| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
BCL-XL
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
DT2216 是一种 Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 连接酶靶向 BCL-XL 蛋白水解靶向嵌合体 (PROTAC),可指导 BCL-XL 降解。由于VHL在血小板中表达较差,DT2216对血小板的毒性明显低于ABT263,使其对多种BCL-XL依赖性白血病和癌细胞更有效。 [1]
DT2216通过以vhl依赖的方式降解Bcl-xL,选择性杀死依赖Bcl-xL的TCL细胞系。DT2216能与ABT199联合体外协同杀伤TCL PDX细胞。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
作为单药或与其他化疗药物联合使用,DT2216 可有效减缓体内多种异种移植肿瘤的生长,而不会显着增加血小板减少症。 [1]
DT2216是一种比ABT263更有效的抗肿瘤药物,体内血小板毒性降低[1]
在体内,单独DT2216对小鼠MyLa TCL异种移植物非常有效,而不会引起明显的血小板减少或其他毒性。此外,在依赖Bcl-2和Bcl-xL的TCL PDX小鼠模型中,DT2216联合ABT199(一种选择性Bcl-2抑制剂)协同降低了疾病负担并提高了生存率。[2] DT2216联合其他BCL-2家族蛋白抑制剂增强抗肿瘤活性[1] DT2216与常规化疗的协同作用[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
AlphaScreen用于测定DT2216-BCL-XL、BCL-2和BCL-W的结合亲和力[1]
为了评估DT2216和ABT263对BCL-XL、BCL-2和BCL-W的结合亲和力,我们进行了alphasgreen竞争结合实验。实验在室温下进行,试剂在含有250 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 1 M NaCl, 1% BSA和0.05% Tween-20的缓冲液中稀释。将纯化的重组his标记的BCL-XL (0.1 nM)、BCL-2 (0.2 nM)或BCL-W (0.2 nM)与增加浓度的DT2216或ABT263和15 nM生物素标记的BAD (biotin- lwaaqrygrelrrmsdefgsfkgl n-末端)或30 nM BIM肽(Biotin-MRPEIWIAQELRRIGDEFNA n-末端)孵育至96孔PCR板中最终体积为40 μL。BAD肽用于评估化合物与BCL-XL的结合亲和力,而BIM肽用于评估BCL-2和BCL-W的结合亲和力。孵育24 h后,每孔加5 μL 6X his受体珠珠,末浓度为20 μg/mL,孵育1 h,再每孔加5 μL链霉亲和素供体珠珠,末浓度为20 μg/mL,孵育30 min,孵育结束后,将每个样品17 μL转移到384孔代板相邻孔中。在Biotek的Synergy Neo2多模式读卡器上使用Alpha程序扫描该板。通过GraphPad Prism 7软件的非线性回归、单位点、竞争结合、Fit Ki函数计算每个蛋白/肽对的抑制常数(Ki)。 [1] AlphaLISA法测定三元络合物形成[1] 我们使用AlphaLISA检测来监测目标蛋白、PROTAC和E3连接酶之间三元复合物的形成,如前所述44,58。为了验证BCL-XL/BCL-2、DT2216和VHL E3连接酶的形成,将固定浓度的his标记的重组蛋白(100 nM BCL-XL和10 nM BCL-2)和重组活性gst标记的VHL/Elongin B/C复合物(50 nM BCL-XL, 5 nM BCL-2)与不同浓度的测试化合物以4倍连续稀释,在96孔PCR板上培养至最终体积为40 μL。室温孵育30 min后,每孔中加入5 μL α谷胱甘肽供体微球,末浓度为20 μg/mL,孵育15 min。之后,每孔中加入5 μL 6X his受体微球,末浓度为20 μg/mL,室温孵育45 min。然后,在384孔代板的相邻孔中抽取17 μL的样品,在Biotek的Synergy Neo2多模板阅读器上使用Alpha程序对代板进行扫描。数据以平均AlphaLISA信号表示,并针对不同浓度的化合物绘制。 |
| 细胞实验 |
然后将指定浓度的 DT2216 或 ABT263 应用于 MOLT-4 细胞,在将 MOLT-4 细胞接种到 60 mm 培养皿(5 mL 完整细胞培养基/培养皿中的 2.5 × 106 个细胞)后 24 小时。冰-乙醇浴中的冻融循环或冰上孵育 30 分钟都是在 1X 细胞裂解缓冲液中裂解细胞的有效方法。
细胞热移测定(CETSA)[1] CETSA测定法改编自Smith等人。简单地说,用1 μM DT2216或DMSO处理2.5 × 107 MOLT-4或RS4细胞6小时,然后收获,用PBS洗涤,并在含有蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂的PBS中重悬。在MOLT-4细胞中加入10 μM MG132抑制BCL-XL的降解。将重悬细胞用液氮冷冻解冻4次。每次冻融循环后,裂解液进行短暂的旋涡以确保均匀解冻。将可溶性部分从细胞碎片中分离出来,在20000 ×g下4℃离心30 min,然后在42℃至69.5℃梯度温度下加热3 min,再冷却到25℃下3 min。处理后的样品在20000 ×g下4℃离心30 min,去除变性蛋白,然后进行免疫印迹分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
Pharmacodynamics of BCL-XL degradation by DT2216[1]
MOLT-4 xenografts were established in female CB-17 SCID-beige mice as described in following methods. Tumor-bearing mice were treated with single injection of vehicle or DT2216 (15 mpk/i.p.) when the tumors were ~600 mm3. Two mice each from vehicle and DT2216-treated groups were euthanized at each time point as indicated in the figure legend of Fig. 4b and tumors were harvested. The proteins were extracted from tumors and used for BCL-XL degradation by immunoblot analysis. Some portion of these tumors were used for DT2216 analysis as described in the previous method. In vivo platelet toxicity assays[1] Single dosing with DT2216 or ABT263[1] Female 5–6 weeks old CB-17 SCID-beige mice were treated with single i.p. doses of DT2216 (7.5, 15 and 25 mpk) or single p.o. doses of ABT263 (25, 50 and 100 mpk). Approximately 50 μL of blood was collected at different time points from each mouse as mentioned in Fig. 4c legend via submandibular plexus route in EDTA-tubes and platelets were enumerated using an automated hematology analyzer HEMAVET 950FS.