| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Topoisomerase II; Daunorubicins/Doxorubicins
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:在反映柔红霉素给药后血浆峰值浓度的药物浓度下,主要机制可能是通过与拓扑异构酶 II 相互作用,这可能是通过信号通路导致生长停滞和/或细胞杀伤的主要触发事件至少在白血病细胞和胸腺细胞中。醌结构允许柔红霉素在氧化还原酶(包括细胞色素 P450 还原酶、NADH 脱氢酶和黄嘌呤氧化酶)介导的反应中充当电子受体。当柔红霉素浓度超过约 2-4 μM 时,自由基介导的毒性和 DNA 交联可能会变得明显。 Daunorubicin 在 0.2 至 2 μM 的浓度范围内抑制 HeLa 细胞中的 DNA 和 RNA 合成。 Daunorubicin 在 4 μM 浓度范围内抑制艾利希腹水肿瘤细胞中的两种 DNA 合成。 Daunorubic 在 HL-60 或 U-937 人白血病细胞中在 0.5 和 1 μM 浓度下触发细胞凋亡。 Daunorubicin 通过激活神经酰胺合酶进行从头合成,从而刺激 P388 和 U937 细胞中的神经酰胺升高和细胞凋亡。 Daunorubicin 剂量依赖性地增加人脐静脉内皮细胞的磷脂酰丝氨酸暴露和随后的促凝血活性。 Daunorubicin (0.2 mM) 显着增强内皮微粒的释放,这些微粒在人脐静脉内皮细胞中具有高度促凝血作用。细胞测定:当用从急性淋巴细胞白血病患者分离的白血病细胞进行治疗时,柔红霉素显着抑制 DNA 和 RNA 大分子的生物合成。
|
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
与对照组相比,盐酸柔红霉素(RP 13057 盐酸盐)(3 mg/kg,静脉注射)组的尿蛋白排泄、血清肌酐和血尿素氮(BUN)水平显着增加。与对照组相比,柔红霉素(DNR)的给药导致肾组织中丙二醛(MDA)水平显着增加。
|
|
| 酶活实验 |
柔红霉素在0.2至2μM的浓度范围内抑制HeLa细胞中的DNA和RNA合成。
|
|
| 细胞实验 |
当给予从急性淋巴细胞白血病患者分离的白血病细胞时,柔红霉素显着抑制 DNA 和 RNA 大分子的生物合成。
|
|
| 动物实验 |
|
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Daunorubicin was found to have a tmax of 2 h and a cmax of 24.8 μg/mL after a 90 min infusion of the liposomal formulation at a dose of 44 mg/m2. Daunorubicin is eliminated hepatically. 40% of daunorubicin is excreted in the bile while 25% is excreted in an active form (daunorubicin or daunorubicinol) in the urine. In the liposomal formulation, only 9% of active molecules are excreted in the urine. Daunorubicin has a steady-state volume of distribution of 1.91 L/m2 reported with the liposomal formulation. The average volume of distribution reported for the liposomal formulation is 6.6 L. Daunorubicin has a clearance of 68.4 mL/h/m2 determined using the liposomal formulation. Note: Liposomal encapsulation can substantially affect a drug's functional properties relative to those of the unencapsulated drug. In addition, different liposomal drug products may vary from one another in the chemical composition and physical form of the liposomes. Such differences can substantially affect the functional properties of liposomal drug products. Encapsulation of daunorubicin citrate in liposomes substantially alters the pharmacokinetics of the drug relative to conventional iv formulations (ie, nonencapsulated drug) with resultant decreased distribution into the peripheral compartment, increased distribution into Kaposi's lesions, and decreased plasma clearance Daunorubicin hydrochloride is extremely irritating to tissues and, therefore, must be administered iv. Following iv infusion of a single 40-mg/sq m dose of liposomal daunorubicin citrate as a liposomal injection in patients with AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, mean peak plasma daunorubicin (mostly bound to liposomes) concentrations are approximately 18 mug/mL following a 30-60 minute infusion. Peak plasma concentrations of daunorubicin are higher following iv administration of liposomal daunorubicin citrate than those attained following iv administration of conventional (nonencapsulated) daunorubicin hydrochloride. In one study in patients with disseminated malignancies receiving a single 80-mg/sq m iv dose of nonencapsulated daunorubicin, peak plasma concentrations of the drug were 0.4 ug/mL while in patients with solid tumors (including those with Kaposi's sarcoma) who received a single 80-mg/sq m iv dose of liposomal daunorubicin, peak plasma concentrations of daunorubicin were about 44 ug/mL (about 100-fold greater than those receiving a comparable dose of the nonencapsulated drug); area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) was about 36-fold greater than that observed with conventional daunorubicin hydrochloride. Following iv administration of liposomal daunorubicin, peak plasma concentrations and AUCs of daunorubicin generally increase linearly with increasing doses (at doses of 10-80 ug/mL). For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for DAUNORUBICIN (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Daunorubicin hydrochloride is