| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Thyroid hormone receptors TRα and TRβ
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
添加海藻氨酸(T3,100 nM)后,过度表达 TRβ1 的妊娠细胞会增殖 [1]。人 β1 甲状腺激素受体 (hTRβ1) 的结构构象因石氨酸与其结合而改变。碘塞罗宁可以刺激循环、控制新陈代谢并促进生长[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
为了了解人类β1甲状腺激素受体(h-TRβ1)激素依赖性转录调控的结构基础,我们研究了3,3',5-三碘-L-甲状腺素(T3)结合诱导的h-TRβ-1的构象变化。h-TRβ1单独用胰蛋白酶处理或在T3、甲状腺激素反应元件(TRE)或T3与TRE一起存在的情况下处理。在没有T3的情况下,h-TRβ1被胰蛋白酶完全消化。TRE的结合对胰蛋白酶消化模式没有影响。然而,T3结合的h-TRβ1对胰蛋白酶消化产生了抗性,并产生了分子量为28000和24000的胰蛋白酶抗性肽片段。胰凝乳蛋白酶消化也产生了T3保护的24Kd肽片段。使用抗h-TRβ1抗体和氨基酸测序,28Kd片段被鉴定为Ser202-Asp456。发现24Kd胰蛋白酶片段为Lys239-Asp456和Phe240-Asp456。24Kd的糜蛋白酶片段被鉴定为Lys235-Asp456。T3结合导致的结构变化可以作为调节h-TRβ1基因调节活性的转导信号[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
为了了解甲状腺激素核受体(TRs)在肝癌发生中的作用,我们对9种人肝癌细胞系中的TRs进行了表征。TR蛋白的表达依赖于受体亚型和细胞类型。TRα1蛋白在九个细胞系中的每一个中都以低水平类似地表达。相比之下,TRβ1在分化较差的肝癌细胞中过表达。此外,发现甲状腺激素刺激TRβ1过表达的细胞增殖。这些结果表明,TRβ1最有可能参与肝癌细胞的分化和增殖。我们的研究为理解TR在肝癌发生中的作用提供了新的思路[1]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Thyroid hormones are well absorbed orally. From these hormones, liothyronine is almost completely absorbed and it does not present changes in the absorption rate due to concomitant administration of food.liothyronin Multiple administration of 50 mcg of liothyronine provided a maximal plasma concentration of total T3 of 346 ng/dL in about 2.5 hours with an AUC of 4740 ng.h/dL. The main elimination of thyroid hormones is known to be done via the kidneys from which less than 2.5% of the excreted drug is represented by the unchanged drug. This elimination route is reduced with age. A portion of the metabolic products of liothyronine is excreted to the bile and gut where they can be part of enterohepatic recirculation. The reported volume of distribution of liothyronine is reported to be of 0.1-0.2 L/kg. There are no reports obtaining this value specifically. WHILE TRIIODOTHYRONINE IS MUCH LESS FIRMLY BOUND /TO PROTEIN THAN IS THYROXINE/, THE QUANTITY THAT IS FREE IS STILL SMALL PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL. THE DAILY SECRETION OF /TRIIODOTHYRONINE/ IN NORMAL MAN IS APPROXIMATELY...25 UG. LIOTHYRONINE IS ERRATICALLY ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT, & 30 TO 40% MAY BE RECOVERED FROM STOOLS. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF THYROID HORMONES WERE MARKEDLY DIMINISHED AFTER INTESTINAL BYPASS SURGERY & RESTORED TO NORMAL AFTER REVERSAL OF SHUNT. Liothyronine sodium is almost completely absorbed from the GI tract (about 95%) following oral administration. /Liothyronine sodium/ Metabolism / Metabolites Liothyronine is mainly metabolized in the liver where it is deiodinated to diiodothyronine and monoiodothyronine followed by conjugation with glucuronides and sulfates. One of the formed metabolites formed by the conjugation and decarboxylation is tiratricol. The iodine released by the metabolism of liothyronine is later taken and used within the thyroid cells. THE LIVER CONJUGATES THYROXINE & TRIIODOTHYRONINE WITH GLUCURONIC & SULFURIC ACIDS THROUGH THE PHENOLIC HYDROXYL GROUP, & EXCRETES THESE CONJUGATES & SMALL AMT OF FREE COMPOUNDS IN THE BILE. Triiodothyronine has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[4-[4-[(2S)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl]-2,6-diiodophenoxy]-2-iodophenoxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. Half Life: 2.5 days Biological Half-Life The half-life of liothyronine is reported to be between 1 and 2 days. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The hormones, T4 and T3, are tyrosine-based hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Iodine is an important component in their synthesis. