| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
AMPA receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
虽然 NBQX 二钠 (FG9202 二钠) 对 NMDA 受体复合物上的谷氨酸识别位点几乎没有亲和力,但它对 AMPA 和红藻氨酸结合位点具有显着的亲和力 [1]。
海马体是一个重要的大脑区域,与阿尔茨海默病、精神分裂症和癫痫等神经系统疾病有关。众所周知,嗜离子性谷氨酸受体,即n -甲基- d -天冬氨酸(NMDA)受体(NMDARs)、α-氨基-3-羟基-5-甲基-4-异恶唑丙酸(AMPA)受体(AMPARs)和kainic酸(KA)受体(KARs)通过介导长期增强、兴奋毒性或两者兼有参与这些疾病。为了预测作用于这些受体的候选药物的治疗效果和神经元毒性,分析脑区域特异性人类神经细胞的生理相关系统是必要的。在这里,我们表征了人类胎儿海马来源的神经干/祖细胞-即HIP-009细胞的功能分化。钙升高实验表明,分化4周后,细胞对NMDA有反应(EC50= 7.5±0.4µM;n= 4), AMPA (EC50= 2.5±0.1µM;n= 3),或KA (EC50= 33.5±1.1µM;N = 3),呈浓度依赖性。在没有脱敏抑制剂环噻嗪的情况下,观察到ampa诱发的钙升高。此外,这些激动剂诱导的钙升高被每种受体的拮抗剂所抑制,即NMDA刺激的MK-801 (IC50= 0.6±0.1µM;n= 4)和NBQX对AMPA和KA刺激(IC50分别为0.7±0.1和0.7±0.03µM);n= 3)。分化的HIP-009细胞的基因表达谱与未分化的细胞不同,与成人海马的基因表达谱非常相似。我们的研究结果表明,HIP-009细胞是获得人类海马神经细胞的独特工具,并且作为一种生理相关的体外模型,适用于测定嗜离子性谷氨酸受体的系统。[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
NBQX 二钠(FG9202;20 mg/kg,腹腔注射;持续 3 天)可减轻 PTZ 诱发的癫痫发作[2]。当 MCA 阻断时和一小时后再次静脉推注 30 mg/kg 剂量时,NBQX 二钠在局部缺血大鼠模型中发挥神经保护作用 [1]。
癫痫是一种严重的脑部疾病,具有多种发作类型和癫痫综合征。AMPA受体拮抗剂2,3-二羟基-6-硝基-7-磺胺酰基-苯醌-2,3-二酮(NBQX)减轻大鼠自发性复发性癫痫发作。然而,NBQX在慢性癫痫模型中的抗癫痫作用尚不清楚。神经周围网络(PNNs)是一种特殊的细胞外基质结构,围绕着小蛋白阳性抑制性中间神经元,在神经元细胞发育和突触可塑性中起着关键作用。在这里,我们关注的是pnn在NBQX治疗癫痫中的潜在参与。大鼠连续28天腹腔注射戊四唑(PTZ, 50 mg/kg),建立慢性癫痫模型。随后注射NBQX (20 mg/kg, ig) 3 d,观察癫痫行为指标。采用免疫组织化学染色法检测紫藤凝集素(WFA)标记的pnn。Western blot法检测PNNs三组分tenascin-R、aggrecan、neurocan的表达水平。结果显示,注射PTZ后大鼠内侧前额叶皮层(mPFC)的PNNs减少,tenascin-R、aggrecan和neurocan减少。然而,NBQX治疗使pnn、tenascin-R、aggrecan和neurocan水平正常化。NBQX足以通过增加癫痫发作潜伏期、缩短癫痫发作持续时间和降低癫痫发作严重程度评分来减少癫痫发作。此外,软骨素酶ABC (ChABC)降解mPFC pnn加重了ptz治疗大鼠的癫痫发作。最后,将ChABC预处理成mPFC后,NBQX的抗癫痫作用被逆转。这些发现表明,pnn在mPFC中的降解参与了癫痫的病理生理,增强pnn可能对癫痫的治疗有效。[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
荧光法测定钙含量[1]
将在Neural Differentiation Medium中培养3 d的HIP-009细胞,以3.7 × 104个细胞/孔的速率,在黑壁、清底、涂有pdl的96孔板上,培养4周后分化为神经细胞。未分化的HIP-009细胞以6.4 × 103个细胞/孔的速度在StemCell Growth Medium中接种于相同类型的96孔板(也手工涂有层粘连蛋白),培养至80%至100%的融合。在检测当天,除去培养基,将细胞加载钙4染料(用于谷氨酸浓度依赖性检测)或钙5染料(用于其他检测),并在37°C的检测缓冲液中重构probenecid (2.5 mM) 1 h。实验缓冲液的组成如下:20 mM HEPES和不含酚红的含钙镁的Hank平衡盐溶液(NaOH将pH调至7.4)用于谷氨酸浓度依赖性实验;137 mM NaCl、4 mM KCl、1.8 mM CaCl2、10 mM HEPES和10 mM d -葡萄糖(NaOH调节pH至7.4)用于NMDARs和MK-801和NBQX的共处理试验;和140 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 3 mM CaCl2, 2 mM MgCl2, 10 mM HEPES, 24 mM D-glucose和10µM MK-801 (pH调节到7.4与NaOH)用于ampar和KARs。化合物在测定缓冲液中稀释,并转移到化合物板上。孵育1小时后,除谷氨酸浓度依赖性实验外,细胞洗涤两次,并用实验缓冲液替换。在谷氨酸浓度依赖性测定的情况下,洗涤步骤被跳过。用功能药物筛选系统6000测量钙的升高,同时监测板上每孔的荧光变化。添加复合溶液前记录基线12 s,每0.3 s间隔记录一次,共记录1.75 min(激发波长480 nm;发射光谱,540 nm)。
|
| 细胞实验 |
电生理学[1]
