| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
EGFR (IC50 = 0.3 nM); EGFRL858R (IC50 = 0.2 nM); EGFRExon 19 deletion (IC50 = 0.2 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:在 H3255 (L858R) 细胞中,AZD3759 抑制 EGFR 磷酸化,IC50 为 7.2 nM。 AZD3759 对 pEGFR 通路和 EGFR 突变衍生细胞 PC-9 和 H3255 的细胞增殖具有抑制作用,IC50 分别为 7.7 nM 和 7 nM,对 H838 细胞的细胞增殖显示出抑制活性。激酶测定:根据制造商的说明,使用CisBio均质时间分辨荧光方法(HTRF,目录号62TK0PEJ)评估化合物对EGFR WT和突变酶的抑制效力。对于 EGFR 野生型、L858R 和 Exon19Del,本测定中使用的最终酶浓度分别为 0.1 nM、0.03 nM 和 0.026 nM,对应于 EGFR 酶的 Km 值的 ATP 为 0.8 μM、4 μM 和 25 μM相应地应用。简而言之,将 3 μL ATP 和 2 μMTK 生物素肽底物在存在或不存在连续稀释化合物的情况下于室温下在 384 孔 Greiner 白色聚苯乙烯测定板中孵育。通过添加可磷酸化底物肽的 3 μL 激酶来启动反应,测定缓冲液包含 1 mM DTT、5 mM MgCl2、1 mM MnCl2 和 0.01% CHAPS。孵育 30 分钟后,添加 6 μl 检测试剂混合物(含有 250 nM Strep-XL665 和稀释在检测缓冲液中的 TK Ab 铕穴状化合物)来终止反应。将板孵育 1 小时,然后使用 Perkin Elmer 的 EnVision Multilabel Reader 使用标准 HTRF 设置,分别在 615 nm 和 665 nm 处测量荧光,激发波长为 320 nm。计算得出的 665 nm/615 nm 信号比与激酶活性成正比。使用四参数逻辑拟合计算对相应激酶产生 50% 抑制 (IC50) 的化合物浓度。细胞测定:细胞增殖测定通过MTS方法测定。简而言之,将细胞(PC-9(外显子 19Del)、H3255(L858R)和 H838(wt)细胞)接种到 96 孔板中(密度要允许在 72 小时测定期间对数生长)并在37 °C 和 5% CO2。然后将细胞暴露于浓度范围为 30 至 0.0003 mM 的化合物中 72 小时。对于 MTS 终点,细胞增殖通过 CellTiter AQueous 非放射性细胞增殖测定试剂根据制造商的方案进行测量。使用 Tecan Ultra 仪器测量吸光度。进行给药前测量,并使用吸光度读数确定将处理的细胞的生长减少到未处理的细胞的一半(GI50)值所需的浓度。
候选药物佐利伐替尼/Zorifertinib (AZD3759)的体外特征/1m[1] 在相应的Km和2mM ATP浓度下测试1m/佐非替尼(AZD3759)对EGFR酪氨酸激酶(EGFR TK)野生型和突变型酶的抑制作用(表6)。在Km-ATP浓度下,EGFR TK野生型、L858R突变体和Exon 19Del酶的抑制IC50值分别为0.3、0.2和0.2 nM。在细胞EGFR磷酸化和增殖研究中,使用了PC-9(外显子19Del)、H3255(L858R)和H838(野生型EGFR)细胞(详见支持信息)。结果如表6所示。化合物1m在7.0-7.7 nM的范围内是EGFR激活突变细胞系(PC-9和H3255细胞系)中细胞磷酸化或增殖的同等强效抑制剂,表明对所有这些临床相关的EGFR突变都有很高的效力。在细胞磷酸化研究中,1m还证明了EGFR激活突变细胞系比EGFR野生型细胞系(H838细胞系)具有9倍的抑制选择性。当ATP浓度从Km增加到2mM(假设的细胞ATP浓度)时,这与生化测定的结果一致,表明1m的ATP竞争结合模式可能与突变型和野生型EGFR具有不同的结合亲和力。尽管1m/Zorifertinib(AZD3759)在H838细胞中显示出对pEGFR的一些活性,但由于这些细胞不依赖于EGFR途径的激活来增殖,我们没有看到1m对H838细胞增殖的活性。相比之下,1m对EGFR突变衍生的细胞PC-9和H3255的pEGFR通路和细胞增殖都有抑制作用,表明这些细胞依赖于EGFR通路的激活进行增殖。为了广泛评估化合物的选择性,我们在激酶小组和二级药理学小组中筛选了1m(详见支持信息)。在Millipore筛选的激酶组由124种重组蛋白激酶和脂质激酶组成。在每种激酶的单一浓度(1μM)下测试了1m的抑制百分比。在该浓度下,1m对115种激酶的抑制率小于50%,对其他9种激酶(包括面板中的EGFR激酶)的抑制率大于50%。这八个非靶点的抑制率分别为EphB4 83%、Flt 57%、Fyn 58%、KDR 62%、活化Lck 61%、Lyn 74%、Src 69%和Yes 87%。Cerep的二级药理学小组涵盖了150个不同的分子靶点。检测以浓度-反应模式进行。研究发现,147个分子靶标的IC50大于1μM,3个靶标的IC50小于1μM。这些IC50小于1μM的活性分子靶标是KDR(156 nM)、Src(622 nM)和D2(797 nM)。这些面板筛查的结果表明,1m是一种高度选择性的化合物。此外,1m/Zorifertinib(AZD3759)既不是CYP1A2、CYP2B6、CYP2C8、CYP2C9、CYP2C19、CYP2D6或CYP3A4/5亚型的直接抑制剂(IC50>50μM),也不是时间依赖性抑制剂。在化合物的预测最大总浓度(0.3μM)下,该试剂对CYP1A2、CYP2B6和CYP3A4的mRNA诱导作用小于3倍,表明酶诱导的可能性较低。此外,在传统的手动全细胞膜片钳研究中,该候选物显示出可接受的hERG抑制活性,IC50为13.3μM。 Zorifertinib(AZD3759)是一种酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,在治疗非小细胞肺癌脑转移方面具有令人鼓舞的前景。在这里,我们确定AZD3759抑制了肝癌细胞系HepG2细胞的存活率,并诱导了它们的凋亡,这表明Zorifertinib (AZD3759))在肝细胞癌(HCC)治疗中具有新的治疗潜力。此外,我们发现p53-SMAD家族成员4(SMAD4)正反馈回路的激活参与了佐非他尼/Zorifertinib (AZD3759)治疗诱导HepG2细胞大量凋亡的过程。在这个正反馈回路中,p53通过直接促进SMAD4的转录来诱导SMAD4的表达,如p53可以与SMAD4启动子结合所示;SMAD4反过来又促进了p53的核转位,这增加了促凋亡基因的转录,包括PUMA和BAX(两个p53靶基因),最终导致细胞凋亡。据我们所知,p53诱导的SMAD4转录和SMAD4确定p53的亚定位尚未有报道。综上所述,我们的研究结果表明,AZD3759可能是治疗HCC的替代策略,激活p53-SMAD4正反馈回路可能会增强其对HCC的治疗效果[2]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
