical tumor models. In a phase I study, INNO-206 showed a good safety profile at doses up to 260 mg/m2 doxorubicin equivalents. Although not the primary end point of the phase I study, INNO-206 was able to induce tumor regressions in breast cancer, small cell lung cancer and sarcoma. Phase II studies against gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer and sarcoma are planned for the end of 2010.[2] Elastin-like polypeptide (ELP) is a macromolecular carrier with thermally responsive properties that can passively accumulate in solid tumors and additionally aggregate in tumor tissue when exposed to hyperthermia. In this study, ELP was conjugated to the anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOXO) and three different cell penetrating peptides (CPP) in order to inhibit tumor growth in mice compared to free doxorubicin. Fluorescence microscopy studies in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells demonstrated that the three different CPP-ELP-DOXO conjugates delivered doxorubicin to the cell nucleus. All CPP-ELP-DOXO conjugates showed cytotoxicity with IC(50) values in the range of 12-30 μM at 42 °C, but the ELP carrier with SynB1 as the cell penetrating peptide had the lowest intrinsic cytotoxicity. Therefore, the antitumor efficacy of SynB1-ELP-DOXO was compared to doxorubicin under hyperthermic conditions. C57BL/6 female mice bearing syngeneic E0771 murine breast tumors were treated with either free doxorubicin or the SynB1-ELP-DOXO conjugate with or without focused hyperthermia on the tumor. Under hyperthermic conditions, tumor inhibition with SynB1-ELP-DOXO was 2-fold higher than under therapy with free doxorubicin at the equivalent dose, and is thus a promising lead candidate for optimizing thermally responsive drug polymer conjugates.[4] |
| 分子式 |
C37H43CLN4O13
|
|---|---|
| 精确质量 |
786.251
|
| CAS号 |
1361563-03-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Aldoxorubicin;1361644-26-9
|
| PubChem CID |
10056071
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
268Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
8
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
15
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
55
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1510
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
6
|
| SMILES |
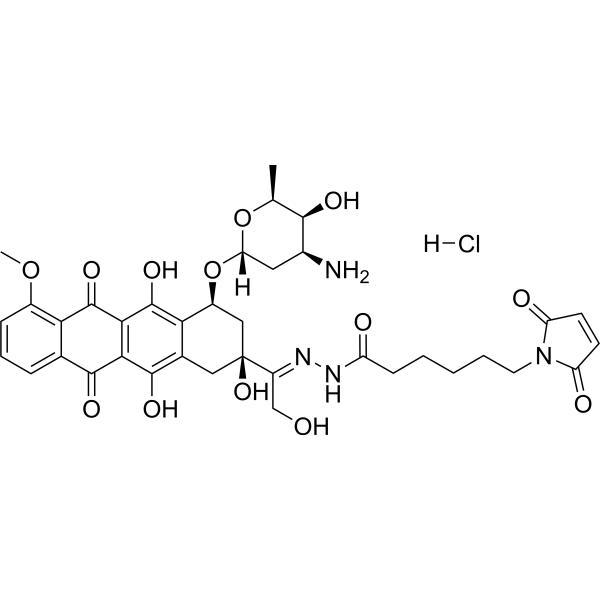
Cl.O([C@H]1C[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C)O1)O)N)[C@@H]1C2C(=C3C(C4C(=CC=CC=4C(C3=C(C=2C[C@@](/C(/CO)=N/NC(CCCCCN2C(C=CC2=O)=O)=O)(C1)O)O)=O)OC)=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
NGKHWQPYPXRQTM-UKFSEGPMSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C37H42N4O13.ClH/c1-17-32(46)20(38)13-27(53-17)54-22-15-37(51,23(16-42)39-40-24(43)9-4-3-5-12-41-25(44)10-11-26(41)45)14-19-29(22)36(50)31-30(34(19)48)33(47)18-7-6-8-21(52-2)28(18)35(31)49;/h6-8,10-11,17,20,22,27,32,42,46,48,50-51H,3-5,9,12-16,38H2,1-2H3,(H,40,43);1H/b39-23+;/t17-,20-,22-,27-,32+,37-;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
N-[(E)-[1-[(2S,4S)-4-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-2,5,12-trihydroxy-7-methoxy-6,11-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-1H-tetracen-2-yl]-2-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-6-(2,5-dioxopyrrol-1-yl)hexanamide;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
480998-12-7; ALDOXORUBICIN HYDROCHLORIDE; MC-DOXHZN hydrochloride; INNO-206 hydrochloride; Aldoxorubicin?HCl; 1361563-03-2; Aldoxorubicin (hydrochloride); Aldoxorubicin Hydrochloride [USAN];
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。