| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
HIF-PHD
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GSK360A是一种强效(纳摩尔)HIF PHDs抑制剂(PHD1>PHD2=PHD3),能够在包括新生大鼠心室肌细胞和H9C2细胞在内的多种细胞类型中激活HIF-1α通路。[1]
GSK360A增加了红细胞生成素(EPO)、血红素加氧酶-1(HO1)和葡萄糖转运蛋白1(Glut1)转录物,所有HIF1α靶基因,并促进了OGD后神经元和少突胶质细胞的存活。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在完善的心室衰竭模型中,GSK360A(30 mg/kg ig)可改善死亡率、血管分布和长期心室功能[1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
白细胞计数与血浆EPO测定[2]
从大鼠身上采集血液,并将其转移到含有EDTA的埃彭多夫管中。使用Hemavet 1500血液分析仪测量新鲜血液中的白细胞计数。对于血浆制备,将血液以1000 g离心15分钟,并将血浆上清液储存在−80°C的冰箱中以备进一步使用。如前所述,通过基于Luminex珠的多重ELISA测量血浆EPO,并通过Bio-Plex Manager软件定量。 |
| 细胞实验 |
氧-葡萄糖剥夺(OGD)模型和细胞活力测定[2]
通过细胞特异性神经元(MAP2)或少突胶质细胞(Rip)标记物(Sun等人,2010),证实了第17天胚胎大鼠大脑的原代培养皮层神经元和出生后第0-2天新生大鼠大脑中的少突胶质母细胞(OLs)的细胞纯度(>85%)。在无葡萄糖和脱氧的细胞培养基中,用GSK360A(3和30μM)预处理体外10天(DIV)的神经元和5-DIV的OLs 30分钟,并将其转移到厌氧室中,在37°C下通过连续流量的气体混合物(5%CO2和95%N2)预平衡1%的氧浓度2小时。用常规细胞培养基代替培养基,并将培养基放回5%CO2培养箱中。神经元和OLs的存活率通过细胞计数试剂盒-8在三个以上的独立实验中测量。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Lewis rat ventricular dysfunction model [1]
Doses: 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage) Experimental Results: Circulating levels of erythropoietin and hemoglobin and blood oxygenation in the heart and skeletal muscle of male rats Enzyme-1 expression is increased. GSK360A was delivered by intracerebroventricular (ICV, 12μg /5μg/ 10 g body-weight), intranasal (IN, 30 or 60μg/ 10 g) or intraperitoneal (IP, 100~500μg/ 10 g) as previously described (Bao et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2013a; 2013b; 2013c; Zhou et al., 2017). GSK360A powder were dissolved in 30% hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HBC) solution to a final concentration of 2.5μg/ μg. ICV or IP administration of GSK360A was performed at 30 min after HI, and IN-GSK360A delivery was given twice at 30 and 60 min after HI. The ICV injection of 5μg saline or GSK360A with the speed 1μg/min was performed with a Hamilton syringe at right hemisphere as previously described (Yang et al., 2009). The stereotaxic coordinates were 2.0 mm rostral and 1.5 mm lateral to the right from the lambda point, and at a depth of 2.0 mm from the surface of brain. The Rice-Vannucci model of neonatal HI was performed in 7-day-old (P7) Wistar rats, as described (Yang et al., 2009). Briefly, pups of both genders were anesthetized by 2% isoflurane mixed with compressed air when the right common carotid artery was ligated. After a 1 h recovery period, pups were exposed to 10% O2 balanced by 90% nitrogen for 90 min in glass chambers submerged in a 37°C water bath. The pups were returned to dams after hypoxia induction for recovery. The C57BL/6 mice were obtained from Charles River Laboratories and applied in the experiments of HIF1α immunoblots and tissue staining (Fig. 1, Fig. 2C--E,E, Fig. 5A). The ODD-luciferase (HIF1α-Luc) mice were obtained from the Jackson Laboratories (Stock# 006206) and the brains were harvested for luciferase activity assay using the Dual-Luciferase® reporter assay system. Whole blood from P7 rats were collected for complete blood counts measurement by a Hemavet 1500 blood analyzer (1500 R series). All experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) and conducted according to the National Institutes of Health Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Experiments are performed and reported in accordance with the ARRIVE.[2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1α) is a major regulator of cellular adaptation to hypoxia and oxidative stress, and recent advances of prolyl-4-hydroxylase (P4H) inhibitors have produced powerful tools to stabilize HIF1α for clinical applications. However, whether HIF1α provokes or resists neonatal hypoxic-ischemic (HI) brain injury has not been established in previous studies. We hypothesize that systemic and brain-targeted HIF1α stabilization may have divergent effects. To test this notion, herein we compared the effects of GSK360A, a potent P4H inhibitor, in in-vitro oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) and in in-vivo neonatal HI via intracerebroventricular (ICV), intraperitoneal (IP), and intranasal (IN) drug-application routes. We found that GSK360A