AZD3759 在狗中表现出良好的口服生物利用度,并广泛渗透到猴脑中。在脑转移 PC-9 (Exon19Del) 模型中,Zorifertinib (AZD3759)(15 mg/kg) 产生显着的剂量依赖性抗肿瘤功效。
体内抗肿瘤疗效研究[1] 通过脑内注射荧光素酶转染的PC-9(Exon19Tel)细胞产生脑转移模型。通过IVIS Xenogen成像系统监测肿瘤生长。Zorifertinib(AZD3759)显示出显著的剂量依赖性抗肿瘤疗效(治疗4周后,7.5 mg/kg qd时肿瘤生长抑制率约为78%,15 mg/kg qd后肿瘤消退),体重减轻<20%,而厄洛替尼在该模型中的效果有限(图2A)。研究结束时,收集脑组织进行组织学评估。在7.5和15mg/kg的剂量下,通过Zorifertinib (AZD3759)治疗,观察到肿瘤面积显著减小(图2B)。此外,在给药后1小时以15mg/kg的剂量单次给药Zorifetinib(AZD3759)可检测到pEGFR的调节,这证实了Zorifetini(AZD37529)的靶向作用(图2C)。 微剂量正电子发射断层扫描(PET)研究[1] 通过微剂量PET研究了佐非他尼/Zorifertinib (AZD3759)在猴子体内的脑分布,以证实大鼠的PK数据。将放射性标记的[11C]-Zorifertinib (AZD3759)(0.28μg,150 MBq和0.35μg,155 MBq)注射到两只雄性食蟹猴(分别为PET1和PET2)体内。使用2问题隔室模型估算整个大脑区域的PET分布体积(VT)。表8总结了分布体积和估计的游离脑与血浆分配系数(Cu,脑/Cu,血浆)。分配系数值(PET1和PET2分别为0.50和0.53)表明Zorifertinib (AZD3759)广泛渗透到猴脑中。两只猴子的PET图像(图1)也表明,放射性标记的化合物在整个大脑中分布良好。 |
| 酶活实验 |
按照制造商的说明,使用 CisBio 均相时间分辨荧光方法(HTRF,目录号 62TK0PEJ)评估化合物对 EGFR WT 和突变酶的抑制效力。该测定采用以下最终酶浓度:EGFR野生型、L858R和Exon19Del分别为0.1 nM、0.03 nM和0.026 nM。 EGFR 酶的相应 Km 值适用于 0.8 μM、4 μM 和 25 μM ATP。总之,将 384 孔 Greiner 白色聚苯乙烯测定板与 3 μL ATP 和 2 μMTK 生物素肽底物在室温下孵育,无论有或没有连续稀释的化合物。检测缓冲液包含 1 mM DTT、5 mM MgCl2、1 mM MnCl2 和 0.01% CHAPS。通过添加 3 μL 激酶开始反应,该激酶具有磷酸化底物肽的能力。反应孵育 30 分钟后,通过添加 6 μl 检测试剂混合物来终止反应,其中含有检测缓冲液中稀释的 TK Ab 铕穴状化合物和 250 nM Strep-XL665。将板孵育一小时后,使用 Perkin Elmer 的 EnVision Multilabel Reader 分别测量 615 nm 和 665 nm 处的荧光,激发波长为 320 nm,采用标准 HTRF 设置。激酶活性与计算的 665 至 615 纳米信号比呈负相关。四参数逻辑拟合方法用于确定导致相应激酶 50% 抑制的化合物浓度 (IC50)。
[1]
1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759)的激酶选择性[1] 1m/Zorifertinib(AZD3759)在Millipore激酶组的124种激酶中,以1μM的单一浓度进行测试,ATP浓度在其相应表观Km值的15μM以内。详细方案可从Millipore获得。简而言之,重组激酶在含有肽底物和放射性标记的γ33P-ATP的适当缓冲液中孵育,同时存在或不存在所需的抑制剂浓度。通过加入ATP/Mg2+混合物引发反应。在室温下孵育40分钟后,通过加入3%磷酸溶液停止反应。将一部分反应混合物点样到P30过滤垫上以捕获肽,并用磷酸洗涤三次5分钟以去除非特异性γ33P-ATP。然后通过闪烁计数测量磷酸化底物,该计数确定了与对照反应相比的激酶活性抑制水平。 |
| 细胞实验 |
MTS 技术用于确定细胞增殖测试的结果。总之,细胞以允许在 72 小时实验中对数生长的密度接种在 96 孔板中,然后在 37 °C 和 5% CO2 下孵育整晚。随后,将浓度范围为 30 至 0.0003 mM 的化合物暴露于细胞,持续 72 小时。 CellTiter 水性非放射性细胞增殖测定试剂用于按照制造商的方案测量 MTS 终点的细胞增殖。 Tecan Ultra 设备用于测量吸光度。进行给药前测量,并使用吸光度读数来计算将处理的细胞生长限制为未处理细胞的一半(GI50)值所需的浓度。
细胞增殖试验[1] 采用MTS法测定细胞增殖试验。简而言之,将细胞接种在96孔板中(密度允许在72小时的测定中对数生长),并在37°C和5%CO2下孵育过夜。然后将细胞暴露于30至0.0003 mM浓度的化合物中72小时。对于MTS终点,根据制造商的方案,使用CellTiter AQueous非放射性细胞增殖测定试剂测量细胞增殖。使用Tecan Ultra仪器测量吸光度。进行了给药前测量,并使用吸光度读数确定了将处理细胞的生长减少到未处理细胞的一半所需的浓度(GI50)值。 检测细胞活力、凋亡和BAX+/PUMA+/SMAD4+细胞[2] 如前所述,使用MTT比色测定试剂盒定量细胞存活率。如前所述,使用流式细胞术检测凋亡细胞(膜联蛋白V+细胞)和BAX+/PUMA+/SMAD4+细胞。使用荧光素标记抗体,包括抗Annxin V-PE、抗BAX-FITC、抗PUMA-FITC和抗SMAD4-FITC,对细胞进行染色。 萤光素酶活性测定[2] 详细的方法已在前面描述过。简而言之,用含有PUMA或BAX或SMAD4启动子的启动子报告质粒转染细胞。