[1] Daily dosing with ABT263 or once a week DT2216[1] Female CB-17 SCID-beige mice were treated with ABT263 (50 mpk/day/p.o.) or DT2216 (15 mpk/week/i.p.). Approximately 50 μL of blood was collected from each mouse 6 h (0.25 d) after each dose of ABT263 or collected from each mouse after 0.25 d, 1.25 d, 2.25 d, 3.25d, 4.25 d, 5.25 d, 6.25 d, 7.25 d, 8.25 d, 9.25 d, 10.25 d, 11.25 d, 12.25 d, 17.25 d and 24.25 d of once a week dosing with DT2216. Platelets were enumerated using HEMAVET 950FS. MOLT-4 T-ALL xenograft mouse model[1] To test the effect of DT2216 on tumor growth in MOLT-4 T-ALL xenografts, MOLT-4 T-ALL cells were harvested and suspended in regular RPMI medium and mixed with Matrigel (1:1). The cells (5 × 106 cells) suspended in 100 μL of RPMI medium-Matrigel mixture were subcutaneously (s.c.) implanted in the right flank of CB-17 SCID mice. Tumor growth was monitored daily and tumors were measured twice a week using Vernier caliper or digital calipers. Tumor volume was determined using the formula; [(L × W2) × 0.5], where L is length/long dimension in millimeter (mm) and W is the width/short dimension in mm. The treatment started once the average tumor volume reached 150–200 mm3. The animals were randomly assigned into separate groups (n = 6–8) in a way that each group had nearly equal starting average tumor volume. Mice were weighed twice a week and the treatments were given according to average mouse weight within each group before initiation of treatment. DT2216 and ABT263 for i.p. administration were formulated in 50% PHOSAL 50 PG, 45% MIGLYOL® 810 N and 5% Polysorbate 80. DT2216 and ABT263 were administered via i.p. injection at 15 mpk/week in 100 μL vehicle (Extended Data Fig. 8). ABT263 for oral administration was formulated in 10% ethanol, 30% PEG 400 and 60% PHOSAL 50 PG (Fig. 4). Control mice received 100 μL vehicle via i.p. injection. The mice were euthanized when the maximum tumor size in a mouse reached the humane endpoint according to institutional policy concerning tumor endpoints in rodents. In addition, to prevent excessive pain or distress, the mice were euthanized if the tumors became ulcerated or the mice showed any signs of ill health. Mice were euthanized by CO2 suffocation followed by cervical dislocation and various tissues including tumors were harvested for further analyses. H146 SCLC xenograft model[1] To test the effect of DT2216 alone or in combination with ABT199 on tumor growth in H146 SCLC xenografts, 5 × 106 H146 SCLC cells were suspended in regular RPMI medium, mixed with Matrigel, and s.c. implanted in the right flank of female CB-17 SCID mice as described in the previous method. Tumor growth was monitored, tumors were measured, and the tumor volume was determined as mentioned in the above method. The treatment started after four weeks of cell implantation as shown in Fig. 5c. The animals were randomly assigned into groups treated with vehicle, DT2216 15 mpk/week (i.p. injection), ABT263 15 mpk/week (i.p. injection), ABT199 50 mpk/day (oral administration), and DT2216 + ABT199. DT2216 and ABT263 were formulated as described above. ABT199 was formulated for oral dosing in 60% PHOSAL 50 PG, 30% polyethylene glycol (PEG) 400 and 10% ethanol. All the animals were euthanized in accordance with the institutional policy and various tissues were harvested. Tumors were weighed and used for BCL-XL, BCL-2 and MCL-1 expression by immunoblotting. MDA-MB-231 BC xenograft model[1] To test the