increased the erythropoietin (EPO), heme oxygenase-1 (HO1) and glucose transporter 1 (Glut1) transcripts, all HIF1α target-genes, and promoted the survival of neurons and oligodendrocytes after OGD. Neonatal HI insult stabilized HIF1α in the ipsilateral hemisphere for up to 24 h, and either ICV or IN delivery of GSK360A after HI increased the HIF1α target-gene transcripts and decreased brain damage. In contrast, IP-injection of GSK360A failed to reduce HI brain damage, but elevated the risk of mortality at high doses, which may relate to an increase of the kidney and plasma EPO, leukocytosis, and abundant vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNAs in the brain. These results suggest that brain-targeted HIF1α-stabilization is a potential treatment of neonatal HI brain injury, while systemic P4H-inhibition may provoke unwanted adverse effects.[2]
Background: Hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) are transcription factors that are regulated by HIF-prolyl 4-hydroxylases (PHDs) in response to changes in oxygen tension. Once activated, HIFs play an important role in angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, proliferation, cell survival, inflammation, and energy metabolism. We hypothesized that GSK360A, a novel orally active HIF-PHD inhibitor, could facilitate local and systemic HIF-1 alpha signaling and protect the failing heart after myocardial infarction (MI).[1] Methods and results: GSK360A is a potent (nanomolar) inhibitor of HIF-PHDs (PHD1>PHD2 = PHD3) capable of activating the HIF-1 alpha pathway in a variety of cell types including neonatal rat ventricular myocytes and H9C2 cells. Male rats treated orally with GSK360A (30 mg x kg x d) had a sustained elevation in circulating levels of erythropoietin and hemoglobin and increased hemoxygenase-1 expression in the heart and skeletal muscle. In a rat model of established heart failure with systolic dysfunction induced by ligation of left anterior descending coronary artery, chronic treatment with GSK360A for 28 days prevented the progressive reduction in ejection fraction, ventricular dilation, and increased lung weight, which were observed in the vehicle-treated animals, for up to 3 months. In addition, the microvascular density in the periinfarct region was increased (>2-fold) in GSK360A-treated animals. Treatment was well tolerated (survival was 89% in the GSK360A group vs. 82% in the placebo group).[1] Conclusions: Chronic post-myocardial infarction treatment with a selective HIF PHD inhibitor (GSK360A) exerts systemic and local effects by stabilizing HIF-1 alpha signaling and improves long-term ventricular function, remodeling, and vascularity in a model of established ventricular dysfunction. These results suggest that HIF-PHD inhibitors may be suitable for the treatment of post-MI remodeling and heart failure.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C17H17FN2O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
348.3304
|
| 精确质量 |
348.112
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 58.62; H, 4.92; F, 5.45; N, 8.04; O, 22.97
|
| CAS号 |
931399-19-8
|
| PubChem CID |
54685147
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as white to off-white solids at room temperature
|
| LogP |
2.035
|
| tPSA |
112.12
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
616
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
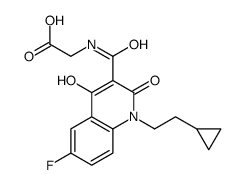
C1CC1CCN2C3=C(C=C(C=C3)F)C(=C(C2=O)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)O
|
| InChi Key |
TYHRZQVUPPODPT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H17FN2O5/c18-10-3-4-12-11(7-10)15(23)14(16(24)19-8-13(21)22)17(25)20(12)6-5-9-1-2-9/h3-4,7,9,23H,1-2,5-6,8H2,(H,19,24)(H,21,22)
|
| 化学名 |
{[1-(2-Cyclopropyl-ethyl)-6-fluoro-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-quinoline-3-carbonyl]-amino}-acetic acid
|
| 别名 |
GSK-360A; GSK 360A; GSK360A
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8708 mL | 14.3542 mL | 28.7084 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5742 mL | 2.8708 mL | 5.7417 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2871 mL | 1.4354 mL | 2.8708 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。