为了进行电生理记录,将HIP-009细胞接种在涂有层粘连蛋白和PDL的玻璃罩上。分化4周后,使用全细胞膜片钳记录技术对细胞进行表征。信号在3khz低通滤波,并通过使用Digidata 1322A接口在20khz采样。采用pCLAMP 10.2软件进行数据记录和分析。胞外溶液中含有140 mM NaCl、5 mM KCl、1 mM CaCl2、1 mM MgCl2、10 mM HEPES和24 mM d -葡萄糖(NaOH调节pH至7.4)。细胞内溶液含有130 mM KCl、1 mM EGTA、1 mM MgCl2、5 mM HEPES和5 mM Na2-ATP (pH随KOH调节至7.2)。采用PB-7吸液器制备硼硅酸盐玻璃毛细管贴片微移液器。使用Axopatch 200B放大器进行电流箝位和电压箝位记录。对于电流钳记录,电流脉冲通过贴片电极注入分化的HIP-009细胞,从−10 pA到+100 pA的步进增加10 pA。对于电压钳记录,细胞在−100 mV保持电位下从−80 mV到+80 mV进行20 mV步进去极化。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Wistar rats, body weight 220-240 g, Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) [2]
Doses: 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; 3 days Experimental Results: Effective reversal of chronic PTZ administration in rats (50 mg/kg; intraperitoneal; for 28 days) causing seizures and behavioral abnormalities. NBQX was freshly dissolved in saline as sodium salt. ChABC were dissolved in 0.1 m PBS (vehicle) for microinjection into the medial prefrontal cortex and prepared in stock solutions of 0.02 U/μl.To observe anti-epileptic effects of NBQX in PTZ induced epilepsy, we divided rats into four groups: rats in saline + saline group were treated with saline only; rats in PTZ + saline group were treated with 50 mg/kg of PTZ (i.p.) and saline for 28 days; rats in saline + NBQX group were treated with saline for 28 days, and 20 mg/kg of NBQX (i.p.) for next 3 days; rats in PTZ + NBQX group were treated with 50 mg/kg of PTZ (i.p.) for 28 days and were treated with 20 mg/kg of NBQX (i.p.) for next 3 days. Behavioral tests and neurochemical analysis were performed on the following 2 days (Fig 2A). The doses for PTZ and NBQX were selected regarding to previous studies.[2] To determine whether PNNs degradation by ChABC can reverse the anti-epileptic effect of NBQX, we injected rats with PTZ for 28 days and separated them into four groups: rats in vehicle group were treated with vehicle without NBQX, and were microinjected with penicillinase into mPFC on d 24; rats in vehicle + ChABC group were treated with vehicle plus microinjection of ChABC into mPFC on d24; rats in NBQX + penicillinase group were treated with penicillinase on d24 and were treated with NBQX injection on d 29 to d31; rats in NBQX + ChABC group were treated with microinjection of ChABC into mPFC on d24 plus NBQX (20 mg/kg, i.p.) on d 29 to d31. Behavioral tests were performed on day 32.[2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
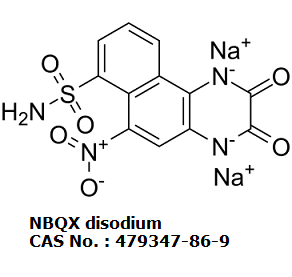
2,3-Dioxo-6-nitro-7-sulfamoylbenzo(f)quinoxaline is a member of naphthalenes and a sulfonic acid derivative.
