| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
PD-1 signaling pathway
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:AUNP-12(也称为 Aur-012、Aurigene-012 和 Aurigene NP-12)是 Aurigene Discovery Technologies 开发的一种新型有效的免疫检查点调节剂,是 PD-1 信号通路的抑制剂。 AUNP-12 正在开发用于治疗多种癌症。它是该途径中唯一的肽治疗药物,与目前的方法相比,例如纳武单抗 (BMS)、兰博利珠单抗 (Merck-3475)、CT-011 (Curetech)、MDX-1105 (BMS) 等抗体,可能提供更有效、更安全的组合机会)、MPDL3280 (GNE) 和 MEDI-4736 (Medimmune-AZ) 或 Amplimmune 的 PD-L2-FC 融合蛋白。激酶测定:AUNP-12 在使用表达 hPDL2 的 HEK293 细胞抑制 PD1 与 PD-L2 结合时显示 EC50 = 0.72 nM,在使用表达 hPDL1 的 MDA 的大鼠外周血单核细胞 (PBMC) 增殖测定中显示 EC50 = 0.41 nM -MB231细胞。这与 AUNP-012 报道的“破坏 PD1-PDL1/2 相互作用的亚纳摩尔效力”很好地对应。细胞测定:AUNP-12 在使用表达 hPDL2 的 HEK293 细胞抑制 PD1 与 PD-L2 结合时显示 EC50 = 0.72 nM,在使用表达 hPDL1 MDA 的大鼠外周血单核细胞 (PBMC) 增殖测定中显示 EC50 = 0.41 nM -MB231细胞。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
AUNP-12 抑制小鼠皮下注射的 B16F10 小鼠黑色素瘤细胞的 44% 肿瘤生长(5 mg/kg,皮下注射,每天一次,14 天);它减少静脉注射 B16F10 细胞的肺转移。小鼠(5 mg/kg,皮下注射,每天一次,11 天);将原位注射至小鼠乳腺脂肪垫的 4T1 细胞(3 mg/kg,皮下注射,每天一次,40 天)抑制 44% 的肿瘤生长。接受 AUNP-12 治疗的动物中,10% 的动物肿瘤生长完全消退,另外 10% 的动物肿瘤生长部分消退。安乐死后测量,AUNP-12治疗的动物的肺转移平均减少>60%。
|
| 酶活实验 |
AUNP-12 在使用表达 hPDL2 的 HEK293 细胞抑制 PD1 与 PD-L2 结合时显示 EC50 = 0.72 nM,在使用表达 hPDL1 的 MDA-MB231 细胞的大鼠外周血单核细胞 (PBMC) 增殖测定中显示 EC50 = 0.41 nM 。这与 AUNP-012 报道的“破坏 PD1-PDL1/2 相互作用的亚纳摩尔效力”很好地对应。
|
| 细胞实验 |
AUNP-12 在使用表达 hPDL2 的 HEK293 细胞抑制 PD1 与 PD-L2 结合时显示 EC50 = 0.72 nM,在使用表达 hPDL1 的 MDA-MB231 细胞的大鼠外周血单核细胞 (PBMC) 增殖测定中显示 EC50 = 0.41 nM 。
|
| 动物实验 |
AUNP-12 is active in vivo in a lung metastasis model of B16F10 melanoma
in mice, showing a 64% reduction in metastasis at 5 mg/kg (subcutaneous, once daily, 14 days).[2]
Pharmacokinetics of AUNP-12 in Balb/c mice[3] All animal experimental procedures used in these studies including pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and efficacy experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethical Committee based on the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision on Experiments on Animals (India) guidelines. AUNP-12 was administered either intravenously or subcutaneously to the animals at a dose of 3 mg/kg to determine the pharmacokinetic parameters using 5% dextrose water as formulation. After administration, blood samples were collected at regular intervals until 24 hours and centrifuged to obtain the plasma fraction. The plasma samples were processed by SPE method and the eluent were analyzed by LC/MS-MS to determine the plasma concentration of the compound. From intravenous administration, plasma concentration after injection (C0 minutes), the area under the concentration−time curve from time zero to infinity (AUC 0−∞), the mean residence time, volume of distribution (Vdss), and clearance (CL) for each mouse were obtained. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax), time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax), and AUC 0−∞ were obtained from subcutaneous administration of AUNP-12 . On the basis of the intravenous and subcutaneous parameters, bioavailability of AUNP-12 was calculated. Syngeneic mouse studies[3] In all in vivo tumor growth inhibition (TGI) studies, tumor volumes were measured two times weekly using digital calipers and the volume was expressed in mm3 using the formula V = 0.5a × b2, where a and b are the long and short diameters of the tumor, respectively. Body weights and clinical signs were monitored twice a week. AUNP-12 was dissolved in 5% dextrose water for all the in vivo studies, except for B16F10 mouse melanoma and Renca tumor models where 1 × PBS was used. Fresh formulation was prepared every day. Compound and vehicle controls were dosed subcutaneously once a day at a dosing volume of 10 mL/kg body weight. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Further in vivo studies revealed that AUNP-12/AUR-012 exhibits an excellent PK-PD correlation with sustained PD for >24 h. In preclinical models of melanoma, breast and kidney cancers, AUR012/AUNP-12 showed superior efficacy compared to therapeutic agents currently used in the clinic in inhibition of both primary tumor growth and metastasis. Interestingly, dosing once in three days was equally efficacious as once a day dosing with no signs of overt toxicity and generation of neutralizing activity.