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4). This is converted to the more active liothyronine form by deiodinases in peripheral tissues. Liothyronine acts on the body to increase the basal metabolic rate, affect protein synthesis and increase the body's sensitivity to catecholamines (such as adrenaline). The thyroid hormones are essential to proper development and differentiation of all cells of the human body. To various extents T4 and T3 regulate protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism. Their most pronounced effect is on how human cells use energetic compounds. The thyroid hormone derivatives bind to the thyroid hormone receptors initially to initiate their downstream effects. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Liothyronine (T3) is a normal component of human milk. If replacement doses of liothyronine are required by the mother, it is not necessarily a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. However, because no information is available on the use of exogenous liothyronine during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred. The American Thyroid Association recommends that subclinical and overt hypothyroidism should be treated with levothyroxine in lactating women seeking to breastfeed. Liothyronine dosage requirement may be increased in the postpartum period compared to prepregnancy requirements patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. However, the thyroid hormone content of human milk from the mothers of very preterm infants appears not to be sufficient to affect the infant’s thyroid status. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Adequate thyroid hormone serum levels are required for normal lactation. Replacing deficient thyroid levels should improve milk production caused by hypothyroidism. Supraphysiologic doses of liothyronine would not be expected to further improve lactation. Protein Binding Liothyronine presents a very large binding to plasma proteins and around 99.7% of the administered dose can be found bound. Liothyronine is found to be bound to thyroxine-binding globulin, thyroxine-binding prealbumin and albumin. It is important to consider that only the little unbound portion of liothyronine is metabolically active. Interactions USE OF PROPRANOLOL IN CONJUNCTION WITH REPLACEMENT THERAPY HAS BEEN REPORTED TO DECR RISK OF ARRHYTHMIA & ANGINA... THYROID COMPOUNDS THAT PRODUCE HYPERMETABOLIC STATE (LIOTHYRONINE...) INCR RATE OF DECAY OF VITAMIN K-DEPENDENT CLOTTING FACTORS, & IN PRESENCE OF ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS /EG, WARFARIN/, NORMAL COMPENSATION BY INCR SYNTHESIS IS PREVENTED. THERE IS CONSIDERABLE CLINICAL EVIDENCE THAT A PATIENT'S THYROID STATE AFFECTS RESPONSE TO TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS. ADDITION OF LIOTHYRONINE (25 UG/DAY) MAY PREVENT RELATIVELY LONG LAG TIME THAT OCCURS BEFORE CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS OF TRICYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANTS IS OBSERVED. CHOLESTYRAMINE MAY CAUSE CLINICALLY SIGNIFICANT DECR IN ABSORPTION OF THYROID HORMONE WHEN THESE DRUGS ARE GIVEN SIMULTANEOUSLY. /THYROID HORMONE/ For more Interactions (Complete) data for LIOTHYRONINE (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
LIOTHYRONINE SODIUM...MAY BE USEFUL...WHEN HYPOTHYROIDISM HAS RECENTLY SUPERVENED FROM OVERTREATMENT WITH ANTITHYROID DRUG OR FOLLOWING TREATMENT WITH RADIOIODINE OR THYROIDECTOMY, & IN RARE EVENT OF COMA DUE TO MYXEDEMA. /LIOTHYRONINE SODIUM/ WITH THIS DOSE /EXPERIMENTAL DOSE OF 1 MG SC ADMIN/, A METABOLIC RATE OF MINUS 40% CAN BE RAISED TO NORMAL WITHIN 24 HR. MAXIMAL RESPONSE OCCURS IN 2 DAYS OR LESS. Triiodothyronine (liothyronine sodium) may be used occasionally when a quicker onset of action is desired as, for example, in the rare presentation of myexedema coma or for preparing a patient for (131)I therapy for treatment of thyroid cancer. MEDICATION (VET):: USED FOR...OBESITY, BILATERAL ALOPECIA, ACANTHOSIS, DRY SKIN, WRINKLED SKIN, POOR HAIR COLOR, STRAIGHTNESS IN CURLY HAIR COATS, LACK OF "WIRE" IN WIRE-HAIRED BREEDS, LETHARGY, SLOW GROWTH, UNTHRIFTINESS, LIBIDO LOSS, POOR BREEDING EFFICIENCY, URINARY INCONTINENCE, & LACK OF MENTAL & PHYSICAL VIGOR ESP IN OLDER ANIMALS. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for LIOTHYRONINE (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings VET: AVOID EXCESSIVE DOSAGE IN CASES WITH WEAK HEARTS. LIOTHYRONINE LABELED WITH EITHER (125)I OR (131)I...FOR IN VITRO EVALUATION OF THYROID FUNCTION. DUE TO HIGH SPECIFIC ACTIVITY REQUIRED, RADIATION DAMAGE CAN EASILY OCCUR. ... DOSE IS NOT FOR INTERNAL USE. IN ABSENCE OF HYPERTHYROIDISM, THYROID HORMONES DO NOT IMPROVE SKIN CONDITIONS, MENTAL DEPRESSION, FATIGUE, LETHARGY, IRRITABILITY, NERVOUSNESS, MENSTRUAL IRREGULARITIES, & OTHER ENDOCRINE & REPRODUCTIVE DISORDERS, & THERE IS DANGER THAT UNTOWARD EFFECTS MAY BE PRODUCED. ...THYROID HORMONES /EG, LIOTHYRONINE/ OR MIXTURES CONTAINING THEM SHOULD NOT BE USED WITHOUT SPECIFIC INDICATION OF DEFICIENCY. ...TO EFFECT WEIGHT LOSS IN EUTHYROID OBESE INDIVIDUALS...THYROID HORMONES OR PREPN CONTAINING THEM SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR THIS PURPOSE. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for LIOTHYRONINE (17 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics In hormonal replacement, liothyronine is more potent and present a faster action when compared to levothyroxine but the time of action is significantly shorter. The type of treatment needs to be well evaluated as the fast correction of thyroid hormones in certain diseases presents additional risks such as heart failure. The onset of activity is observed a few hours after administration and the maximum effect is observed after 2-3 days. Treatment with liothyronine has been shown to produce normal plasma levels of T3 hormone but to have no effect on the T4 plasma concentration. |
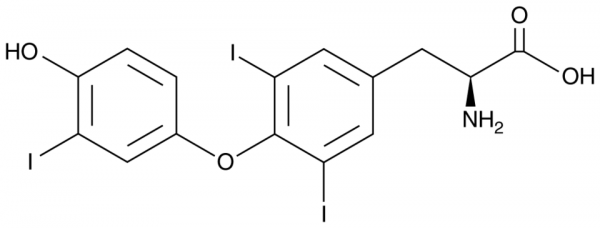
| 分子式 |
C15H12I3NO4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
650.9735
|
| 精确质量 |
650.79
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 27.68; H, 1.86; I, 58.48; N, 2.15; O, 9.83
|
| CAS号 |
6893-02-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Liothyronine sodium;55-06-1;Liothyronine-13C9,15N;1213569-04-0;Liothyronine-13C6-1;1213431-76-5;Liothyronine sodium hydrate;345957-19-9;Liothyronine hydrochloride;6138-47-2; 6138-47-2 (HCl); 6893-02-3 (free)
|
| PubChem CID |
5920
|
| 外观&性状 |
CRYSTALS
|
| 密度 |
2.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
563.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
234-238 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
294.6±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.763
|
| LogP |
5.08
|
| tPSA |
92.78
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
23
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
402
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
IC1C(=C(C([H])=C(C=1[H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C(=O)O[H])N([H])[H])I)OC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C(C=1[H])I)O[H]
|
| InChi Key |
AUYYCJSJGJYCDS-LBPRGKRZSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H12I3NO4/c16-9-6-8(1-2-13(9)20)23-14-10(17)3-7(4-11(14)18)5-12(19)15(21)22/h1-4,6,12,20H,5,19H2,(H,21,22)/t12-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-2-amino-3-[4-(4-hydroxy-3-iodophenoxy)-3,5-diiodophenyl]propanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
liothyronine; triiodothyronine; 3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine; 6893-02-3; Liothyronin; Tresitope; 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine; 3,5,3'-Triiodo-L-thyronine;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~76.81 mM)
1M NaOH : 50 mg/mL (~76.81 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5362 mL | 7.6808 mL | 15.3617 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3072 mL | 1.5362 mL | 3.0723 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1536 mL | 0.7681 mL | 1.5362 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。