相对光单位值被归一化为β-半乳糖苷酶信号。所有转染均使用每种指定的启动子报告质粒和pRSVβ-半乳糖苷酶质粒各1微克。 mRNA和蛋白质水平的检测[2] 如前所述,实时PCR和免疫印迹分析用于检测mRNA和蛋白质水平。简而言之,mRNA含量被标准化为管家基因β-actin的表达。实时PCR使用以下特异性引物序列:β-actin、5′-GCCTGAGGCACTCTCCA-3'(正向)和5′-CCGGATGTCCACGTCACTT-3'(反向)。BAX、PUMA和SMAD4引物从PrimePCR TM SYBR Green®检测试剂盒中获得。这些抗体包括抗p5、抗半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶3、抗切割半胱氨酸天冬氨酸酯3、抗β-肌动蛋白、抗SMAD4和抗Lamin B1,用于免疫印迹检测。 染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和亚细胞分级分析[2] ChIP的详细程序已在之前的研究中进行了描述。检测p53的抗体用于免疫沉淀与相关蛋白质相互作用的DNA片段。我们之前的研究中描述了核和细胞质提取物的分离方法。 |
| 动物实验 |
In Vivo Animal Models [1]
PC-9 cells (EGFR Exon19 deletion) were cultured with RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) at 37 °C. To monitor tumor growth in the brain, we stably transfected PC-9 cells with pGL4.50[luc2/CMV/Hygro] vector containing luciferase, and the bioluminescence signals were measured by a Xenogen imaging system. A brain metastasis model was established by intracerebral (ICB) injection of PC-9_Luc cells using the method by Lal with modifications. In brief, after a sagittal incision over the parieto-occipital bone, a hole was punctured on the skull at 2.5 mm to the right of the bregma and 1 mm anterior to the coronal suture. Then, the syringe was placed perpendicular to the skull through the hole and placed 3 mm deep below the skull surface, and the PC-9_Luc cell suspension was slowly injected. After injection, a sterile bone gel was applied to the hole, the scalp was pulled back to cover the skull, and the wound was closed. The mouse was gently put on a heating pad to recover, and closely monitored after surgery. Xenograft tissues were obtained from the PC-9 model after treatment with Zorifertinib (AZD3759) for assessment of histology and pEGFR modulation. Samples were harvested following formalin fixation and paraffin embedding (FFPE) for further study. pEGFR(Tyr1068) IHC was performed on 3 μm FFPE sections using a Ventana automation for staining. In each PET measurement a sterile solution of [11C]-Zorifertinib (AZD3759) was injected as a bolus into a sural vein during 5 sec with simultaneous start of PET-data acquisition. Injected radioactivity was 150 and 155 MBq. The unbound fraction for [11C]-Zorifertinib (AZD3759) in plasma was measured using a previously described ultrafiltration method (Varrone, A.; Stepanov, V.; Nakao, R.; Toth, M.; Gulyas. B.; Emond, P.; et al. Imaging of the striatal and extrastriatal dopamine transporter with 18F-LBT-999: quantification, biodistribution, and radiation dosimetry in nonhuman primates. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1313- 1321).[1] Rats: Zorifertinib (AZD3759) is administered orally to male Han Wistar rats at a dose of 2 mg/kg in 1% methylcellulose. Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) is extracted from the cisterna magna at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 7 hours post-dose. Blood samples (>60 μL/time point/each site) are obtained by cardiac puncture, placed into individual EDTA-coagulated tubes, and then promptly diluted with three times the volume of water. After being removed, brain tissue is homogenized in three times the volume of 100 mM phosphate buffered saline (pH7.4). All samples are kept cold until they are analyzed using LC/MS/MS. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Agent 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) exhibited the best pharmacokinetic profile with moderate blood clearance at 17 mL min–1 kg–1 and volume of distribution of 5.2 L/kg. The intrinsic clearance (Clint) of 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) is 11.4 μL min–1 10–6 cells in human hepatocytes, and the predicted clearance of the agent in humans is 7.7 mL min–1 kg–1 by in vitro–in vivo extrapolation (IVIVe). Liver blood flow (LBF) method with blood protein binding correction was applied to generate individual estimates of unbound human hepatic clearance (CLhepatic) using available data from each preclinical species. The predicted human clearance by the LBF method from rat is 8.1 mL min–1 kg–1, which is very similar to that derived from IVIVe. Following oral dosing in rats at 2 mg/kg, absorption of 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) was rapid with blood Cmax of 0.58 μM achieved at 1.0 h. Subsequently, blood concentrations of 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) declined monoexponentially with a mean elimination half-life of 4.3 h, which was close to the same parameter obtained from intravenous dosing of 4.1 h. The bioavailability following an oral dose in rats was 91%. Given its promising PK properties, CNS penetration, and in vitro potency, 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) was selected as the candidate for comprehensive biological profiling.[1]
Dog Pharmacokinetics [1] Blood pharmacokinetic parameters of 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) in male dogs were determined following both a single dose intravenous infusion and oral administration. These data are summarized in Table 7. Following the IV dose in dogs, 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) blood clearance was determined as 14 mL min–1 kg–1, and the volume of distribution was 6.4 L/kg. Its elimination half-life was 6.2 h. Absorption of 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) was rapid with blood Cmax (698 nM) occurring between 0.5 and 1.5 h. The oral bioavailability of 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759) was excellent at 90%. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
AZD-3759 is under investigation in clinical trial NCT03360929 (Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Anti-tumor Activity of AZD3759).