[9] Rescue of proliferation of immune cells analyzed upon stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD-28 indicated a complete rescue of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Interestingly, the proliferation of CD4+, Foxp3+ T cells was completely abolished with AUR-012/AUNP-12 treatment indicating a complete suppression of regulatory T cells. Sustained activation of circulatory immune cells and their ability to secrete IFN-γ up to 72 h indicate that pharmacodynamic effects persist even after the clearance of the compound in animal models, thus supporting a dosing interval of up to 3 days. In models of melanoma, breast, kidney and colon cancers, AUR-012/AUNP-12 showed efficacy in inhibition of both primary tumor growth and metastasis. Additionally, anti-tumor activity of the compound in a pre-established CT26 model correlated well with pharmacodynamic effects as indicated by intratumoral recruitment of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and a reduction in PD1+ T cells (both CD4+ & Page 7/12 CD8+) in tumor and blood. In 14-day repeated dose toxicity studies, AUR-012/AUNP-12 was well tolerated at 100 times the efficacious doses. [2]
AUNP-12, likely to be identical to the compound previously known under the codenames Aur-012, Aurigene-012, or Aurigene NP-12, is an inhibitor of the so-called PD-1 pathway, and will be in development for several cancer indications. It is so far the only peptide therapeutic in this pathway and could offer more effective and safer combination opportunities compared to current approaches,[2-4] e.g. antibodies such as Nivolumab (BMS), Lambrolizumab (Merck-3475), CT-011 (Curetech), MDX-1105 (BMS), MPDL3280 (GNE) and MEDI-4736 (Medimmune-AZ), or Amplimmune’s PD-L2-FC fusion protein. PD-1, or Programmed cell death 1, is an immunoreceptor belonging to the CD28 family, and plays an important role in negatively regulating immune responses. The amino acid protein structure includes an extracellular amino acid IgV domain followed by a transmembrane region and an intracellular tail. PD-1 is expressed on the surface of activated T cells, B cells, and macrophages, and has two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, which are members of the B7 family. PD-L1 is expressed on almost all murine tumor cell lines, whereas PD-L2 expression is more restricted and is expressed mainly by DCs and a few tumor lines. Blocking of PD-1 signaling pathways has been shown to result in restoration of defective immune cell functions in cancer and chronic infections. Recent advances in achieving highly durable clinical responses via inhibition of immune checkpoint proteins including PD-1 using antibodies or fusion proteins have revolutionized the outlook for cancer therapy. However, along with impressive clinical activity, severe immune-related adverse events (irAEs) due to the breaking of immune selftolerance are becoming increasingly evident. Sustained target inhibition as a result of a long halflife (>15-20 days) and >70% target occupancy for months are likely contributing to severe irAEs observed in the clinic with antibodies targeting immune checkpoint proteins.[2] Pioneering success of antibodies targeting immune checkpoints such as PD-1 and CTLA4 has opened novel avenues for cancer immunotherapy. Along with impressive clinical activity, severe immune-related adverse events (irAE) due to the breaking of immune self-tolerance are becoming increasingly evident in antibody-based approaches. As a strategy to better manage severe adverse effects, we set out to discover an antagonist targeting PD-1 signaling pathway with a shorter pharmacokinetic profile. Herein, we describe a peptide antagonist NP-12 that displays equipotent antagonism toward PD-L1 and PD-L2 in rescue of lymphocyte proliferation and effector functions. In preclinical models of melanoma, colon cancer, and kidney cancers, NP-12 showed significant efficacy comparable with commercially available PD-1-targeting antibodies in inhibiting primary tumor growth and metastasis. Interestingly, antitumor activity of NP-12 in a preestablished CT26 model correlated well with pharmacodynamic effects as indicated by intratumoral recruitment of CD4 and CD8 T cells, and a reduction in PD-1+ T cells (both CD4 and CD8) in tumor and blood. In addition, NP-12 also showed additive antitumor activity in preestablished tumor models when combined with tumor vaccination or a chemotherapeutic agent such as cyclophosphamide known to induce "immunologic cell death." In summary, NP-12 is the first rationally designed peptide therapeutic targeting PD-1 signaling pathways exhibiting immune activation, excellent antitumor activity, and potential for better management of irAEs.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C142H226N40O48
