| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
CFTR
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:VX-661,被称为 CTFR 校正剂,允许 F508del 突变通道逃避降解并转运至细胞膜。激酶测定:在体外,与单独使用 VX-661 相比,VX-661 和 ivacaftor 的组合可产生更高的 CFTR 活性。细胞测定:VX-661 单独处理或与 ivacaftor 联合处理已显示可增强 F508del-CFTR 向细胞表面的运输。 VX-661已处于2期研究
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
体内肺功能、汗液氯化物和营养参数的改善[2]
在体外证明S945L-CFTR活性恢复后,通过审查参与者的临床参数来评估tezacaftor (VX-661; TEZ)/ivacaftor(IVA)的体内效果。TEZ/IVA前12个月的平均ppFEV1为77.19,TEZ/IVB后12个月改善至80.79(表1)。TEZ/IVA后12个月ppFEV1与基线(TEZ/IVA前)相比的绝对和相对变化分别为15.17个百分点和21.11%(表1)。肺功能下降斜率(ppFEV1)在TEZ/IVA开始后的24个月内发生了显著变化(p=0.02),变为阳性(图1A)。此外,营养参数的轨迹有所改善,包括体重(p<0.0001,图1B)和身高百分位数(p<0.00001,图1C)。开始TEZ/IVA治疗后,BMI百分位数的变化斜率没有显著差异(图1D、E)。在TEZ/IVA开始前的24个月里,参与者需要七次入院以优化肺功能,包括静脉注射抗生素治疗,并报告了一次胰腺炎发作(表1)。在TEZ/IVA开始后的24个月内,不需要入院,也没有胰腺炎发作的报告。在TEZ/IVA启动后,参与者的汗液氯化物浓度也降低了40 mmol/L(表明CFTR功能有所改善)。汗液氯化物浓度从68降至28 mmol/L,降至CF诊断值(>60 mmol/L)和CF不确定值(30-59 mmol/L)以下。
|
| 细胞实验 |
CFTR调节剂治疗分化的气道上皮细胞[2]
在实验前,将分化的hNEC与3μM VX-809(LUM,Selleckchem S1565)、5μMtezacaftor (VX-661; TEZ)或载体对照(0.01%DMSO)一起孵育48小时(基底侧)。对于ELX/TEZ/IVA治疗,使用3μM VX-445(ELX)和18μM VX-661。预处理48小时后,将分化的hNEC安装在循环Ussing室中(见“分化气道细胞模型中CFTR介导的离子转运的定量”一节)。在CFTR介导的离子转运试验中,将10μM VX-770(IVA,Selleckchem S1144)或0.01%DMSO急性加入Ussing室的顶端室。
|
| 动物实验 |
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) results from over 400 different disease-causing mutations in the CF Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) gene. These CFTR mutations lead to numerous defects in CFTR protein function. A novel class of targeted therapies (CFTR modulators) have been developed that can restore defects in CFTR folding and gating. This study aimed to characterize the functional and structural defects of S945L-CFTR and interrogate the efficacy of modulators with two modes of action: gating potentiator [ivacaftor (IVA)] and folding corrector [tezacaftor (VX-661; TEZ)]. The response to these modulators in vitro in airway differentiated cell models created from a participant with S945L/G542X-CFTR was correlated with in vivo clinical outcomes of that participant at least 12 months pre and post modulator therapy. In this participants' airway cell models, CFTR-mediated chloride transport was assessed via ion transport electrophysiology. Monotherapy with IVA or TEZ increased CFTR activity, albeit not reaching statistical significance. Combination therapy with TEZ/IVA significantly (p = 0.02) increased CFTR activity 1.62-fold above baseline. Assessment of CFTR expression and maturation via western blot validated the presence of mature, fully glycosylated CFTR, which increased 4.1-fold in TEZ/IVA-treated cells. The in vitro S945L-CFTR response to modulator correlated with an improvement in in vivo lung function (ppFEV1) from 77.19 in the 12 months pre TEZ/IVA to 80.79 in the 12 months post TEZ/IVA. The slope of decline in ppFEV1 significantly (p = 0.02) changed in the 24 months post TEZ/IVA, becoming positive. Furthermore, there was a significant improvement in clinical parameters and a fall in sweat chloride from 68 to 28 mmol/L. The mechanism of dysfunction of S945L-CFTR was elucidated by in silico molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. S945L-CFTR caused misfolding of transmembrane helix 8 and disruption of the R domain, a CFTR domain critical to channel gating. This study showed in vitro and in silico that S945L causes both folding and gating defects in CFTR and demonstrated in vitro and in vivo that TEZ/IVA is an efficacious modulator combination to address these defects. As such, we support the utility of patient-derived cell models and MD simulations in predicting and understanding the effect of modulators on CFTR function on an individualized basis.