effect of DT2216 in combination with Docetaxel on tumor growth in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer xenografts, 5 × 106 MDA-MB-231 cells were suspended in regular RPMI medium, mixed with Matrigel, and s.c. implanted in the right flank of female NOD-SCID mice. The animals were randomly assigned to vehicle, DT2216 (15 mpk/q4d/i.p.), Docetaxel (7.5 mpk/q14d/i.v.) and DT2216 + Docetaxel groups when the average tumor volume reached ~ 130 mm3. Docetaxel was dissolved in 5% DMSO + 30% PEG 300 + 5% Tween 80 + 60% dH2O. The solution was filter sterilized to obtain clear solution for intravenous administration. DT2216 was administered two days before starting dosing with Docetaxel, as also mentioned in Fig. 6c. T-ALL PDX models[1] To establish T-ALL PDX mouse models, 8 weeks old NSG mice were sublethally irradiated (0.25 Gy) 24 h prior to cell inoculation. PDX cells (1 × 106) were suspended in PBS and injected into mice through the tail vein. Tumor engraftment was determined by co-staining for human and murine anti-CD45 in bone marrow aspiration samples (CUL76 and D115 T-ALL) or in peripheral blood (332X-Luci) at 10 days post injection. Mice were randomized into different groups. CUL76 PDX were treated with DT2216 (15 mpk/q4d/i.p.), ABT199 (100 mpk/day/p.o.), chemotherapy (vincristine 0.15 mpk + dexamethasone 5 mpk + L-asparaginase 1000 Units/kg, i.p., weekly), combination of DT2216 and ABT199 or chemotherapy, or ABT199 plus chemotherapy as shown in Fig. 6f. D115 and 332X-Luci PDXs were treated with DT2216, chemotherapy, or combination of DT2216 and chemotherapy as shown in Extended Data Fig. 10. Mice were monitored for disease progression by weekly assessing leukemic (hCD45+) cells in the peripheral blood or bone marrow aspirates and followed for survival. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Bcl-XL Proteolysis Targeting Chimera DT2216 is an anti-apoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-XL) targeted protein degrader, using the proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) technology, with potential pro-apoptotic, immunomodulating and antineoplastic activities. DT2216 is composed of a Bcl-XL ligand attached to a Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 ligase ligand. Upon administration of DT2216, the Bcl-XL binding moiety specifically targets and binds to Bcl-XL which is expressed on tumor-infiltrating regulatory T-cells (Tregs) in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and cancer cells that are dependent on Bcl-XL for their survival, such as certain Bcl-XL-dependent T-cell malignancies. In turn, the VHL E3 ligase ligand is recruited to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Bcl-XL is tagged by ubiquitin. This causes ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of Bcl-XL. The degradation of Bcl-XL leads to an inhibition of the anti-apoptotic activity of Bcl-XL and restores apoptotic processes in and causes depletion of Bcl-XL-expressing Tregs and Bcl-XL-dependent cancer cells. Reduction of Tregs may activate anti-tumor CD8-positive-mediated immune responses. This leads to the inhibition of tumor growth. Bcl-XL, a protein belonging to the Bcl-2 family, plays an important role in the negative regulation of apoptosis. Their expression in tumors is associated with increased Tregs survival. Tregs play a key role in cancer progression and tumor immunosuppression. Compared to other Bcl-XL inhibitors, DT2216 does not cause platelet toxicity as the VHL E3 ligase is not highly expressed in platelets.
