| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
MELK (IC50 = 0.41 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
OTSSP167 阻断 MELK 过表达的癌细胞 A549、T47D、DU4475 和 22Rv1,IC50 值分别为 6.7、4.3、2.3 和 6.0 nM。 OTSSP167 阻止两种新型 MELK 底物 PSMA1(蛋白酶体 α 亚基 1 型)和 DBNL(类 Drebrin)的磷酸化,这两种底物对于干细胞特性和侵袭性至关重要。通过抑制 PSMA1 磷酸化,OTSSP167 可以防止乳腺癌细胞形成乳腺球。 [1]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在小鼠体内使用乳腺癌、肺癌、前列腺癌和胰腺癌细胞系进行的异种移植研究中,通过静脉内和口服给药,OTSSP167 表现出显着的肿瘤生长抑制作用。 OTSSP167以20mg/kg的剂量每两天一次静脉注射至MDA-MB-231模型,TGI为73%。每日一次口服剂量 10 mg/kg 时,TGI 为 72%。 OTSSP167 以剂量和 MELK 依赖性方式治疗各种癌症类型,且体重几乎没有减轻。 [1]
OTSSP167在异种移植小鼠模型中的生长抑制作用[1] 随后,我们通过使用MDA-MB-231细胞(MELK-阳性、三阴性乳腺癌症细胞)的异种移植模型研究了OTSSP167的体内抗肿瘤作用。在肿瘤大小达到约100mm3后,将该化合物给予携带异种移植物的小鼠14天。肿瘤大小被测量为药物反应的替代标志物(肿瘤生长抑制(TGI))。每两天静脉注射一次20mg/kg的OTSSP167,TGI为73%(图3A)。由于该化合物的生物利用度预计非常高(数据未显示),我们尝试口服该化合物。口服10mg/kg,每天一次,TGI为72%(图3B)。由于对各种癌症细胞系具有强烈的生长抑制作用,我们使用其他类型的癌症细胞系进一步研究了体内生长抑制效应,并发现OTSSP167以剂量依赖的方式对多种癌症类型显着抑制肿瘤生长,没有或有少量体重损失(图3和补充图S1)。例如,携带A549(肺癌)异种移植物的小鼠通过静脉内施用1、5和10 mg/kg OTSSP167每天一次治疗,其TGI分别为51%、91%和108%(图3C),而通过口服施用5和10 mg/kg每天一次的小鼠显示TGI分别为95%和124%(图3D)。此外,我们通过每天一次口服10 mg/kg检查了DU145(癌症)和MIAPaCa-2(癌症)异种移植物模型,并观察到TGI分别为106和87%(图3E和F)。为了进一步验证MELK特异性体内肿瘤抑制作用,我们检测了几乎无法检测到MELK表达的PC-14肺癌细胞(图3G)。口服10mg/kg OTSSP167,每天一次,持续14天,对PC-14异种移植物没有肿瘤生长抑制作用(图3H),进一步支持了OTSSP177的MELK依赖性抗肿瘤活性。 OTSSP16治疗在临床前GC患者衍生的异种移植物(PDX)小鼠模型中的疗效[2] 从我们建立的数据库中选择了两个MELK阳性和一个MELK阴性的GC-PDX模型,以评估MELK是否是GC体内的有效治疗靶点(图6A、6B和6C)。本实验使用第三代PDX小鼠。当肿瘤移植物体积达到100-200mm3时,PDX小鼠每隔一天静脉注射一次OTSSP167(15mg/kg)或赋形剂,持续两周。通过肿瘤生长抑制(TGI)定量对OTSSP167的反应。在两种MELK阳性模型中,给药结束时TGI值分别为106%和112%(图6D和6E,右图)。在MELK负模型中,TGI值仅为19%(图6F,右图)。随后通过IHC评估肿瘤移植物组织中的MELK表达水平。在这两种MELK阳性病例中,OTSSP167治疗后,肿瘤移植物中的MELK表达被消除,但载体治疗后没有消除(图6D和6E,中间图)。这些数据有力地表明MELK可能是治疗癌症的有效分子靶点。 |
| 酶活实验 |
将 MELK 重组蛋白 (0.4 μg) 与 5 μg 每种底物在 20 μL 激酶缓冲液中混合,该缓冲液含有 30 mM Tris-HCl (pH)、10 mM DTT、40 mM NaF、10 mM MgCl2、0.1 mM EGTA,50 μM 冷溶液-ATP 和 10 Ci 的 [γ-32P]ATP 在 30 °C 下持续 30 分钟。在 SDS-PAGE 之前,通过添加 SDS 样品缓冲液并煮沸 5 分钟来终止反应。在室温下,将凝胶干燥并用增感屏进行放射自显影。孵育前,将 DMSO 溶解的 OTSSP167(终浓度 10 nM)添加到激酶缓冲液中。
