| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
设计用于测量MPS1酶活性抑制的体外激酶测定法鉴定出三种得分最高的化合物:Mps-BAY1,一种三唑并吡啶,以及Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b,两种咪唑并吡嗪(补充图1)。这两类化合物都含有氢键供体/受体氮原子,这在与蛋白激酶的ATP口袋和相关铰链区结合的分子中很常见。Mps-BAY1Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b抑制人MPS1,IC50范围在1至10 nM之间(补充表1)。当以高浓度(10μM)使用时,Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b对220种人类激酶显示出有限的抑制作用,与广谱激酶抑制剂瑞香和蒽[1,9-cd]吡唑-6(2H)-酮(SP600125)相比(补充表2)。10,15值得注意的是,Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2 a和Mps-BAY2b未能抑制几种已知在有丝分裂中起作用的激酶。Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b以130nM的IC50抑制SAC的激活,分别为95 nM和670 nM,如在对300 nM诺考达唑有反应的HeLa细胞中评估组蛋白3(H3)磷酸化(在前期/中期发生的翻译后修饰)消失的测定中监测的(数据未显示)。因此,Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b被培养的细胞有效吸收,并能够达到其分子靶点。根据这一概念,所有这些MPS1抑制剂都降低了绝大多数原代和转化的人类和大鼠细胞的增殖,并对小鼠细胞产生了更高的抗增殖作用(补充表3)。Mps-BAY2a在一组人结肠癌细胞系中引起异质性抗增殖反应,敏感性(IC50)范围为160 nM至>10μM(补充表4)。值得注意的是,CIN和微卫星不稳定性(MIN)均与人类结直肠癌癌症细胞系对Mps-BAY2a的耐药性/敏感性无关(补充表4)。Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b对人结直肠癌HCT 116(图1和补充图2)和人宫颈癌HeLa细胞(补充图3和4)的细胞周期进展和存活有重大影响,这两种细胞对这些化合物特别敏感(补充表3)。因此,Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b诱导了细胞周期的剂量和时间依赖性扰动,表现为出现超倍体DNA含量(>4n)的细胞频率增加(图1a-c和补充图2和3),以及死亡细胞(即失去线粒体跨膜电位Δψm的细胞)和细胞尸体(质膜破裂)的逐渐积累(图1d和补充图4)。这些发现确定Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b是具有强效抗增殖和细胞毒性作用的新型MPS1抑制剂[1]。
Mps-BAY1和Mps-BAY2a[1] 诱导的细胞周期扰动特征 然后,我们研究了MPS1抑制剂对细胞周期进程的精确影响。在施用Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2a或Mps-BAY2b后,HCT 116细胞中掺入DNA前体5-乙炔基-2′-脱氧尿苷(EdU,仅在细胞周期的S期被吸收)的比例随着时间的推移而降低,尽管这种抑制作用在SP600125中更为明显(图2a)。值得注意的是,即使在暴露于MPS1抑制剂48小时后,仍有相当一部分细胞复制了它们的DNA。然后,我们对细胞周期蛋白E和B1的水平进行了深入的细胞荧光测定和(荧光)显微镜分析,这两种标记物分别在细胞周期的G1期和G2期积累。针对Mps-BAY1、Mps-BAY2a和Mps-BAY2b(标准剂量:1μM,分别为1μM和3μM),细胞周期蛋白B1+HCT 116细胞的频率降低,尽管这些影响不如SP600125介导的一致(图2b和c)。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
最后,研究人员评估了Mps-BAY2b联合紫杉醇在体内对免疫缺陷小鼠中生长的HeLa Matu宫颈癌的治疗潜力。研究人员使用Mps-BAY2b,因为它显示出比Mps-BAY1和Mps-BAY2a更高的体内稳定性(补充表5)。通过免疫组织化学测定,紫杉醇给药24小时后,HeLa Matu细胞衍生的异种移植物显示出比未治疗的肿瘤更高的磷酸化H3水平。经紫杉醇治疗的荷瘤小鼠短时间(1小时)暴露于Mps-BAY2b导致H3磷酸化减少(图8a)。这一发现表明,Mps-BAY2b在体内有效分布,到达异种移植肿瘤并穿透癌症细胞以抑制MPS1。在这种异种移植物模型中,Mps-BAY2b和紫杉醇的组合诱导了比单独干预更高水平的凋亡和更高的巨型单核细胞(核直径>25μm)发生率(图8b)。此外,与载体和紫杉醇或Mps-BAY2b单独给药相比,紫杉醇和Mps-BAY2b联合给药具有更优的抗肿瘤作用(图8c)。总之,这些数据强调了有利地将MPS1抑制剂与MT靶向剂结合的可能性[1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞荧光测定研究[1]
为了同时定量质膜完整性和Δψm,收集细胞并在37°C下用1μg/ml碘化丙啶和40 nM 3,3′-二己基氧杂碳菁碘化物(DiOC6)染色30分钟。为了评估细胞周期分布,收集细胞,用50μg/ml PI染色,并如前所述通过细胞荧光法进行分析。对于EdU掺入试验,根据制造商的说明,将细胞与10μM EdU在37°C下孵育30分钟,固定、渗透并用荧光染料叠氮化物和PI染色。为了同时测量DNA含量和细胞周期蛋白B1水平,将固定细胞与10 μM 4′,6-二脒基-2-苯基吲哚和先前报道的针对细胞周期蛋白B1的小鼠抗血清。在配备70μm喷嘴的FACSCalibur细胞荧光计或Gallios细胞荧光计上进行细胞荧光采集。 免疫荧光和视频显微镜[1] 根据常规程序进行免疫荧光显微镜检查。使用蔡司Axio Observer捕获58张图像。配备ApoTome系统的Z1显微镜。对于视频显微镜,稳定表达H2B-GFP嵌合体的HCT 116细胞在标准条件下在黑色/透明96孔成像板上生长,并用BD途径855自动活细胞显微镜进行脉冲观察(每13分钟一次,持续72小时)。使用开源软件ImageJ对图像进行分析。细胞命运曲线如前所述。 |
| 动物实验 |
For the quantification of circulating MPS1 inhibitors, Mps-Bay1, Mps-BAY2a and Mps-BAY2b were administered to female athymic nu/nu mice p.o. in a solubilized form (n=2 mice per compound and time point). Serum samples were prepared 1, 7 and 24 h after administration and precipitated with ice-cold 1 : 5 (v:v) acetonitrile/water. Supernatants were analyzed for Mps-BAY1, Mps-BAY2a and Mps-BAY2b content via liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectroscopy. For tumor xenograft studies, 50-day-old female athymic nu/nu mice with an average body weight of 20–22 g were used after an acclimation period of 14 days. Human HeLa-Matu cervical carcinoma cells derived from exponentially growing cultures were resuspended in 1 : 1 (v:v) FBS-free growth medium/Matrigel (BD Biosciences) to a final concentration of 1.5 × 107 cells/ml. Thereafter, 