| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
脑血管舒张和神经源性炎症被认为是偏头痛发病机制的原动力。 5-HT1B 的激活可逆转脑血管舒张,5-HT1D 的激活可预防神经源性炎症。夫罗曲坦对 5-HT1B 和 5-HT1D 受体具有高亲和力,对 5-HT1A 和 5-HT1F 受体亚型具有中等亲和力。夫罗曲坦对 5-HT7 受体具有中等亲和力,这种作用与狗的冠状动脉松弛有关[1]。
|
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
夫罗曲坦的口服生物利用度为22%-30%,且不受食物影响。虽然血浆中的最大浓度在2-3小时内达到,但其中60%-70%是在1小时内达到的。 4-5 天内达到稳定状态。血浆蛋白结合率低至 15%。最独特的特点是相对终末半衰期长约26小时。夫罗曲坦主要由 CYP1A2 代谢,并由肾脏和肝脏清除,使得任一器官的中度衰竭不再是治疗的限制因素[1]。夫罗曲坦(0.1、0.2 和 0.3 mg/kg;十二指肠内单次推注给药)治疗会增加颈动脉血管阻力,这种情况在犬中可持续至少 5 小时[2]。
|
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Frovatriptan is rapidly absorbed from the duodenum, but has low oral bioavailability. Radiolabeled compounds excreted in urine were unchanged frovatriptan, hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan and desmethyl frovatriptan, together with several other minor metabolites. Less than 10% of frovatriptan was excreted in urine after an oral dose. 4.2 L/kg [males] 3 L/kg [females] 220 mL/min [male receiving IV dose of 0.8 mg] 130 mL/min [Female receiving IV dose of 0.8 mg] Protein binding: Low (approximately 15%) to serum proteins. Volume of distribution (VolD): Steady state : 4.2 L/kg in males and 3.0 L/kg in females. The absolute bioavailability of an oral dose of frovatriptan is about 20% in males and 30% in females. The rate and extent of absorption are not affected by administration with food. Elimination: Renal: Following a single oral 2.5 mg dose of radiolabeled frovatriptan, 32% of the dose was recovered in urine. Radiolabeled compounds excreted in the urine were unchanged frovatriptan, hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, desmethyl frovatriptan and several other minor metabolites. Fecal: Following a single oral 2.5 mg dose of radiolabeled frovatriptan, 62% of the dose was recovered in feces. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for FROVATRIPTAN (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites In vitro, cytochrome P450 1A2 appears to be the principal enzyme involved in the metabolism of frovatriptan to several metabolites including hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan and desmethyl frovatriptan, and several other minor metabolites. Desmethyl frovatriptan has lower affinity for 5-HT1B/1D receptors compared to the parent compound. The N-acetyl desmethyl metabolite has no significant affinity for 5-HT receptors. The activity of the other metabolites is unknown. In vitro, cytochrome P450 1A2 appears to be the principal enzyme involved in the metabolism of frovatriptan. Following administration of a single oral dose of radiolabeled frovatriptan 2.5 mg to healthy male and female subjects, 32% of the dose was recovered in urine and 62% in feces. Radiolabeled compounds excreted in urine were unchanged frovatriptan, hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan and desmethyl frovatriptan, together with several other minor metabolites. Desmethyl frovatriptan has lower affinity for 5-HT1B/1D receptors compared to the parent compound. The N-acetyl desmethyl metabolite has no significant affinity for 5-HT receptors. The activity of the other metabolites is unknown. In vitro, cytochrome P450 1A2 appears to be the principal enzyme involved in the metabolism of frovatriptan to several metabolites including hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan and desmethyl frovatriptan, and several other minor metabolites. Desmethyl frovatriptan has lower affinity for 5-HT1B/1D receptors compared to the parent compound. The N-acetyl desmethyl metabolite has no significant affinity for 5-HT receptors. The activity of the other metabolites is unknown. Route of Elimination: Radiolabeled compounds excreted in urine were unchanged frovatriptan, hydroxylated frovatriptan, N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan, hydroxylated N-acetyl desmethyl frovatriptan and desmethyl frovatriptan, together with several other minor metabolites. Less than 10% of frovatriptan was excreted in urine after an oral dose. Half Life: 26 hours Biological Half-Life 26 hours Elimination: Intravenous administration: Approximately 26 hours. |
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Three distinct pharmacological actions have been implicated in the antimigraine effect of the triptans: (1) stimulation of presynaptic 5-HT1D receptors, which serves to inhibit both dural vasodilation and inflammation; (2) direct inhibition of trigeminal nuclei cell excitability via 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonism in the brainstem and (3) vasoconstriction of meningeal, dural, cerebral or pial vessels as a result of vascular 5-HT1B receptor agonism. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation There is no published experience with frovatriptan during breastfeeding. If frovatriptan is required by the mother of an older infant, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding, but until more data become available, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Painful, burning nipples and breast pain have been reported after doses of sumatriptan and other triptans. This has occasionally been accompanied by a decrease in milk production. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk A review of four European adverse reaction databases found 26 reported cases of, painful, burning nipples, painful breasts, breast engorgement and/or painful milk ejection in women who took a triptan while nursing. Pain was sometimes intense and occasionally led to decreased milk production. Pain generally subsided with time as the drug was eliminated. The authors proposed that triptans may cause vasoconstriction of the arteries in the breast, nipples, and the arteries surrounding the alveoli and milk ducts, causing a painful sensation and a painful milk ejection reflex. Protein Binding Binding to serum proteins is low (approximately 15%). Reversible binding to blood cells at equilibrium is approximately 60%. Interactions Concurrent use /of frovatriptan/ with oral contraceptives has resulted in a 30% increase in the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) and peak plasma concentration of frovatriptan. Concurrent use /of frovatriptan/ with ergotamine tartrate has resulted in a 25% decrease in the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) and peak plasma concentration of frovatriptan. Concurrent use /of frovatriptan with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, such as: fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine or sertraline/ may result in weakness, hyperreflexia, and incoordination; careful observation of the patients is recommended. Concurrent use /of frovatriptan/ with propranolol increased the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) in males by 60% and in females by 29%. the peak plasma concentration was increased by 23% in males and 16% in females; however the half-life of frovatriptan in both populations, though slightly longer in females was not affected by concomitant administration of propranolol. A delay of 24 hours between administration of dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, or methylsergide or other 5-hydroxytryptamine agonists and frovatriptan is recommended because of the possibility of additive and/or prolonged vasoconstriction. |
|
| 参考文献 | ||
| 其他信息 |
Frovatriptan is a member of carbazoles.
Frovatriptan is a triptan drug developed by Vernalis for the treatment of migraine headaches, in particular those associated with menstruation. Frovatriptan causes vasoconstriction of arteries and veins that supply blood to the head. Frovatriptan is a Serotonin-1b and Serotonin-1d Receptor Agonist. The mechanism of action of frovatriptan is as a Serotonin 1b Receptor Agonist, and Serotonin 1d Receptor Agonist. Frovatriptan (Frova™) is a triptan drug developed by Vernalis for the treatment of migraine headaches, in particular those associated with menstruation. The product is licensed to Endo Pharmaceuticals in North America and Menarini in Europe.[1] Frovatriptan causes vasoconstriction of arteries and veins that supply blood to the head. It is available as 2.5 mg tablets. Frovatriptan has mean terminal elimination half-life of approximately 26 hours, which is substantially longer than other triptans. Frovatriptan is available only by prescription in the United States, where a secondary New Drug Approval (sNDA) was filed in July 2006[2] and which is currently pending.[3] The FDA anticipates completing its review of this application on or before the current PDUFA (Prescription Drug User Fee Act) review date of August 19, 2007. If the sNDA is approved, Frova™ will be the only medication indicated in the U.S. for the short-term prevention of menstrual migraine (MM). See also: Frovatriptan Succinate (has salt form). Drug Indication For the acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without aura in adults. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Three distinct pharmacological actions have been implicated in the antimigraine effect of the triptans: (1) stimulation of presynaptic 5-HT1D receptors, which serves to inhibit both dural vasodilation and inflammation; (2) direct inhibition of trigeminal nuclei cell excitability via 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonism in the brainstem and (3) vasoconstriction of meningeal, dural, cerebral or pial vessels as a result of vascular 5-HT1B receptor agonism. Frovatriptan is believed to act on extracerebral, intracranial arteries and to inhibit excessive dilation of these vessels in migraine. In anesthetized dogs and cats, intravenous administration of frovatriptan produced selective constriction of the carotid vascular bed and had no effect on blood pressure (both species) or coronary resistance (in dogs). Frovatriptan succinate is a selective agonist of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) type 1B and 1D receptors. Frovatriptan is structurally distinct from, but pharmacologically related to, other selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists (e.g., almotriptan, naratriptan, rizatriptan, sumatriptan). Because the mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of migraine are not clearly understood, the precise mechanism of action of 5-HT1 receptor agonists in the management of migraine has yet to be established. However, current data suggest that 5-HT1 receptor agonists, including frovatriptan, may ameliorate migraine through selective constriction of certain intracranial blood vessels, inhibition of neuropeptide release, and/or reduced transmission in the trigeminal pain pathway. Frovatriptan has no significant effects on GABAA mediated channel activity and has not significant affinity for benzodiazepine binding sites. Frovatriptan is believed to act on extracerebral, intracranial arteries