用于底物筛选的重组蛋白和体外激酶测定[1] 如前所述生成MELK重组蛋白。通过RT-PCR扩增每种MELK底物候选物的完整编码序列,并将其克隆到pGEX6p-1载体中。GST标记的重组蛋白在BL21密码子加RIL感受态细胞中表达,并根据供应商的说明使用谷胱甘肽琼脂糖4B珠纯化。根据供应商的说明,PreScission蛋白酶去除了GST标签。对于体外激酶测定,将MELK重组蛋白(0.4μg)与5μg每种底物在20μl激酶缓冲液中混合,该缓冲液含有30 mM Tris-HCl(pH)、10 mM DTT、40 mM NaF、10 mM MgCl2、0.1 mM EGTA、50μM冷ATP和10 Ci[γ-32P]ATP,在30°C下混合30分钟。通过加入SDS样品缓冲液终止反应,并在SDS-PAGE之前煮沸5分钟。将凝胶干燥,并在室温下用增感屏进行放射自显影OTSSP167(终浓度为10nM)溶解在DMSO中,并在孵育前加入激酶缓冲液。 体外激酶测定[3] 激酶作为从大肠杆菌纯化的重组蛋白或从有丝分裂细胞裂解物中纯化的免疫沉淀物提供。对于IP激酶测定,免疫沉淀物用补充有蛋白酶抑制剂(蛋白酶抑制剂鸡尾酒组III,不含EDTA)和磷酸酶抑制剂(100 mM NaF,1mM Na3VO4,60 mMβ-甘油磷酸)的细胞裂解缓冲液(1×PBS,10%甘油,0.5%NP-40)洗涤两次,用1×激酶缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.5,60mMß-甘油磷酸,10mM MgCl2)洗涤两遍。髓鞘碱性蛋白购自Sigma,组蛋白H3.3和H10购自新英格兰实验室作为底物。对于激酶反应,将4μl的5×激酶缓冲液与重组或免疫沉淀的激酶、底物、5μCi 32P-ATP或冷ATP混合。加入H2O,使最终体积为20μl。反应在30°C下孵育30分钟,然后加入20μl 2×SDS样品缓冲液终止。样品经过SDS-PAGE,然后转移到PVDF膜上。通过放射自显影或磷酸特异性抗体观察底物的磷酸化。 |
| 细胞实验 |
使用 Cell Counting Kit-8 通过比色测定来测量体外细胞活力。将细胞以 100 μL 的密度接种在 96 孔板中,以产生持续线性生长(A549,1×103 个细胞;T47D,3×103 个细胞;DU4475,4×103 个细胞;22Rv1,6×103 个细胞;和 HT1197) ,2×103 个细胞,每孔 100 μL)。让细胞粘附过夜,然后在 37°C 下暴露于 OTSSP167 72 小时。在 450 nm 波长下,分光光度计读取板的读数。每个测定进行三个副本。
|
| 动物实验 |
Injections of MDA-MB-231 cells are made into NOD's mammary fat pads.Mice CB17-Prkdcscid/J. Female BALB/cSLC-nu/nu mice are subcutaneously injected with 1 105 A549), MIAPaCa-2, and PC-14 cells. Male BALB/cSLC-nu/nu mice receive a subcutaneous injection of DU145 cells in the left flank. Animals are randomized into groups of 6 mice (apart from PC-14, for which groups of 3 mice are used) when MDA-MB-231, A549, DU145, MIAPaCa-2, and PC-14 xenografts have reached average volumes of 100, 210, 110, 250, and 250 mm3, respectively. OTSSP167 and other substances are prepared for oral administration in a vehicle containing 0.5% methylcellulose and administered orally according to the prescribed dose and schedule. Compounds are prepared in 5% glucose for intravenous administration and injected into the tail vein. For both administration routes, a volume of 10 mL per kg of body weight is used. Every other day, tumor volumes are measured using a caliper.