[2]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The Cmax, Tmax and AUC of tezacaftor, when administered with ivacaftor, are 5.95 mcg/ml, 2-6 h, and 84.5 mcg.h/ml respectively. Exposure of tezacaftor/ivacaftor increases 3-fold when it is administered with a high-fat meal. After oral administration, the majority of tezacaftor dose (72%) is found excreted in the feces either unchanged or as its metabolite, M2. About 14% of the administered dose is found excreted in the urine as the metabolite, M2. It was noted that less than 1% of the administered dose is excreted unchanged in the urine and thus, renal excretion is not the major elimination pathway. The apparent volume of distribution of tezacaftor was 271 L in a study of patients in the fed state who received 100 mg of tezacaftor every 12 hours. The apparent clearance of tezacaftor has been measured at 1.31 L/h for patients in the fed state during a clinical trial. Metabolism / Metabolites Tezacaftor is metabolized extensively in humans by the action of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. There are three main circulating metabolites; M1, M2, and M5. The M1 is an active metabolite with similar activity to the parent drug, tezacaftor. The M2 metabolite is significantly less active and M5 is considered an inactive metabolite. An additional circulating metabolite, M3, corresponding to the glucuronide form of tezacaftor. Biological Half-Life The apparent half-life of tezacaftor is approximately 57.2 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Tezacaftor is approximately 99% bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. In study VX18-561-101, participants treated with deutivacaftor 150 mg once daily (n=23) or deutivacaftor 250 mg once daily (n=24) had mean absolute changes in ppFEV1 of 3·1 percentage points (95% CI -0·8 to 7·0) and 2·7 percentage points (-1·0 to 6·5) from baseline at week 12, respectively, versus -0·8 percentage points (-6·2 to 4·7) with ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 h (n=11); the deutivacaftor safety profile was consistent with the established safety profile of ivacaftor 150 mg every 12 h. In study VX18-121-101, participants with F/MF genotypes treated with vanzacaftor (5 mg)-tezacaftor-deutivacaftor (n=9), vanzacaftor (10 mg)-tezacaftor-deutivacaftor (n=19), vanzacaftor (20 mg)-tezacaftor-deutivacaftor (n=20), and placebo (n=10) had mean changes relative to baseline at day 29 in ppFEV1 of 4·6 percentage points (-1·3 to 10·6), 14·2 percentage points (10·0 to 18·4), 9·8 percentage points (5·7 to 13·8), and 1·9 percentage points (-4·1 to 8·0), respectively, in sweat chloride concentration of -42·8 mmol/L (-51·7 to -34·0), -45·8 mmol/L (95% CI -51·9 to -39·7), -49·5 mmol/L (-55·9 to -43·1), and 2·3 mmol/L (-7·0 to 11·6), respectively, and in CFQ-R respiratory domain score of 17·6 points (3·5 to 31·6), 21·2 points (11·9 to 30·6), 29·8 points (21·0 to 38·7), and 3·3 points (-10·1 to 16·6), respectively. Participants with the F/F genotype treated with vanzacaftor (20 mg)-tezacaftor-deutivacaftor (n=18) and tezacaftor-ivacaftor (n=10) had mean changes relative to baseline (taking tezacaftor-ivacaftor) at day 29 in ppFEV1 of 15·9 percentage points (11·3 to 20·6) and -0·1 percentage points (-6·4 to 6·1), respectively, in sweat chloride concentration of -45·5 mmol/L (-49·7 to -41·3) and -2·6 mmol/L (-8·2 to 3·1), respectively, and in CFQ-R respiratory domain score of 19·4 points (95% CI 10·5 to 28·3) and -5·0 points (-16·9 to 7·0), respectively. The most common adverse events overall were cough, increased sputum, and headache. One participant in the vanzacaftor-tezacaftor-deutivacaftor group had a serious adverse event of infective pulmonary exacerbation and another participant had a serious rash event that led to treatment discontinuation. For most participants, adverse events were mild or moderate in severity. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Description