Zorifertinib is an orally available inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, zorifertinib binds to and inhibits the activity of EGFR as well as certain mutant forms of EGFR. This prevents EGFR-mediated signaling, and may lead to both induction of cell death and inhibition of tumor growth in EGFR-overexpressing cells. EGFR, a receptor tyrosine kinase mutated in many tumor cell types, plays a key role in tumor cell proliferation and tumor vascularization. Recent reports suggest that an increasing number of patients with lung cancer, especially those with activating mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), also present with brain metastases and leptomeningeal metastases. These patients have poor prognosis as there are no approved drugs for these indications. Available agents have poor efficacy for these patients even at well above their standard dose. Herein, we report the discovery of (4-[(3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)amino]-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl (2R)-2,4-dimethylpiperazine-1-carboxylate 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759), an investigational drug currently in Phase 1 clinical trial, which has excellent central nervous system penetration and which induces profound regression of brain metastases in a mouse model. [1] By correctly balancing physicochemical properties, such as permeability, solubility, and efflux ratio, we were able to identify compound 1a. This early lead has significantly improved CNS penetration without compromising the in vitro potency. Replacement of the methylene group present in 1a by carbamate linker led to compound 1e. This compound significantly improved metabolic stability. The terminal basic nitrogen in 1e was found to be an essential element to achieve good exposures in both brain and blood. By incorporating a methyl group into the piperazine moiety, we further improved PK properties of 1e, leading to successful discovery of clinical candidate 1m/Zorifertinib (AZD3759). 1m exhibited excellent free compound distribution in brain, CSF, and blood. The extensive in vitro evaluation, including biochemical, cellular, and panel screening, indicates that this agent is highly potent against EGFR-activating mutants and highly selective toward these targets. Importantly, 1m showed tumor regression in the mouse model with brain metastasis. The promising data package for 1m strongly supported its selection as a drug candidate for development. The results from additional in vivo studies are due to be published separately.