MDA-MB-231 cells were injected into the mammary fat pads of NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid/J mice. A549, MIAPaCa-2 and PC-14 cells (1 × 107 cells) were injected subcutaneously in the left flank of female BALB/cSLC-nu/nu mice. DU145 cells were injected subcutaneously in the left flank of male BALB/cSLC-nu/nu mice. When MDA-MB-231, A549, DU145, MIAPaCa-2, and PC-14 xenografts had reached an average volume of 100, 210, 110, 250, and 250 mm3, respectively, animals were randomized into groups of 6 mice (except for PC-14, for which groups of 3 mice were used). For oral administration, compounds such as /OTSSP167 were prepared in a vehicle of 0.5% methylcellulose and given by oral garbage at the indicated dose and schedule. For intravenous administration, compounds were formulated in 5% glucose and injected into the tail vein. An administration volume of 10 ml per kg of body weight was used for both administration routes. Concentrations were indicated in main text and Figures. Tumor volumes were determined every other day using a caliper. The results were converted to tumor volume (mm3) by the formula length × width2 × 1/2. The weight of the mice was determined as an indicator of tolerability on the same days. The animal experiments using A549 xenografts were conducted by a CRO company in accordance with their Institutional Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The other animal experiments were conducted at a CRO company. in accordance with their Institutional Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was calculated according to the formula {1 – (T – T0) / (C – C0)}×100, where T and T0 are the mean tumor volumes at day 14 and day 0, respectively, for the experimental group, and C – C0 are those for the vehicle control group. [1] MELK-positive and -negative GC-PDX mouse models were randomly selected according to the results of IHC performed on the original GC and TumorGraft tissues. When tumor volume reached 100-200 mm3, the mice were randomly assigned to treatment and control groups and dosing was initiated. OTSSP167 was administered at 15 mg/kg intravenously to the third-generation mice once every two days for 2 weeks. The control group was treated with vehicle (PBS) in the same way. Tumor size was monitored every two days by caliper measurements. The weight of the mice was also measured as an indicator of treatment toleration. Tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was assessed in accordance with the formula {1–(T–T0) / (C–C0)} × 100, where T and T0 are the mean tumor volumes at the end of the drug administration and day 0, respectively, for the treated group, and C−C0 are those for the vehicle control group.[2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
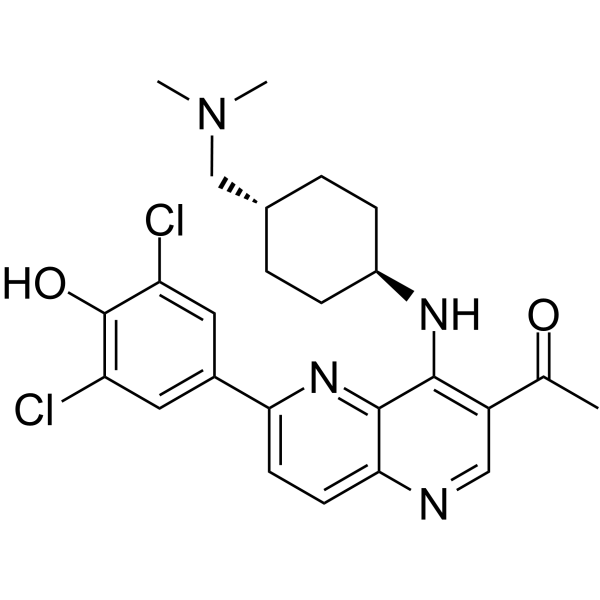
4-[7-acetyl-8-[[4-[(dimethylamino)methyl]cyclohexyl]amino]-1H-1,5-naphthyridin-2-ylidene]-2,6-dichloro-1-cyclohexa-2,5-dienone is a naphthyridine derivative.