A recent investigation suggested that chondroitin sulfate-degrading enzyme ChABC enhanced the lateral mobility of the AMPA receptor, and consequently promote short-term synaptic plasticity. ChABC may degrade various PNNs components, and consequently destroy the PNNs structure. In the current study, pretreatment with ChABC blocked the anti-epileptic effects of NBQX in PTZ-induced seizures, suggesting that normalization of PNNs in mPFC might underlie the therapeutic action of AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX. Further study is needed to evaluate the effect of upregulation of PNNs in the mPFC on the epilepsy induced by PTZ and on the treatment benefits of NBQX. The finding that the fast movements of AMPA receptors are involved in the modulation of synaptic transmission suggests that AMPAR mobility regulates the availability of naive receptors for synapses. Previous studies showed that removal of the PNNs leads to an increase of AMPAR exchange between extrasynaptic and synaptic sites, and may modulate synaptic properties. Our results revealed that chronic epilepsy induced a reduction of components of PNNs, tenascin-R, aggrecan and neurocan in mPFC, while AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX increased the levels of these proteins, suggesting that PNNs might be essential for the functionality of synaptic transmission. Thus, future studies targeting at PNNs can shed light on development of novel antiepileptic drugs with good efficacy and acceptable tolerability for therapy in epilepsy.[2] In addition, we investigated the contribution of each receptor to the calcium rise upon glutamate stimulation by co-treatment with MK-801 and NBQX. We estimated that ~45% of the total glutamate-evoked calcium rise was through NMDARs, and ~34% of the rise was through AMPARs and KARs. The remaining activity level of about 20% implied that there was a contribution from other glutamate receptors—that is, metabotropic glutamate receptors—although there would also be a contribution from residual KARs that were not inhibited completely by 30 µM NBQX.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C12H7N4NAO6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
380.24384
|
| 精确质量 |
379.98
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 37.91; H, 1.59; N, 14.73; Na, 12.09; O, 25.25; S, 8.43
|
| CAS号 |
479347-86-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
NBQX;118876-58-7
|
| PubChem CID |
6098006
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as Brown to dark brown solid at room temperature
|
| LogP |
3.93
|
| tPSA |
186.26
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
575
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1=CC2=C3C(=CC(=C2C(=C1)S(=O)(=O)N)[N+](=O)[O-])N=C(C(=N3)[O-])[O-].[Na+].[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
XFHCQLPOJLVQQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H8N4O6S.2Na/c13-23(21,22)8-3-1-2-5-9(8)7(16(19)20)4-6-10(5)15-12(18)11(17)14-6/h1-4H,(H4,13,14,15,17,18,21,22)/q2*+1/p-2
|
| 化学名 |
sodium 6-nitro-2,3-dioxo-7-sulfamoyl-2,3-dihydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-1,4-diide
|
| 别名 |
NBQX disodium; FG9202; FG-9202; NBQX disodium salt; NBQX disodium; 479347-86-9; NBQX (disodium); FSU8N86V27; 11876-58-7; FG 9202 disodium;FG9202 disodium;FG-9202 disodium; Benzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-nitro-2,3-dioxo-, sodium salt (1:2); FG 9202
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6299 mL | 13.1496 mL | 26.2992 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5260 mL | 2.6299 mL | 5.2598 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2630 mL | 1.3150 mL | 2.6299 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。