[1] Our study demonstrated that SMAD4 was a p53 target gene when HepG2 cells were treated with AZD3759. We believe that other factors induced by Zorifertinib (AZD3759) treatment are required for p53 to induce SMAD4 transcription or this phenomenon is just a unique property of HepG2 cells. But no matter what the reason is, the finding that p53 cooperates with SMAD4 to form the positive loop, which amplifies p53-induced apoptosis, opens a new avenue for the research of p53-mediated cell death. The finding that SMAD4 could induce p53 nuclear translocation in the presence of Zorifertinib (AZD3759)treatment also first uncovered a new role of SMAD4 on determining p53 sub-localization. The exact mechanisms by which SMAD4 induces p53 nuclear localization will be detected at the proper time in future, since nuclear p53-mediated transcriptional activation/inhibition results in dramatic effects on the physiological and pathological processes of cells [2]. Taken together, our results uncover a new potential usage of AZD3759 for HCC treatment, since this chemical compound can activate p53-SMAD4 positive feedback loop to induce apoptosis and suppress the cell viability in hepatoma cells.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C22H24CL2FN5O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
496.36
|
| 精确质量 |
495.124
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.24; H, 4.87; Cl, 14.28; F, 3.83; N, 14.11; O, 9.67
|
| CAS号 |
1626387-81-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Zorifertinib;1626387-80-1
|
| PubChem CID |
78322366
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
79.8
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
649
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
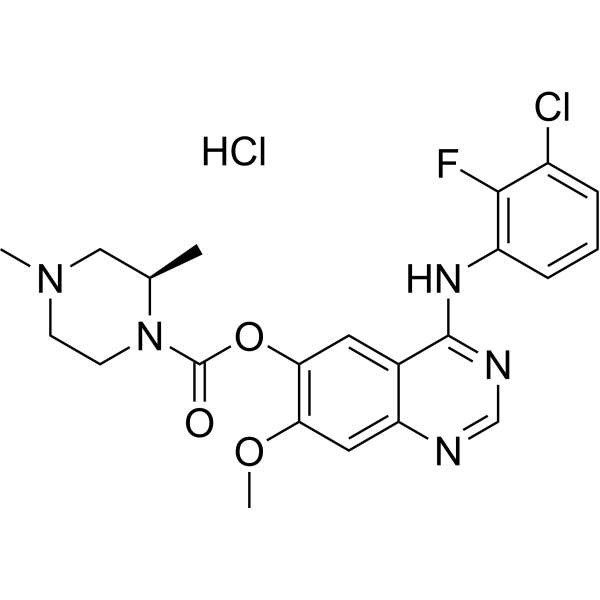
ClC1=CC=CC(=C1F)NC1=C2C(C=C(C(=C2)OC(N2CCN(C)C[C@H]2C)=O)OC)=NC=N1.Cl
|
| InChi Key |
IFVBAZHARMVMRV-BTQNPOSSSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H23ClFN5O3.ClH/c1-13-11-28(2)7-8-29(13)22(30)32-19-9-14-17(10-18(19)31-3)25-12-26-21(14)27-16-6-4-5-15(23)20(16)24;/h4-6,9-10,12-13H,7-8,11H2,1-3H3,(H,25,26,27);1H/t13-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
[4-(3-chloro-2-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl] (2R)-2,4-dimethylpiperazine-1-carboxylate;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
AZD3759 hydrochloride; 1626387-81-2; AZD-3759 hydrochloride; Zorifertinib (hydrochloride); AZD3759hydrochloride; 05Z3WK3SO6; [4-(3-chloro-2-fluoroanilino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl] (2R)-2,4-dimethylpiperazine-1-carboxylate;hydrochloride; (R)-4-((3-Chloro-2-fluorophenyl)amino)-7-methoxyquinazolin-6-yl 2,4-dimethylpiperazine-1-carboxylate hydrochloride;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0147 mL | 10.0733 mL | 20.1467 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4029 mL | 2.0147 mL | 4.0293 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2015 mL | 1.0073 mL | 2.0147 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。