MELK Inhibitor OTS167 is an orally available inhibitor of maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, OTS167 binds to MELK, which prevents both MELK phosphorylation and activation; thus inhibiting the phosphorylation of downstream MELK substrates. This may lead to an inhibition of both cell proliferation and survival in MELK-expressing tumor cells. MELK, a serine/threonine kinase, is involved in cancer cell survival, invasiveness and cancer-stem cell formation and maintenance; it is highly upregulated in various types of cancer cells and absent in normal, healthy cells. We previously reported MELK (maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase) as a novel therapeutic target for breast cancer. MELK was also reported to be highly upregulated in multiple types of human cancer. It was implied to play indispensable roles in cancer cell survival and indicated its involvement in the maintenance of tumor-initiating cells. We conducted a high-throughput screening of a compound library followed by structure-activity relationship studies, and successfully obtained a highly potent MELK inhibitor OTSSP167 with IC₅₀ of 0.41 nM. OTSSP167 inhibited the phosphorylation of PSMA1 (proteasome subunit alpha type 1) and DBNL (drebrin-like), which we identified as novel MELK substrates and are important for stem-cell characteristics and invasiveness. The compound suppressed mammosphere formation of breast cancer cells and exhibited significant tumor growth suppression in xenograft studies using breast, lung, prostate, and pancreas cancer cell lines in mice by both intravenous and oral administration. This MELK inhibitor should be a promising compound possibly to suppress the growth of tumor-initiating cells and be applied for treatment of a wide range of human cancer. [1] Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) is upregulated in a variety of human tumors, and is considered an attractive molecular target for cancer treatment. We characterized the expression of MELK in gastric cancer (GC) and measured the effects of reducing MELK mRNA levels and protein activity on GC growth. MELK was frequently overexpressed in primary GCs, and higher MELK levels correlated with worse clinical outcomes. Reducing MELK expression or inhibiting kinase activity resulted in growth inhibition, G2/M arrest, apoptosis and suppression of invasive capability of GC cells in vitro and in vivo. MELK knockdown led to alteration of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated proteins. Furthermore, targeting treatment with OTSSP167 in GC patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models had anticancer effects. Thus, MELK promotes cell growth and invasiveness by inhibiting apoptosis and promoting G2/M transition and EMT in GC. These results suggest that MELK may be a promising target for GC treatment.[2] OTSSP167 was recently characterized as a potent inhibitor for maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK) and is currently tested in Phase I clinical trials for solid tumors that have not responded to other treatment. Here we report that OTSSP167 abrogates the mitotic checkpoint at concentrations used to inhibit MELK. The abrogation is not recapitulated by RNAi mediated silencing of MELK in cells. Although OTSSP167 indeed inhibits MELK, it exhibits off-target activity against Aurora B kinase in vitro and in cells. Furthermore, OTSSP167 inhibits BUB1 and Haspin kinases, reducing phosphorylation at histones H2AT120 and H3T3 and causing mislocalization of Aurora B and associated chromosomal passenger complex from the centromere/kinetochore. The results suggest that OTSSP167 may have additional mechanisms of action for cancer cell killing and caution the use of OTSSP167 as a MELK specific kinase inhibitor in biochemical and cellular assays.[3] Murine protein serine/threonine kinase 38 (MPK38), also known as maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase (MELK), has been associated with various human cancers and plays an important role in the formation of cancer stem cells. OTSSP167, a MELK selective inhibitor, exhibits a strong in vitro activity, conferring an IC50 of 0.41nM and in vivo effect on various human cancer xenograft models. Here, we report the crystal structure of MPK38 (T167E), an active mutant, in complex with OTSSP167 and describe its detailed protein-inhibitor interactions. Comparison with the previous determined structure of MELK bound to the nanomolar inhibitors shows that OTSSP167 effectively fits into the active site, thus offering an opportunity for structure-based development and optimization of MELK inhibitors.[4] |
| 分子式 |
C25H28CL2N4O2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
487.42
|
|
| 精确质量 |
486.158
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 61.60; H, 5.79; Cl, 14.55; N, 11.49; O, 6.56
|
|
| CAS号 |
1431697-89-0
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
OTSSP167 hydrochloride;1431698-10-0
|
|
| PubChem CID |
135398499
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
619.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
328.2±31.5 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.644
|
|
| LogP |
6.41
|
|
| tPSA |
81.32
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
648
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1=CC(C2=CC=C(N=CC(C(C)=O)=C3N[C@H]4CC[C@H](CN(C)C)CC4)C3=N2)=CC(Cl)=C1O
|
|
| InChi Key |
DKZYXHCYPUVGAF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H28Cl2N4O2/c1-14(32)18-12-28-22-9-8-21(16-10-19(26)25(33)20(27)11-16)30-24(22)23(18)29-17-6-4-15(5-7-17)13-31(2)3/h8-12,15,17,33H,4-7,13H2,1-3H3,(H,28,29)
|
|
| 化学名 |
1-[6-(3,5-dichloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-[[4-[(dimethylamino)methyl]cyclohexyl]amino]-1,5-naphthyridin-3-yl]ethanone
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0516 mL | 10.2581 mL | 20.5162 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4103 mL | 2.0516 mL | 4.1032 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2052 mL | 1.0258 mL | 2.0516 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Status | Interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02926690 | Recruiting | Drug: OTS167PO | Relapsed/Refractory Locally Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer and Triple Negative Breast Cancer |
OncoTherapy Science, Inc. | May 29, 2017 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02768519 | Completed | Drug: OTS167IV Other: Cherry syrup |
Healthy | OncoTherapy Science, Inc. | January 2016 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01910545 | Completed | Drug: OTS167IV | Solid Tumors Metastatic Tumors |
OncoTherapy Science, Inc. | August 23, 2013 | Phase 1 |
|
|---|
|
|