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
3261.55
|
| 精确质量 |
3259.65
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 52.29; H, 6.98; N, 17.18; O, 23.55
|
| CAS号 |
1353563-85-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
AUNP-12 TFA
|
| PubChem CID |
154701623
|
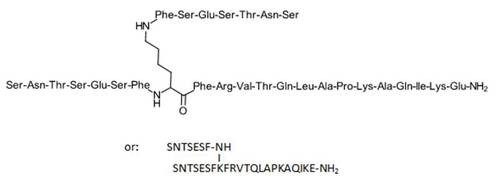
| 序列 |
H-Ser-Asn-Thr-Ser-Glu-Ser-Phe-Lys(1)-Phe-Arg-Val-Thr-Gln-Leu-Ala-Pro-Lys-Ala-Gln-Ile-Lys-Glu-NH2.H-Ser-Asn-Thr-Ser-Glu-Ser-Phe-(1)
|
| 短序列 |
SNTSESFK(SNTSESF-NH)FRVTQLAPKAQIKE-NH2
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
-23.2
|
| tPSA |
1480
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
51
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
53
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
112
|
| 重原子数目 |
230
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
7520
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
33
|
| SMILES |
CC[C@H](C)[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)N)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCCCN)NC(=O)[C@@H]1CCCN1C(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCCNC(=N)N)NC(=O)[C@H](CC2=CC=CC=C2)NC(=O)[C@H](CCCCNC(=O)[C@H](CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(=O)N)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)N)NC(=O)[C@H](CC4=CC=CC=C4)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(=O)N)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)N
|
| InChi Key |
ZBJUUYIGBAQYBN-QKLNNLIKSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C142H226N40O48/c1-12-70(6)109(137(226)165-84(37-23-26-52-144)119(208)158-81(113(151)202)43-48-105(196)197)178-125(214)87(42-47-102(148)193)159-114(203)71(7)156-118(207)82(36-22-25-51-143)164-135(224)100-40-29-55-182(100)141(230)72(8)157-126(215)90(56-68(2)3)169-121(210)86(41-46-101(147)192)166-138(227)112(75(11)191)181-136(225)108(69(4)5)177-124(213)85(39-28-54-155-142(152)153)161-127(216)92(58-77-32-18-14-19-33-77)171-120(209)83(160-128(217)93(59-78-34-20-15-21-35-78)172-134(223)97(65-186)174-123(212)89(45-50-107(200)201)163-132(221)99(67-188)176-140(229)111(74(10)190)180-130(219)95(61-104(150)195)168-116(205)80(146)63-184)38-24-27-53-154-117(206)91(57-76-30-16-13-17-31-76)170-133(222)96(64-185)173-122(211)88(44-49-106(198)199)162-131(220)98(66-187)175-139(228)110(73(9)189)179-129(218)94(60-103(149)194)167-115(204)79(145)62-183/h13-21,30-35,68-75,79-100,108-112,183-191H,12,22-29,36-67,143-146H2,1-11H3,(H2,147,192)(H2,148,193)(H2,149,194)(H2,150,195)(H2,151,202)(H,154,206)(H,156,207)(H,157,215)(H,158,208)(H,159,203)(H,160,217)(H,161,216)(H,162,220)(H,163,221)(H,164,224)(H,165,226)(H,166,227)(H,167,204)(H,168,205)(H,169,210)(H,170,222)(H,171,209)(H,172,223)(H,173,211)(H,174,212)(H,175,228)(H,176,229)(H,177,213)(H,178,214)(H,179,218)(H,180,219)(H,181,225)(H,196,197)(H,198,199)(H,200,201)(H4,152,153,155)/t70-,71-,72-,73+,74+,75+,79-,80-,81-,82-,83-,84-,85-,86-,87-,88-,89-,90-,91-,92-,93-,94-,95-,96-,97-,98-,99-,100-,108-,109-,110-,111-,112-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(4S)-5-amino-4-[[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2S)-5-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-5-amino-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2,6-bis[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-4-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-5-carbamimidamidopentanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoyl]amino]-3-methylpentanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
Aur-012; AUNP-12; 1353563-85-5; AUNP-12?; CHEMBL4635204; AUNP-12, AUR-012; EX-A7438; NONYLPHENOL POLYOXYETHYLENE ETHER; G13071; Aurigene-012
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.3066 mL | 1.5330 mL | 3.0660 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.0613 mL | 0.3066 mL | 0.6132 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0307 mL | 0.1533 mL | 0.3066 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。