1.5 × 106 cells were subcutaneously implanted into the inguinal region. Tumor area (monitored with a common caliper and approximated to the product of the longest diameter by its perpendicular) and body weight were determined twice a week. When tumors reached an area of approximately 21 mm2, animals were randomized into the following groups (eight mice per group): control, receiving 3 : 1 (v:v) polyethylene glycol/water (vehicle) once a week p.o.; Mps-BAY2b, receiving 30 mg/kg Mps-BAY2b in 3 : 1 polyethylene glycol/water once a week p.o.; paclitaxel, receiving 10 mg/kg paclitaxel in 1 : 1 : 18 (v:v:v) cremophor/ethanol/PBS once a week i.v.; and Mps-BAY2b plus paclitaxel, receiving 30 mg/kg Mps-BAY2b in 3 : 1 polyethylene glycol/water p.o. plus 10 mg/kg paclitaxel in 1 : 1 : 18 cremophor/ethanol/PBS once a week i.v. When tumor area exceeded 150 mm2, animals were euthanized according to the German Animal Welfare Guidelines. For immunohistochemical studies, when tumors reached a size of 40–50 mm2, animals were randomized into the following groups (three mice per group): control, receiving 3 : 1 polyethylene glycol/water (vehicle) once p.o.; Mps-BAY2b, receiving 30 mg/kg Mps-BAY2b in 3 : 1 polyethylene glycol/water once p.o.; and paclitaxel, receiving 30 mg/kg paclitaxel in 1 : 1 : 18 cremophor/ethanol/PBS once i.p. For hematoxylin and eosin staining, when tumors reached a size of 50–80 mm2, animals were randomized into the following groups (four mice per group): control, receiving 3 : 1 polyethylene glycol/water (vehicle) twice daily for 2 days p.o.; Mps-BAY2b, receiving 30 mg/kg Mps-BAY2b in 3 : 1 polyethylene glycol/water twice daily for 2 days p.o.; paclitaxel, receiving 8 mg/kg paclitaxel in 1 : 1 : 18 cremophor/ethanol/PBS once i.v.; and Mps-BAY2b plus paclitaxel, receiving 30 mg/kg Mps-BAY2b in 3 : 1 polyethylene glycol/water twice daily for 2 days p.o. plus 10 mg/kg paclitaxel in 1 : 1 : 18 cremophor/ethanol/PBS i.v. once. Seventy-two hours after the first treatment, tumors were recovered, fixed with 4% (w/v) PFA for 4 h and embedded into paraffin. Ten-micrometer-thick tissue sections were then stained with hematoxylin and eosin according to standard protocols and analyzed as previously described.[1]
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1), a mitotic kinase that is overexpressed in several human cancers, contributes to the alignment of chromosomes to the metaphase plate as well as to the execution of the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). Here, we report the identification and functional characterization of three novel inhibitors of MPS1 of two independent structural classes, N-(4-{2-[(2-cyanophenyl)amino][1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyridin-6-yl}phenyl)-2-phenylacetamide (Mps-BAY1) (a triazolopyridine), N-cyclopropyl-4-{8-[(2-methylpropyl)amino]-6-(quinolin-5-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-yl}benzamide (Mps-BAY2a) and N-cyclopropyl-4-{8-(isobutylamino)imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-yl}benzamide (Mps-BAY2b) (two imidazopyrazines). By selectively inactivating MPS1, these small inhibitors can arrest the proliferation of cancer cells, causing their polyploidization and/or their demise. Cancer cells treated with Mps-BAY1 or Mps-BAY2a manifested multiple signs of mitotic perturbation including inefficient chromosomal congression during metaphase, unscheduled SAC inactivation and severe anaphase defects. Videomicroscopic cell fate profiling of histone 2B-green fluorescent protein-expressing cells revealed the capacity of MPS1 inhibitors to subvert the correct timing of mitosis as they induce a premature anaphase entry in the context of misaligned metaphase