| 规格 | 价格 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
p38α MAPK
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
BMS-751324具有氨基甲酰亚甲基连接促进基团,含有羟基苯基乙酸(HPA)衍生的酯和磷酸盐功能。BMS-751324在酸性和中性条件下均稳定且具有水溶性。
碱性磷酸酶人胎盘 ALP 处理 BMS-751324(10 μM;0-60 分钟),而化学酶工厂则不处理 [1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
药物 BMS-751324(1 mg/kg、3 mg/kg;肘部;每天两次,持续一周)用作治疗关节炎相关足部肿胀的拓扑佐剂。它在动物体内进行生物转化,产生 BMS-582949(悬浮液:1 mg/kg-100 mg/kg,猴:10 或 30 mg/kg,5 mL/kg 甲基纤维素悬浮液;并抑制脂多糖诱导的 TNFα 产生 [1]。口服;单剂量)给予患者。
为了寻找解决ph依赖性溶解度和暴露相关的前药1 (BMS-582949),一种先前公开的II期临床p38α MAP激酶抑制剂,一种结构新颖的临床前药2 (BMS-751324),具有含有羟基苯基乙酸(HPA)衍生的酯和磷酸盐功能的氨基甲酰亚甲基连接促进基团。前药2在酸性和中性条件下均稳定且具有水溶性。它在体内通过碱性磷酸酶和酯酶逐步有效地生物转化为母体药物1,与直接给药相比,1的暴露量更高,特别是在更高的剂量范围内。在lps诱导的大鼠TNFα药效学模型和大鼠佐剂关节炎模型中,2和1的疗效相似。最重要的是,临床研究表明,前药2确实有效地解决了与1相关的ph依赖性吸收问题。[2] |
| 动物实验 |
In search for prodrugs to address the issue of pH-dependent solubility and exposure associated with 1 (BMS-582949), a previously disclosed phase II clinical p38α MAP kinase inhibitor, a structurally novel clinical prodrug, 2 (BMS-751324), featuring a carbamoylmethylene linked promoiety containing hydroxyphenyl acetic acid (HPA) derived ester and phosphate functionalities, was identified. Prodrug 2 was not only stable but also water-soluble under both acidic and neutral conditions. It was effectively bioconverted into parent drug 1 in vivo by alkaline phosphatase and esterase in a stepwise manner, providing higher exposure of 1 compared to its direct administration, especially within higher dose ranges. In a rat LPS-induced TNFα pharmacodynamic model and a rat adjuvant arthritis model, 2 demonstrated similar efficacy to 1. Most importantly, it was shown in clinical studies that prodrug 2 was indeed effective in addressing the pH-dependent absorption issue associated with 1.[2]
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
The discovery and characterization of 7k (BMS-582949), a highly selective p38α MAP kinase inhibitor that is currently in phase II clinical trials for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, is described. A key to the discovery was the rational substitution of N-cyclopropyl for N-methoxy in 1a, a previously reported clinical candidate p38α inhibitor. Unlike alkyl and other cycloalkyls, the sp2 character of the cyclopropyl group can confer improved H-bonding characteristics to the directly substituted amide NH. Inhibitor 7k is slightly less active than 1a in the p38α enzymatic assay but displays a superior pharmacokinetic profile and, as such, was more effective in both the acute murine model of inflammation and pseudoestablished rat AA model. The binding mode of 7k with p38α was confirmed by X-ray crystallographic analysis [1].