extensively metabolized in the liver and other tissues, mainly by cytoplasmic aldo-keto reductases, producing daunorubicinol, the major metabolite which has antineoplastic activity. Approximately 40% of the drug in the plasma is present as daunorubicinol within 30 minutes and 60% in 4 hours after a dose of nonencapsulated daunorubicin. Daunorubicinol has been detected only in low concentrations in the plasma following iv administration of daunorubicin citrate liposomal injection. In patients with AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma receiving iv administration of liposomal daunorubicin doses of 40 mg/sq m, the AUC of daunorubicinol represented only 2% of the total daunorubicin AUC. Additional metabolism by reductive cleavage of the glycosidic bond produces aglycones, which have little or no cytotoxic activity and are demethylated and conjugated with sulfate and glucuronide by microsomal enzymes. Metabolites identified in human urine are daunorubicinol, daunorubicinol aglycone, desmethyldeoxydaunorubicinol aglycone, desmethyldeoxyrubicinol aglycone-4-o-sulfate, desmethyloxydaunorubicinol aglycone-4-o-glucuronide, and deoxydaunorubicinol aglycone glucuronide. Extensively metabolized, initially to active alcohol metabolites; further metabolized by liver microsomes to inactive aglycones and demethylated glucuronide and sulfate conjugates. Hepatic Route of Elimination: Twenty-five percent of an administered dose of daunorubicin hydrochloride is eliminated in an active form by urinary excretion and an estimated 40% by biliary excretion. Half Life: 18.5 hours Biological Half-Life Daunorubicin has been determined to have a terminal half-life of 18.5 h (+/- 4.9). Daunorubicinol, the primary active metabolite has been determined to have a terminal half-life of 26.7 h (+/- 12.8). The mean half-life of elimination of liposomal daunorubicin has been reported to be 22.1 h in pharmacokinetic studies and 31.5 h in official FDA labeling. Following rapid iv administration of conventional daunorubicin hydrochloride injection, total plasma concentrations of daunorubicin and its metabolites decline in a triphasic manner, and plasma concentrations of unchanged daunorubicin decline in a biphasic manner. The plasma half-life of nonencapsulated daunorubicin averages 45 minutes in the initial phase and 18.5 hours in the terminal phase. By 1 hour after administration of nonencapsulated daunorubicin, the predominant form of the drug in plasma is the active metabolite daunorubicinol, which has an average terminal plasma half-life of 26.7 hours. The apparent elimination half-life of DaunoXome (daunorubicin citrate liposome injection) is 4.4 hours, far shorter than that of daunorubicin, and probably represents a distribution half-life. |
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Chemotherapy with daunorubicin in combination with other agents is associated with serum enzyme elevations in a proportion of patients depending upon the dose and other agents used. ALT elevations during daunorubicin therapy are usually asymptomatic and transient and may resolve without dose modification. In many instances, it is difficult to attribute the liver test abnormalities to daunorubicin, because of the exposure to other potentially hepatotoxic agents. There have been no convincing instances of acute, clinically apparent idiosyncratic liver injury with jaundice associated with daunorubicin therapy. However, high doses of daunorubicin given in combination with other antineoplastic agents have been linked to cases of sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, typically presenting with right upper quadrant pain 10 to 30 days after the infusion, followed by weight gain, ascites and liver test abnormalities. Fatalities due to hepatic failure have occurred, but most patients recover within 1 to 3 months of onset. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected cause of clinically apparent liver injury). |
|
| 参考文献 |
|
|
| 其他信息 |
Daunomycin can cause cancer according to an independent committee of scientific and health experts.