|
| 分子式 |
C77H96CLF3N10O10S4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
1542.3554
|
| 精确质量 |
1540.58
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.96; H, 6.27; Cl, 2.30; F, 3.70; N, 9.08; O, 10.37; S, 8.31
|
| CAS号 |
2365172-42-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
2365172-42-3;DT2216 HCl; DT2216NC; DT2216-isomer;
|
| PubChem CID |
139331475
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
12.8
|
| tPSA |
321Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
20
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
29
|
| 重原子数目 |
105
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
3130
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
| SMILES |
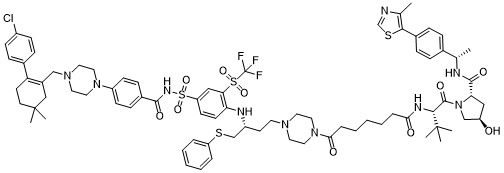
CC1=C(SC=N1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@@H]3C[C@H](CN3C(=O)[C@H](C(C)(C)C)NC(=O)CCCCCC(=O)N4CCN(CC4)CC[C@H](CSC5=CC=CC=C5)NC6=C(C=C(C=C6)S(=O)(=O)NC(=O)C7=CC=C(C=C7)N8CCN(CC8)CC9=C(CCC(C9)(C)C)C1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl)S(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F)O
|
| InChi Key |
PXVFFBGSTYQHRO-REQIQPEASA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C77H96ClF3N10O10S4/c1-51(53-18-20-55(21-19-53)70-52(2)82-50-103-70)83-73(96)66-44-61(92)48-91(66)74(97)71(75(3,4)5)85-68(93)16-12-9-13-17-69(94)90-42-36-87(37-43-90)35-33-59(49-102-62-14-10-8-11-15-62)84-65-31-30-63(45-67(65)104(98,99)77(79,80)81)105(100,101)86-72(95)56-24-28-60(29-25-56)89-40-38-88(39-41-89)47-57-46-76(6,7)34-32-64(57)54-22-26-58(78)27-23-54/h8,10-11,14-15,18-31,45,50-51,59,61,66,71,84,92H,9,12-13,16-17,32-44,46-49H2,1-7H3,(H,83,96)(H,85,93)(H,86,95)/t51-,59+,61+,66-,71+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S,4R)-1-[(2S)-2-[[7-[4-[(3R)-3-[4-[[4-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5,5-dimethylcyclohexen-1-yl]methyl]piperazin-1-yl]benzoyl]sulfamoyl]-2-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)anilino]-4-phenylsulfanylbutyl]piperazin-1-yl]-7-oxoheptanoyl]amino]-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]-4-hydroxy-N-[(1S)-1-[4-(4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)phenyl]ethyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
DT2216 HCl; DT-2216; DT 2216; DT2216; 2365172-42-3; DT-2216; (2s,4r)-1-((s)-2-(7-(4-((r)-3-((4-(N-(4-(4-((4'-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-yl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)benzoyl)sulfamoyl)-2-((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)phenyl)amino)-4-(phenylthio)butyl)piperazin-1-yl)-7-oxoheptanamido)-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl)-4-hydroxy-N-((s)-1-(4-(4-methylthiazol-5-yl)phenyl)ethyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide; Y8JQ9V7JAJ; (2S,4R)-1-[(2S)-2-[[7-[4-[(3R)-3-[4-[[4-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-5,5-dimethylcyclohexen-1-yl]methyl]piperazin-1-yl]benzoyl]sulfamoyl]-2-(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)anilino]-4-phenylsulfanylbutyl]piperazin-1-yl]-7-oxoheptanoyl]amino]-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]-4-hydroxy-N-[(1S)-1-[4-(4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)phenyl]ethyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide; UNII-Y8JQ9V7JAJ; CHEMBL4745523; DT2216
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~64.8 mM)
Ethanol: ~100 mg/mL (~64.8 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.6484 mL | 3.2418 mL | 6.4836 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1297 mL | 0.6484 mL | 1.2967 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0648 mL | 0.3242 mL | 0.6484 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT04886622 | Recruiting | Drug: DT2216 | Solid Tumor Hematologic Malignancy |
Dialectic Therapeutics, Inc | August 25, 2021 | Phase 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|