| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:奈比洛尔对兔肺膜制剂中的 β1-肾上腺素能受体位点表现出高亲和力和选择性(Ki 值 = 0.9 nM,β2/β1 比率 = 50)。在存在 CGP 207.12 A(300 nM,Kiβ2)或 ICI 118.551(50 nM,Kiβ1)的情况下,奈必洛尔表现出 β1-肾上腺素受体选择性,通过与 3H-CGP 12.1777 的竞争实验判断,Ki(β2)/Ki(β1) 值为 40.7 )。奈必洛尔以浓度和时间依赖性方式减少人冠状动脉平滑肌细胞 (haCSMC) 和内皮细胞 (haEC) 的细胞增殖。奈比洛尔治疗 7 天导致 haCSMC 细胞生长显着减少,IC50 为 6.1 μM,并抑制生长因子 PDGF-BB、bFGF 和 TGFβ 刺激的加速 haCSMC 增殖,IC50 值分别为 6.8 μM、6.4 μM 和 7.7 μM 。奈必洛尔 (10-5 M) 对 haCSMC 处理 48 小时,诱导 23% 的中度细胞凋亡,S 期细胞数量从 16% 减少至 5%。奈必洛尔孵育期间,HaCEs 的 NO 形成增加,而内皮素-1 转录和分泌受到抑制。细胞测定:将细胞[人冠状平滑肌细胞(haCSMC)和内皮细胞(haEC)]暴露于不同浓度的奈必洛尔(10-7~10-5 M)中1、2、4、7和14天。通过溴脱氧尿苷 (BrdU) 掺入分析细胞增殖,并通过 PI 或膜联蛋白 V 染色检测细胞凋亡。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
对心肌梗塞 (MI) 大鼠给予奈必洛尔(首先在再灌注 10 分钟内静脉注射,然后口服)可减少心肌细胞凋亡,这是由 NO 调节介导的。奈必洛尔可显着防止左心室 (LV) 压力变化,减少心肌细胞总数和局部凋亡。奈必洛尔治疗可轻微降低心肌梗死大鼠的平均血压(MBP),但不显着。
|
||
| 细胞实验 |
将奈比洛尔 (10-7~10-5 M) 以不同浓度添加到人冠状平滑肌细胞 (haCSMC) 和内皮细胞 (haEC) 中,持续 1、2、4、7 和 14 天。溴脱氧尿苷 (BrdU) 掺入用于分析细胞增殖,而 PI 或膜联蛋白 V 染色用于识别细胞凋亡。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The absorption of nebivolol is not affected by food. Nebivolol has a Tmax of 1.5-4 hours. Bioavailability can range from 12-96% for extensive to poor CYP2D6 metabolizers. For a 20mg dose, d-nebivolol has a Cmax of 2.75±1.55ng/mL, l-nebivolol has a Cmax of 5.29±2.06ng/mL, both enantiomers have a Cmax of 8.02±3.47ng/mL, and nebivolol glucuronides have a Cmax of 68.34±44.68ng/mL. For a 20mg dose, d-nebivolol has an AUC of 13.78±15.27ng\*h/mL, l-nebivolol has an AUC of 27.72±15.32ng\*h/mL, both enantiomers have an AUC of 41.50±29.76ng\*h/mL, and nebivolol glucuronides have an AUC of 396.78±297.94ng\*h/mL. In extensive CYP2D6 metabolizers, 38% is eliminated in the urine and 44% in the feces. In poor CYP2D6 metabolizers, 67% is eliminated in the urine and 13% in the feces. <1% of a dose is excreted as the unmetabolized drug. For a 20mg dose, d-nebivolol has an apparent volume of distribution of 10,290.81±3911.72L, l-nebivolol has an apparent volume of distribution of 8,066.66±4,055.50L, and both enantiomers together have a volume of distribution of 10,423.42±6796.50L. For a 20mg dose, the clearance of d-nebivolol is 1241.63±749.77L/h, l-nebivolol is 435.53±180.93L/h, and both enantiomers is 635.31±300.25L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Nebivolol is metabolized mainly by glucuronidation and CYP2D6 mediated hydroxylation. Metabolism involves n-dealkylation, hydroxylation, oxidation, and glucuronidation. Aromatic hydroxyl and acyclic oxide metabolites are active, while n-dealkylated and glucuronides are inactive. Biological Half-Life d-nebivolol has a half life of 12 hours in CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers and 19 hours in poor metabolizers. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Mild-to-moderate elevations in serum aminotransferase levels occur in less than 2% of patients on beta-blockers and are usually transient and asymptomatic, resolving even with continuation of therapy. There is no information on the rates of ALT elevations during nebivolol therapy. Despite its use in several large clinical trials, nebivolol has not been linked to cases of clinically apparent liver injury. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because no information is available on the use of nebivolol during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Nebivolol is 98% bound to plasma proteins, mostly to serum albumin. |
||
| 参考文献 | |||
| 其他信息 |
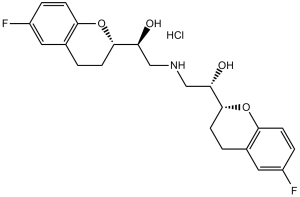
2,2'-iminobis[1-(6-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl)ethanol] is a member of the class of chromanes that is 2,2'-iminodiethanol in which one hydrogen attached to each hydroxy-bearing carbon is replaced by a 6-fluorochroman-2-yl group. It is an organofluorine compound, a secondary amino compound, a secondary alcohol, a diol and a member of chromanes.