Weakly basic compounds which have pH dependent solubility are liable to exhibit pH dependent absorption. In some cases, a subtle change in gastric pH can significantly modulate the plasma concentration of the drug and can lead to sub-therapeutic exposure of the drug. Evaluating the risk of pH dependent absorption and potential drug-drug interaction with pH modulators are important aspects of drug discovery and development. In order to assess the risk around the extent of decrease in the systemic exposure of drugs co-administered with pH modulators in the clinic, a pH effect study is carried out, typically in higher species, mostly dog. The major limitation of a higher species pH effect study is the resource and material requirement to assess this risk. Hence, these studies are mostly restricted to promising or advanced leads. In our current work, we have used in vitro aqueous solubility, in silico simulations using GastroPlus™ and an in vivo rat pH effect model to provide a qualitative assessment of the pH dependent absorption liability. Here, we evaluate ketoconazole and atazanavir with different pH dependent solubility profiles and based on in vitro, in silico and in vivo results, a different extent of gastric pH effect on absorption is predicted. The prediction is in alignment with higher species and human pH effect study results. This in vitro, in silico and in vivo (IVISIV) correlation is then extended to assess pH absorption mitigation strategy. The IVISIV predicts pH dependent absorption for BMS-582949 whereas its solubility enhancing prodrug, BMS-751324 is predicted to mitigate this liability. Overall, the material requirement for this assessment is substantially low which makes this approach more practical to screen multiple compounds during lead optimization. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25960252/ |
| 分子式 |
C32H35N6O10P
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
694.628268480301
|
| 精确质量 |
694.215
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 55.33; H, 5.08; N, 12.10; O, 23.03; P, 4.46
|
| CAS号 |
948842-66-8
|
| PubChem CID |
44540113
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 折射率 |
1.676
|
| LogP |
1.22
|
| tPSA |
211
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
13
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
15
|
| 重原子数目 |
49
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1230
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
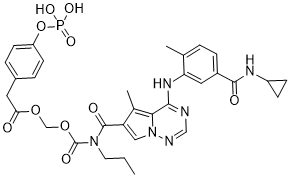
O=C(N(CCC)C(C1C(C)=C2N(N=CN=C2NC2C(C)=CC=C(C(NC3CC3)=O)C=2)C=1)=O)OCOC(CC1C=CC(OP(O)(O)=O)=CC=1)=O
|
| InChi Key |
XAYQDTPEOFCYIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C32H35N6O10P/c1-4-13-37(32(42)47-18-46-27(39)14-21-6-11-24(12-7-21)48-49(43,44)45)31(41)25-16-38-28(20(25)3)29(33-17-34-38)36-26-15-22(8-5-19(26)2)30(40)35-23-9-10-23/h5-8,11-12,15-17,23H,4,9-10,13-14,18H2,1-3H3,(H,35,40)(H,33,34,36)(H2,43,44,45)
|
| 化学名 |
[[4-[5-(cyclopropylcarbamoyl)-2-methylanilino]-5-methylpyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazine-6-carbonyl]-propylcarbamoyl]oxymethyl 2-(4-phosphonooxyphenyl)acetate
|
| 别名 |
BMS-751324; 948842-66-8; 976Z3162LI; UNII-976Z3162LI; Benzeneacetic acid, 4-(phosphonooxy)-, 1-((((((4-((5-((cyclopropylamino)carbonyl)-2-methylphenyl)amino)-5-methylpyrrolo(2,1-f)(1,2,4)triazin-6-yl)carbonyl)propylamino)carbonyl)oxy)methyl) ester; (((4-((5-(cyclopropylcarbamoyl)-2-methylphenyl)amino)-5-methylpyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazine-6-carbonyl)(propyl)carbamoyl)oxy)methyl 2-(4-(phosphonooxy)phenyl)acetate; [[4-[5-(cyclopropylcarbamoyl)-2-methylanilino]-5-methylpyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazine-6-carbonyl]-propylcarbamoyl]oxymethyl 2-(4-phosphonooxyphenyl)acetate; [[4-[5-(cyclopropylcarbamoyl)-2-methylanilino]-5-methylpyrrolo[2,1-f][1,2,4]triazine-6-carbonyl]-propylcarbamoyl]oxymethyl 2-(4-phosphonooxyphenyl)acetate;BMS-751324 (BMS751324);Bms751324;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4396 mL | 7.1981 mL | 14.3962 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2879 mL | 1.4396 mL | 2.8792 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1440 mL | 0.7198 mL | 1.4396 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。