| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
酮咯酸 (RS37619) 盐(0-30 μM;48 小时)可成功杀死口腔癌细胞[4]。在 H357 细胞中,酮咯酸盐(0–5 μM;48 小时)会导致细胞凋亡并抑制 DDX3 蛋白的产生[4]。酮咯酸盐(0-2.5 μM;0-16 小时)可抑制口腔癌细胞生长[4]。通过直接与 DDX3 相互作用,酮咯酸盐 (0–50 μM) 抑制 ATP 酶活性[4]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在兔子中,酮咯酸 (RS37619) 或 0.4% 酮咯酸氨丁三醇滴眼液对眼睛表现出有效的抗炎作用[1]。酮咯酸(4 mg/kg/天,口服;2 周)不会对大鼠牙槽窝骨小梁体积分数产生负面影响[2]。在大鼠中,鞘内注射酮咯酸(60 μg)可减轻脊髓缺血引起的损伤[3]。暴露于酮咯酸盐(20 和 30 mg/kg;腹腔注射;每周两次,持续三周)的小鼠口腔癌发生率较低[4]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [4]
细胞类型: HOK、SCC4、SCC9 和 H357 细胞 测试浓度: 0-30 μM 孵育时间:48小时 实验结果:对H357、SCC4和SCC9细胞的IC50分别为2.6、7.1和8.1 μM。而正常的HOK细胞系没有表现出任何细胞死亡效应。 细胞增殖测定[4] 细胞类型: H357 测试浓度: 0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 和 2.5 μM 孵育时间:0、8和16小时 实验结果:抑制增殖。 蛋白质印迹分析[4] 细胞类型: H357 测试浓度: 1、2.5 和 5 μM 孵育时间:48 小时 实验结果:与 DMSO 处理的细胞相比,DDX3 蛋白表达水平显着降低,但并未完全消除。上调E-钙粘蛋白的表达。 细胞凋亡分析[4] 细胞类型: H357 测试浓度: 2.5 和 5 μM 孵育时间:48小时 实验结果:诱导细胞凋亡。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: New Zealand White rabbits (2.0–2.7 kg), LPS endotoxin-induced ocular inflammation[1]
Doses: 50 μL ketorolac tromethamine ophthalmic solution 0.4% Route of Administration: In eyes, twice, 2 hrs (hours) and 1 hour before LPS challenge Experimental Results: Resulted in a nearly complete inhibition (98.7%) of LPS endotoxin-induced increases in FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate)-dextran in the anterior chamber, and resulted in a nearly complete inhibition (97.5%) of LPS endotoxin-induced increases in aqueous PGE2 concentrations in the aqueous humor. Animal/Disease Models: Male Wistar rats (400–450 g), spinal cord ischemia model[3] Doses: 30 and 60 μg Route of Administration: Intrathecal injection , 1 h before the ischemia induction for once Experimental Results: Dramatically decreased the motor disturbances and improved the survival rate at 60 μg. Animal/Disease Models: Dramatically decreased the motor disturbances and improved the survival rate at 60 μg. Doses: 20 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: IP injection, two times in a week for 3 weeks |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Ketorolac is rapidly, and completely absorbed after oral administration with a bioavailability of 80% after oral administration. Cmax is attained 20-60 minutes after administration, and after intramuscular administration, the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) is proportional to the dose administered. After intramuscular administration, ketorolac demonstrates a time to maximal plasma concentration (tmax) of approximately 45-50 minutes, and a tmax of 30-40 minutes after oral administration. The rate of absorption may be reduced by food; however, the extent of absorption remains unaffected. Ketorolac is primarily renally eliminated and approximately 92% of the dose can be recovered in the urine with 60% of this proportion recovered unchanged, and 40% recovered as metabolites. In addition 6% of a single dose is eliminated in the feces. The apparent volume of distribution of ketorolac in healthy human subjects is 0.25 L/kg or less. The plasma clearance of ketorolac is 0.021 to 0.037 L/h/kg. Further, studies have illustrated that clearance of oral, IM and IV doses of ketorolac are comparable which suggests linear kinetics. It should also be noted that clearance in children is about double the clearance found in adults. Metabolism / Metabolites Ketorolac is heavily metabolized via hydroxylation or conjugation in the liver; however, it appears that the key metabolic pathway is glucuronic acid conjugation. Enzymes involved in phase I metabolism include CYP2C8 and CYP2C9, while phase II metabolism is carried out by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 2B7. Biological Half-Life Ketorolac tromethamine is administered as a racemic mixture, therefore the half-life of each enantiomer must be considered. The half life of the S-enantiomer is ~2.5 hours, while the half life of the R-enantiomer is ~5 hours. Based on this data, the S enantiomer is cleared about twice as fast as the R enantiomer. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Prospective studies show that up to 1% of patients taking ketorolac experience at least transient serum aminotransferase elevations. These may resolve even with drug continuation. Marked aminotransferase elevations (>3 fold elevated) occur in Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected cause of clinically apparent liver injury, largely due to bleeding episodes). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Milk levels of ketorolac are low with the usual oral dosage, but milk levels have not been measured after higher injectable dosages or with the nasal spray. Ketorolac injection is used for a short time (typically 24 hours) after cesarean section in some hospital protocols with no evidence of harm to breastfed infants. However, the ketorolac dose an infant receives in colostrum is very low because of the small volume of colostrum produced. Some evidence suggests that IV ketorolac as part of a multimodal post-cesarean section analgesia reduces percentage of mothers who fail exclusive breastfeeding compared to patient-controlled IV morphine-based analgesia. Ketorolac has strong antiplatelet activity and can cause gastrointestinal bleeding. The manufacturer indicates that ketorolac is contraindicated during breastfeeding, so an alternate drug is preferred after the first 24 to 72 hours when larger volumes of milk are produced, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. Maternal use of ketorolac eye drops would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A randomized, double-blind study compared standard care of mothers receiving a cesarean section delivery (n = 60) to those receiving standard care plus multimodal pain management that included a single dose of 60 mg of intramuscular ketorolac given at the time of fascial closure (n = 60). No significant differences in abnormal neonatal growth, difficulty feeding, neonatal sedation, or respiratory depression rates between the two groups were seen during the first month postpartum. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk A randomized, double-blind study compared standard care of mothers receiving a cesarean section delivery (n = 60) to those receiving standard care plus multimodal pain management that included a single dose of 60 mg of intramuscular ketorolac given at the time of fascial closure (n = 60). No significant differences in breastfeeding rates (78% and 79%, respectively) were seen during the first month postpartum. In a study comparing standard of care to enhanced recovery after cesarean section deliveries, a fixed dose of ketorolac 15 mg every 6 hours intravenously for 24 hours postpartum was part of the enhanced recovery protocol whereas as needed ketorolac 15 mg intravenously was part of the standard protocol. Patients in the enhanced recovery protocol (n = 58) had a greater frequency of exclusive breastfeeding (67%) than those in the standard protocol (48%; n = 60). A retrospective study evaluated 1349 women who had undergone a cesarean section and were given ketorolac within 15 minutes of the end of surgery. The results indicated that there was no difference in pain control in the first 6 hours after surgery nor in the percentage of women who were breastfeeding at discharge. A prospective cohort study of postcesarean pain control compared (1) morphine PCA and scheduled ibuprofen for the first 12 hours followed by continued scheduled ibuprofen with hydrocodone-acetaminophen as needed to a multimodal pain management regimen consisting of (2) acetaminophen 1000 mg orally every 8 hours, ketorolac 30 mg IV once initially, then 15 mg IV every 8 hours for 24 hours, then ibuprofen 600 mg orally every 8 hours for the remainder of the postoperative course with opioids given only as needed. Of women who planned to exclusively breastfeed on admission, fewer women used formula prior to discharge in the multimodal group compared to the traditional group (9% vs. 12%). Protein Binding >99% of Ketorolac is plasma protein bound. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Ketorolac is a non-selective NSAID and acts by inhibiting both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes which are normally responsible for converting arachidonic acid to prostaglandins. The COX-1 enzyme is constitutively active and can be found in platelets, gastric mucosa, and vascular endothelium. On the other hand, the COX-2 enzyme is inducible and mediates inflammation, pain and fever. As a result, inhibition of the COX-1 enzyme is linked to an increased risk of bleeding and risk of gastric ulceration, while the desired anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties are linked to inhibition of the COX-2 enzyme. Therefore, despite it's effectiveness in pain management, ketorolac should not be used long-term since this increases the risk of serious adverse effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcers, and perforations. |
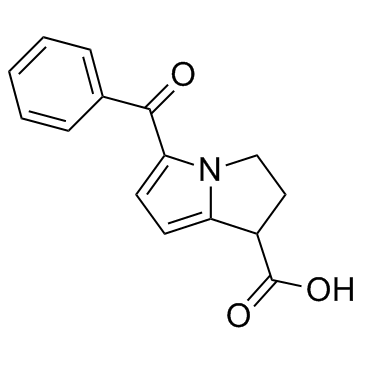
| 分子式 |
C15H13N1O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
255.27
|
|
| 精确质量 |
255.089
|
|
| CAS号 |
74103-06-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Ketorolac tromethamine salt;74103-07-4;(S)-Ketorolac;66635-92-5;(R)-Ketorolac;66635-93-6;Ketorolac-d5;1215767-66-0;Ketorolac hemicalcium;167105-81-9;Ketorolac-d4;1216451-53-4
|
|
| PubChem CID |
3826
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
493.2±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
160-161°C
|
|
| 闪点 |
252.1±27.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.659
|
|
| LogP |
2.08
|
|
| tPSA |
59.3
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
19
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
376
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
OZWKMVRBQXNZKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H13NO3/c17-14(10-4-2-1-3-5-10)13-7-6-12-11(15(18)19)8-9-16(12)13/h1-7,11H,8-9H2,(H,18,19)
|
|
| 化学名 |
5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9174 mL | 19.5871 mL | 39.1742 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7835 mL | 3.9174 mL | 7.8348 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3917 mL | 1.9587 mL | 3.9174 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Dosing of Ketorolac in the Emergency Department
CTID: NCT03464461
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Terminated
Date: 2024-11-05