Anthracycline antibiotic. An anticancer agent. Daunorubicin is a natural product found in Actinomadura roseola. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent and a bacterial metabolite. It is an anthracycline, a member of tetracenequinones, a member of p-quinones and an aminoglycoside antibiotic. It is a conjugate base of a daunorubicin(1+). It derives from a hydride of a tetracene. A very toxic anthracycline aminoglycoside antineoplastic isolated from Streptomyces peucetius and others, used in treatment of leukemia and other neoplasms. Daunorubicin is an Anthracycline Topoisomerase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of daunorubicin is as a Topoisomerase Inhibitor. Daunorubicin is an anthracycline antibiotic that has antineoplastic activity and is used in the therapy of acute leukemia and AIDS related Kaposi sarcoma. Daunorubicin is associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme and bilirubin elevations during therapy, but has not been implicated in cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury with jaundice. Daunorubicin has been reported in Streptomyces, Brassica napus, and other organisms with data available. Daunorubicin is an anthracycline antineoplastic antibiotic with therapeutic effects similar to those of doxorubicin. Daunorubicin exhibits cytotoxic activity through topoisomerase-mediated interaction with DNA, thereby inhibiting DNA replication and repair and RNA and protein synthesis. Daunorubicin is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a very toxic anthracycline aminoglycoside antineoplastic isolated from Streptomyces peucetius and others, used in treatment of leukemia and other neoplasms. [PubChem]Daunorubicin has antimitotic and cytotoxic activity through a number of proposed mechanisms of action: Daunorubicin forms complexes with DNA by intercalation between base pairs, and it inhibits topoisomerase II activity by stabilizing the DNA-topoisomerase II complex, preventing the religation portion of the ligation-religation reaction that topoisomerase II catalyzes. A very toxic anthracycline aminoglycoside antineoplastic isolated from Streptomyces peucetius and others, used in treatment of LEUKEMIA and other NEOPLASMS. See also: Daunorubicin Hydrochloride (annotation moved to). Drug Indication For remission induction in acute nonlymphocytic leukemia (myelogenous, monocytic, erythroid) of adults and for remission induction in acute lymphocytic leukemia of children and adults. Daunorubicin is indicated in combination with [cytarabine] for the treatment of newly-diagnosed therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (t-AML) or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC) in adults and pediatric patients 1 year and older. Mechanism of Action Daunorubicin has antimitotic and cytotoxic activity through a number of proposed mechanisms of action: Daunorubicin forms complexes with DNA by intercalation between base pairs, and it inhibits topoisomerase II activity by stabilizing the DNA-topoisomerase II complex, preventing the religation portion of the ligation-religation reaction that topoisomerase II catalyzes. Daunorubicin is an antineoplastic antibiotic. Daunorubicin has antimitotic and cytotoxic activity. Daunorubicin forms a complex with DNA by intercalation between base pairs. By stabilizing the complex between DNA and topoisomerase II, daunorubicin inhibits the activity of this enzyme, resulting in single-strand and double-strand breaks in DNA. Daunorubicin also may inhibit polymerase activity, affect regulation of gene expression, and be involved in free radical damage to DNA. Although daunorubicin is maximally cytotoxic in the S phase, the drug is not cycle-phase specific. Daunorubicin also has antibacterial and immunosuppressive properties. Anthracyclines are an important reagent in many chemotherapy regimes for treating a wide range of tumors. One of the primary mechanisms of anthracycline action involves DNA damage caused by inhibition of topoisomerase II. Enzymatic detoxification of anthracycline is a major critical factor that determines anthracycline resistance. Natural product, daunorubicin a toxic analogue of anthracycline is reduced to less toxic daunorubicinol by the AKR1B10, enzyme, which is overexpressed in most cases of smoking associate squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and adenocarcinoma. In addition, AKR1B10 was discovered as an enzyme overexpressed in human liver, cervical and endometrial cancer cases in samples from uterine cancer patients. Also, the expression of AKR1B10 was associated with tumor recurrence after surgery and keratinization