plates. Hence, in the presence of MPS1 inhibitors, cells either divided in a bipolar (but often asymmetric) manner or entered one or more rounds of abortive mitoses, generating gross aneuploidy and polyploidy, respectively. In both cases, cells ultimately succumbed to the mitotic catastrophe-induced activation of the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Of note, low doses of MPS1 inhibitors and paclitaxel (a microtubular poison) synergized at increasing the frequency of chromosome misalignments and missegregations in the context of SAC inactivation. This resulted in massive polyploidization followed by the activation of mitotic catastrophe. A synergistic interaction between paclitaxel and MPS1 inhibitors could also be demonstrated in vivo, as the combination of these agents efficiently reduced the growth of tumor xenografts and exerted superior antineoplastic effects compared with either compound employed alone. Altogether, these results suggest that MPS1 inhibitors may exert robust anticancer activity, either as standalone therapeutic interventions or combined with microtubule-targeting chemicals. [1]
Here, we reported the identification and functional characterization of three novel and potent MPS1 inhibitors, the triazolopyridine Mps-BAY1 and the imidazopyrazines Mps-BAY2a and Mps-BAY2b. All these agents were capable of abrogating the functionality of the SAC, as demonstrated by the incapacity of cells exposed to MPS1 inhibitors to sustain a mitotic arrest upon exposure to MT poisons. Even in the absence of SAC activators, both classes of MPS1 inhibitors markedly increased the rate of chromosome misalignments resulting from erroneous MT–KT attachments and promoted a premature anaphase entry (i.e., before the formation of a correct equatorial metaphase plate). These results are in line with previous findings obtained with other MPS1-specific inhibitors, upon MPS1 depletion1 or following the conditional knockout of TTK,11 confirming the central implication of this mitotic kinase in SAC function and chromosome congression. [1] |
| 分子式 |
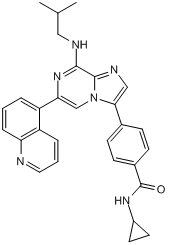
C29H28N6O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
476.58
|
| 精确质量 |
476.232
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 73.09; H, 5.92; N, 17.63; O, 3.36
|
| CAS号 |
1382477-96-4
|
| PubChem CID |
57381882
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 折射率 |
1.716
|
| LogP |
5.34
|
| tPSA |
84.2
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
36
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
750
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
MDYKTGNHXNTATG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C29H28N6O/c1-18(2)15-31-27-28-32-16-26(19-8-10-20(11-9-19)29(36)33-21-12-13-21)35(28)17-25(34-27)23-5-3-7-24-22(23)6-4-14-30-24/h3-11,14,16-18,21H,12-13,15H2,1-2H3,(H,31,34)(H,33,36)
|
| 化学名 |
N-cyclopropyl-4-[8-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-quinolin-5-ylimidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-yl]benzamide
|
| 别名 |
Mps BAY 2a; Mps-BAY-2a; 1382477-96-4; CHEMBL3422104; N-cyclopropyl-4-[8-(2-methylpropylamino)-6-quinolin-5-ylimidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-yl]benzamide; N-Cyclopropyl-4-[8-[(2-methylpropyl)amino]-6-(5-quinolinyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-yl]benzamide; MpsBAY2a
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~10 mg/mL (~20.98 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0983 mL | 10.4914 mL | 20.9828 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4197 mL | 2.0983 mL | 4.1966 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2098 mL | 1.0491 mL | 2.0983 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。