Nebivolol is a racemic mixture of 2 enantiomers where one is a beta adrenergic antagonist and the other acts as a cardiac stimulant without beta adrenergic activity. Treatment with nebivolol leads to a greater decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure than [atenolol], [propranolol], or [pindolol]. Nebivolol and other beta blockers are generally not first line therapies as many patients are first treated with thiazide diuretics. Nebivolol was granted FDA approval on 17 December 2007. Nebivolol is a beta-blocker and antihypertensive medication that has additional vasodilatory activity mediated by nitric oxide release. Nebivolol has yet to be linked to instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Nebivolol is a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist with antihypertensive and vasodilatory activity. Nebivolol binds to and blocks the beta-1 adrenergic receptors in the heart, thereby decreasing cardiac contractility and rate. This leads to a reduction in cardiac output and lowers blood pressure. In addition, nebivolol potentiates nitric oxide (NO), thereby relaxing vascular smooth muscle and exerting a vasodilatory effect. A cardioselective ADRENERGIC BETA-1 RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST (beta-blocker) that functions as a VASODILATOR through the endothelial L-arginine/ NITRIC OXIDE system. It is used to manage HYPERTENSION and chronic HEART FAILURE in elderly patients. See also: Nebivolol Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Nebivolol is indicated to treat hypertension. Mechanism of Action Nebivolol is a highly selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist with weak beta-2 adrenergic receptor antagonist activity. Blocking beta-1 adrenergic receptors by d-nebivolol leads to decreased resting heart rate, exercise heart rate, myocardial contracility, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure. The selectivity of d-nebivolol limits the magnitude of beta blocker adverse effects in the airways or relating to insulin sensitivity. Nebivolol also inhibits aldosterone, and beta-1 antagonism in the juxtaglomerular apparatus also inhibits the release of renin. Decreased aldosterone leads to decreased blood volume, and decreased renin leads to reduced vasoconstriction. l-nebivolol is responsible for beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonist activity that stimulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase, increasing nitric oxide levels; leading to vasodilation, decreased peripheral vascular resistance, increased stroke volume, ejection fraction, and cardiac output. The vasodilation, reduced oxidative stress, and reduced platelet volume and aggregation of nebivolol may lead to benefits in heart failure patients. Pharmacodynamics Nebivolol is a selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist that decreases vascular resistance, increases stroke volume and cardiac output, and does not negatively affect left ventricular function. It has a long duration of action as effects can be seen 48 hours after stopping the medication and a wide therapeutic window as patients generally take 5-40mg daily. Patients should not abruptly stop taking this medication as this may lead to exacerbation of coronary artery disease. Diabetic patients should monitor their blood glucose levels as beta blockers may mask signs of hypoglycemia. |
| 分子式 |
C22H26CLF2NO4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
441.9
|
|
| 精确质量 |
405.175
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 65.17; H, 6.22; F, 9.37; N, 3.45; O, 15.78
|
|
| CAS号 |
118457-14-0
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Nebivolol hydrochloride; 152520-56-4; (Rac)-Nebivolol; 99200-09-6; (rac)-Nebivolol-d4; 1219407-55-2
|
|
| PubChem CID |
71301
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
600.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
223.0-228.0
|
|
| 闪点 |
316.9±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.581
|
|
| LogP |
3.67
|
|
| tPSA |
100.62
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
483
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
FC1=CC=C2C(CC[C@]([C@@H](O)CNC[C@H](O)[C@@]3([H])CCC(C=C(F)C=C4)=C4O3)([H])O2)=C1
|
|
| InChi Key |
KOHIRBRYDXPAMZ-YHDSQAASSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H25F2NO4/c23-15-3-7-19-13(9-15)1-5-21(28-19)17(26)11-25-12-18(27)22-6-2-14-10-16(24)4-8-20(14)29-22/h3-4,7-10,17-18,21-22,25-27H,1-2,5-6,11-12H2/t17-,18-,21-,22+/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(1S)-1-[(2S)-6-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl]-2-[[(2S)-2-[(2R)-6-fluoro-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl]-2-hydroxyethyl]amino]ethanol
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2630 mL | 11.3148 mL | 22.6296 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4526 mL | 2.2630 mL | 4.5259 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2263 mL | 1.1315 mL | 2.2630 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Determination of Drug Levels for Pharmacotherapy of Heart Failure
CTID: NCT06035978
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Not yet recruiting
Date: 2024-01-18
 |
|---|
 |
 |