of squamous cell carcinoma in cervical cancer and estimated to have the potential as a tumor intervention target colorectal cancer cells (HCT-8) and diagnostic marker for non-small-cell lung cancer. This article presents the mechanism of daunorubicin action and a method to improve the effectiveness of daunorubicin by modulating the activity of AKR1B10. ... In the present study using the ATP depleting agents cyanide, azide, or dinitrophenol to inhibit energy dependent transport processes, /investigators/ observed even larger increases in daunorubicin accumulation than were seen with CsA. Similar patterns were seen in a wide range of P-gp negative human cancer cell lines. Also the observed cyanide effect did not correlate with the expression of mRNA for multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP), the only other member of the ABC family of membrane transporters that is known to be capable of effluxing daunorubicin. Thse results suggest that daunorubicin accumulation in many cases of AML is modulated by one or more novel energy-dependent processes that are distinct from P-gp or MRP. /The authors/ speculate that this novel drug transport mechanism(s) may influence the response of AML patients to daunorubicin and other therapeutic agents. Inhibits DNA synthesis and blocks DNA-directed RNA polymerase. It can prevent cell division in doses that do not interfere with nucleic acid synthesis. |
| 分子式 |
C27H29NO10
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
527.53
|
|
| 精确质量 |
527.179
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 61.48; H, 5.54; N, 2.66; O, 30.33
|
|
| CAS号 |
20830-81-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
30323
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Dark Red Solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
770.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
155ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
419.5±32.9 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.692
|
|
| LogP |
2.92
|
|
| tPSA |
185.84
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
38
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
960
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
6
|
|
| SMILES |
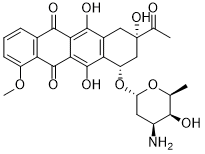
O=C(C(C(OC)=CC=C1)=C1C2=O)C3=C2C(O)=C(C[C@@](O)(C(C)=O)C[C@@H]4O[C@@]5([H])C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O5)C4=C3O
|
|
| InChi Key |
STQGQHZAVUOBTE-VGBVRHCVSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H29NO10/c1-10-22(30)14(28)7-17(37-10)38-16-9-27(35,11(2)29)8-13-19(16)26(34)21-20(24(13)32)23(31)12-5-4-6-15(36-3)18(12)25(21)33/h4-6,10,14,16-17,22,30,32,34-35H,7-9,28H2,1-3H3/t10-,14-,16-,17-,22+,27-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(7S,9S)-9-acetyl-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-4-methoxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione
|
|
| 别名 |
Daunomycin HCl; RP 13057; Rubidomycin; RP-13057; RP13057; Daunomycin hydrochloride; daunomycin HCl; daunorubidomycine; US brand names: Cerubidine; Rubidomycin; Foreign brand names: Cerubidin; Daunoblastin; Daunoblastina; Ondena; Rubilem; Abbreviations: DNM; DNR; DRB; Code names: FI6339; RP13057
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8956 mL | 9.4781 mL | 18.9563 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3791 mL | 1.8956 mL | 3.7913 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1896 mL | 0.9478 mL | 1.8956 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02085408 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Daunorubicin Drug: Cytarabine |
Adult Acute Monocytic Leukemia (M5b) Adult Erythroleukemia (M6a) |
ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group | February 4, 2011 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05939180 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Venetoclax Oral Tablet Drug: Daunorubicin |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia | The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University |
July 1, 2023 | Phase 2 Phase 3 |
| NCT02013648 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Daunorubicin Drug: Idarubicin |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) |
University of Ulm | July 2014 | Phase 3 |
| NCT03709758 | Recruiting | Drug: Daunorubicin Drug: Cytarabine |
Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute | October 17, 2018 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05832320 | Recruiting | Drug: Etoposide Drug: Daunorubicin |
Oral Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Induction Therapy |
Peking University People's Hospital |
January 1, 2023 | Not Applicable |
|
|