and to inhibit excessive dilation of these vessels in migraine. Therapeutic Uses Tryptamines; Carbazoles Frovatriptan is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without aura in adults. /Included in US product labeling/ Drug Warnings As with other 5-HT1 agonists, sensations of pain, tightness, pressure and heaviness have been reported in the chest, throat, neck and jaw after treatment with frova. These events have not been associated with arrhythmias or ischemic ECG changes in clinical trials with FROVA. Because 5-HT1 agonists may cause coronary vasospasm, patients who experience signs or symptoms suggestive of angina following dosing should be evaluated for the presence of CAD. Patients shown to have CAD and those with Prinzmetal's variant angina should not receive 5-HT1 agonists. Patients who experience other symptoms or signs suggestive of decreased arterial flow, such as ischemic bowel syndrome or Raynaud's syndrome following the use of any 5-HT1 agonist are candidates for further evaluation. If a patient has no response for the first migraine attack treated with frova, the diagnosis of migraine should be reconsidered before frovatriptan is administered to treat any subsequent attacks. Cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, stroke and other cerebrovascular events have been reported in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists; and some have resulted in fatalities. In a number of cases, it appears possible that the cerebrovascular events were primary, the agonist having been administered in the incorrect belief that the symptoms experienced were a consequence of migraine, when they were not. It should be noted that patients with migraine may be at increased risk of certain cerebrovascular events (e.g. stroke, hemorrhage, transient ischemic attack). Frovatriptan is not indicated in the management of hemiplegic or basilar migraine. Frovatriptan is not indicated for use in cluster headache, which is present in an older, predominately male population. Safety and efficacy of frovatriptan in this condition have not been established. Frovatriptan is not intended for the prophylactic therapy of migraine. FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: C /RISK CANNOT BE RULED OUT. Adequate, well controlled human studies are lacking, and animal studies have shown risk to the fetus or are lacking as well. There is a chance of fetal harm if the drug is given during pregnancy; but the potential benefits may outweigh the potential risk./ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for FROVATRIPTAN (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Frovatriptan is a second generation triptan 5-HT receptor agonist that binds with high affinity for 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors. It is structurally distinct from, but pharmacologically related to other selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists. Frovatriptan has no significant effects on GABAA mediated channel activity and has no significant affinity for benzodiazepine binding sites. Frovatriptan is believed to act on extracerebral, intracranial arteries and to inhibit excessive dilation of these vessels in migraine. Research has shown that migraine can be caused by the swelling of blood vessels around the brain. Frovatriptan eases the pain associated with migraine by narrowing these blood vessels. Frovatriptan has one of the highest affinities for the 5-HT1B of the second-generation triptan agonists. |
| 分子式 |
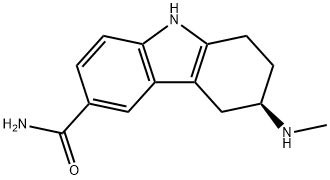
C14H17N3O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
243.31
|
| 精确质量 |
243.137
|
| CAS号 |
158747-02-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Frovatriptan succinate hydrate;158930-17-7;Frovatriptan succinate;158930-09-7;Frovatriptan-d3 hydrochloride
|
| PubChem CID |
77992
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.27g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
515.2ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
265.4ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
1.01E-10mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.667
|
| LogP |
2.618
|
| tPSA |
71.9
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
18
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
333
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
CN[C@@H]1CCC2=C(C3=C(N2)C=CC(C(N)=O)=C3)C1
|
| InChi Key |
XPSQPHWEGNHMSK-SECBINFHSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C14H17N3O/c1-16-9-3-5-13-11(7-9)10-6-8(14(15)18)2-4-12(10)17-13/h2,4,6,9,16-17H,3,5,7H2,1H3,(H2,15,18)/t9-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(6R)-6-(methylamino)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-carbazole-3-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
SB 209509 Miguard Frovatriptan
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1100 mL | 20.5499 mL | 41.0998 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8220 mL | 4.1100 mL | 8.2200 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4110 mL | 2.0550 mL | 4.1100 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Effects of Frovatriptan as Prophylactic Treatment of Cluster Headache, a Multi-Center, Placebo Controlled, Randomized, Double-Blind Prospective Phase III Parallel-Group Trial Comparing Frovatriptan with Placebo
CTID: null
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Prematurely Ended
Date: 2006-11-06