| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral or rectal admin, the onset of action varies from 10-30 min for ... amobarbital ... Following iv admin of the sodium salts of ... amobarbital, the onset of action ranges from almost immediately for pentobarbital ... . About 40 to 60% of amylobarbitone is bound to plasma proteins. Following admin of radioactively labelled amylobarbitone to 2 healthy subjects 79 to 92% was recovered in urine in 6 days and only 4 to 5% in the feces. Unchanged drug was practically absent from both urine and feces. Fluid & tissue specimens collected from 30 subjects at autopsy were assayed for amylobarbitone (amobarbital), butobarbitone (butethal), pentobarbitone (pentobarbital), quinalbarbitone (secobarbital) and the corresponding hydroxylated metabolites by GLC. Where one barbiturate was ingested, an inverse relationship between lipid solubility of the drug and the distribution in fluids and tissues was observed. In most cases the liver, and in the remainder the spleen, contained the highest concn of barbiturate. Bile concn were often in excess of those in the corresponding liver. The metabolites of the 4 sedative barbiturates were usually present in lower amounts than the parent drugs in the fluids and tissues of most subjects, but urine often contained much higher concn of metabolites, sometimes exceeding that of the parent drug in the liver. Admin of 2 or more barbiturates together did not appear to affect the distribution and metabolism of the individual drugs. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Amobarbital (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Amobarbital is metabolized by the liver via penultimate oxidation of the 3-methylbutyl substituent to form a tertiary alcohol, hydroxyamobarbital, which is an inactive metabolite. About 40-50% of an oral hypnotic dose of amobarbital is excreted in urine as hydroxyamobarbital and its glucuronide conjugates. Less than 1% of an oral hypnotic dose of the drug is excreted in urine unchanged. Conjugates of hydroxyamobarbital excreted in feces or urine and/or further oxidation products not yet identified may account for the remainder of the dose. Following admin of radioactively labelled amylobarbitone to two healthy subjects ... less than 50% of the dose was identified as 3'-hydroxyamylobarbitone. A second main metabolite was identified as N-hydroxyamylobarbitone and was found to account for up to 30% of the dose. Relative proportion of amobarbital metabolites in urine is highly variable and observations of plasma half-life give no indication of this variability. A valid estimate of a given person's metabolite pattern can be obtained by studying single urine specimen in postdistributive phase. Two metabolites were measured in urine specimen in the postdistributive phase. The 2 metabolites were 3'-hydroxyamobarbital as product of side chain hydroxylation and N-beta-d-glycopyranosyl amobarbital, a glucose conjugate. N-Hydroxyamylobarbitone was synthesized and its occurrence as a urinary metabolite was studied in 13 subjects taking 200 mg sodium amobarbital. It was concluded that the excretion of free N-hydroxyamylobarbitone is not significant in the metabolism of amobarbital sodium. /Amobarbital sodium/ For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for Amobarbital (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Biological Half-Life Following bolus iv administration, plasma concentrations of amobarbital decline in a biphasic manner with a half-life of about 40 minutes for the first phase and 20-25 hours for the second phase, although the second phase half-life has ranged from 14-42 hours in individual patients. The half-life of amobarbital was investigated in 36 unrelated subjects; half-life (23.8 hr) appeared to be normally distributed. Following im injection of amylobarbitone sodium 200 mg to mildly hypertensive women in labor 0.7 to 3.5 hr before delivery, the plasma-half-life of amylobarbitone was 2.5 times as long in the neonates as in the mothers. /Amobarbital sodium/ |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Amobarbital (like all barbiturates) works by binding to the GABAA receptor at either the alpha or the beta sub unit. These are binding sites that are distinct from GABA itself and also distinct from the benzodiazepine binding site. Like benzodiazepines, barbiturates potentiate the effect of GABA at this receptor. This GABAA receptor binding decreases input resistance, depresses burst and tonic firing, especially in ventrobasal and intralaminar neurons, while at the same time increasing burst duration and mean conductance at individual chloride channels; this increases both the amplitude and decay time of inhibitory postsynaptic currents. In addition to this GABA-ergic effect, barbiturates also block the AMPA receptor, a subtype of glutamate receptor. Glutamate is the principal excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian CNS. Amobarbital also appears to bind neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Interactions To determine the effect of human growth hormone (somatropin) on human metabolism, 6 somatropin deficient children were given single oral doses of amobarbital sodium 3-5 mg 3 times/wk. The half-life of amobarbital sodium rose from 13.89 to 22.75 hr, vol of distribution was unchanged, and clearance fell. Results indicate that somatropin slows the metabolism of amobarbital sodium, probably through an effect on hepatic microsomal drug oxidizing system. /Amobarbital sodium/ Concurrent administration of disulfiram with barbiturates may result in inhibition of metabolism of the barbiturates and an increased incidence of barbiturate toxic effects. /Barbiturates/ Concurrent use with barbiturates may result in increased metabolism, leading to decreased serum concentrations and reduced elimination half-lives of carbamazepine or succinimide anticonvulsants because of induction of hepatic microsomal enzyme activity. Monitoring of serum concentrations as a guide to dosage is recommended, especially when carbamazepine or a succinimide anticonvulsant is added to or withdrawn from an existing regimen. /Barbiturates/ Concurrent use with barbiturates, especially phenobarbital, may induce microsomal metabolism to increase formation of alkylating metabolites of cyclophosphamide, thereby reducing the half-life and increasing the leukopenic activity of cyclophosphamide. /Barbiturates/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for Amobarbital (39 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 250 mg/kg LD50 Rat ip 115 mg/kg /Amobarbital sodium/ LD50 Rat sc 190 mg/kg LD50 Mouse oral 345 mg/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for Amobarbital (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
GABA Modulators; Sedatives, Barbiturate Amobarbital (no longer commercially available in the US) and amobarbital sodium are used principally as hypnotics in the short-term treatment of insomnia for periods up two two weeks in duration ... The drugs are also used for routine sedation and to relieve anxiety and provide sedation preoperatively. Amobarbital sodium may be used ... to control acute episodes of agitated behavior in psychoses such as catatonic, negativistic, or manic reactions, but has little value in longterm management of psychoses. Parenteral amobarbital sodium may also be useful in narcoanalysis, narcotherapy, and as a diagnostic aid in schizophrenia. /Experimental Therapy:/ ... Presurgical screening for temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) includes the intracarotid amobarbital procedure (IAP), consisting of two consecutive injections of amobarbital, ipsilateral and contralateral to the epileptic focus. We studied whether a bilateral IAP has added value to a unilateral, ipsilateral IAP. METHODS: This population-based study included 183 consecutive patients referred for screening for TLE surgery who underwent bilateral IAP. Using multivariable modeling, we assessed the added value of bilateral IAP on the decision for surgery, resection size, amygdalohippocampectomy, post-operative seizure freedom, memory performance, and IQ change. RESULTS: Given the results from the unilateral IAP, the bilateral IAP had added prognostic value for postoperative change in verbal memory (P < 0.01) and verbal IQ (P < 0.01), especially if patients had a left-sided focus. In contrast, information provided by the contralateral IAP was not associated with decision-making or surgical strategy. CONCLUSIONS: A bilateral IAP has added value in predicting post-operative verbal memory and IQ. A bilateral IAP is currently not used to guide surgical strategy, but may be used for this purpose when verbal capacity is of particular concern in patients with a left-sided focus. In other cases, IAP is best performed unilaterally. Medication (Vet): ... used primarily for its hypnotic or sedative action. /Amobarbital sodium/ Drug Warnings Amobarbital (no longer commercially available in the US) and amobarbital sodium share the toxic potentials of the barbiturates, and the usual precautions of barbiturate administration should be observed. Dependence of the barbiturate-alcohol type is liable to occur in susceptible patients given any of the sedatives & hypnotics ... . It is characterized by a strong need to continue taking the drug, a tendency to increase the dose, a psychic dependence on the effects of the drug, and a physical dependence on the effects of the drug for the maintenance of homoeostasis, with a characteristic abstinence syndrome on withdrawal. /Hypnotics & sedatives/ Vet: avoid use of simultaneously administered chloramphenicol which has caused a dramatic increase in anesthesia duration in mice. IV administered amobarbital sodium may cause respiratory depression, apnea, or hypotension, particularly if the drug is administered too rapidly. The drug must be administered slowly at a rate not greater than 100 mg/minute, and personnel and equipment should be readily available for administration of artificial respiration. Safety & efficacy of amobarbital & amobarbital sodium in children younger than 6 yr of age have not been established. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Amobarbital (29 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
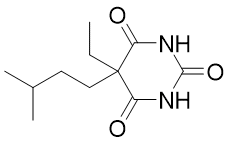
| 分子式 |
C11H18N2O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
226.27
|
| 精确质量 |
226.131
|
| CAS号 |
57-43-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
64-43-7 (hydrochloride)
|
| PubChem CID |
2164
|
| 外观&性状 |
Crystals
White, crystalline powder |
| 熔点 |
313 to 316 °F (NTP, 1992)
|
| LogP |
2.1
|
| tPSA |
75.3
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
303
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
VIROVYVQCGLCII-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C11H18N2O3/c1-4-11(6-5-7(2)3)8(14)12-10(16)13-9(11)15/h7H,4-6H2,1-3H3,(H2,12,13,14,15,16)
|
| 化学名 |
2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-Pyrimidinetrione, 5-ethyl-5-(3-methylbutyl)-
|
| 别名 |
Barbamyl acidAmobarbital AmybalAmobarbitale Amylbarbitone Binoctal
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4195 mL | 22.0975 mL | 44.1950 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8839 mL | 4.4195 mL | 8.8390 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4419 mL | 2.2097 mL | 4.4195 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。