Tezacaftor is a drug of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) potentiator class. It was developed by Vertex Pharmaceuticals and FDA approved in combination with [ivacaftor] to manage cystic fibrosis. This drug was approved by the FDA on February 12, 2018. Cystic Fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by one of several different mutations in the gene for the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) protein, an ion channel involved in the transport of chloride and sodium ions across cell membranes. CFTR is active in epithelial cells of organs such as of the lungs, pancreas, liver, digestive system, and reproductive tract. Alterations in the CFTR gene result in altered production, misfolding, or function of the protein and consequently abnormal fluid and ion transport across cell membranes. As a result, CF patients produce thick, sticky mucus that clogs the ducts of organs where it is produced making patients more susceptible to complications such as infections, lung damage, pancreatic insufficiency, and malnutrition. Drug Indication Tezacaftor is combined with ivacaftor in one product for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 12 years or older with two copies of the _F508del_ gene mutation or at least one mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive to this drug. Tezacaftor, when used in combination with ivacaftor and [elexacaftor] in the product Trikafta, is also indicated for the treatment of CF in patients 12 years of age and older that have at least one _F508del_ mutation in the CFTR gene. FDA Label Mechanism of Action The transport of charged ions across cell membranes is normally achieved through the actions of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (CFTR) protein. This protein acts as a channel and allows for the passage of chloride and sodium. This process affects the movement of water in and out of the tissues and impacts the production of mucus that lubricates and protects certain organs and body tissues, including the lungs. In the _F508del_ mutation of the CFTR gene, one amino acid is deleted at the position 508, therefore, the CFTR channel function is compromised, resulting in thickened mucus secretions. CFTR correctors such as tezacaftor aim to repair F508del cellular misprocessing. This is done by modulating the position of the CFTR protein on the cell surface to the correct position, allowing for adequate ion channel formation and increased in water and salt movement through the cell membrane. The concomitant use of ivacaftor is intended to maintain an open channel, increasing the transport of chloride, reducing thick mucus production. |
| 分子式 |
C26H27F3N2O6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
520.497597932816
|
| 精确质量 |
520.182
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.00; H, 5.23; F, 10.95; N, 5.38; O, 18.44
|
| CAS号 |
1226709-85-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Tezacaftor;1152311-62-0;Tezacaftor-d4;1961280-24-9
|
| PubChem CID |
46199801
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| LogP |
2.9
|
| tPSA |
113
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
37
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
858
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
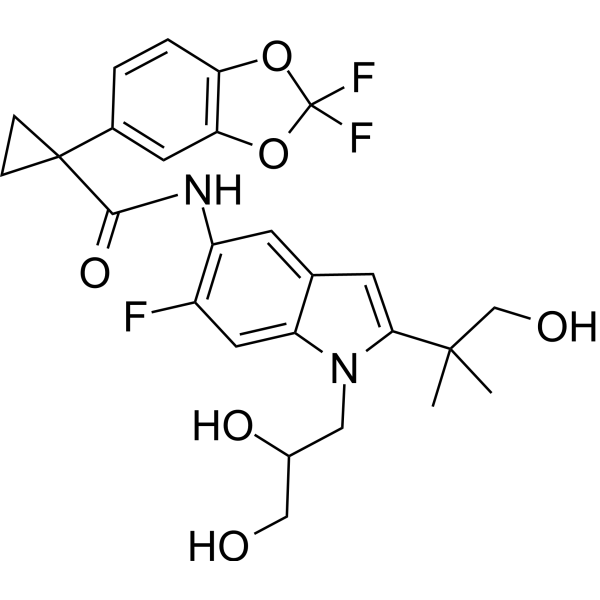
FC1=CC2=C(C=C(C(C)(C)CO)N2CC(CO)O)C=C1NC(C1(C2=CC=C3C(=C2)OC(O3)(F)F)CC1)=O
|
| InChi Key |
MJUVRTYWUMPBTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H27F3N2O6/c1-24(2,13-33)22-8-14-7-18(17(27)10-19(14)31(22)11-16(34)12-32)30-23(35)25(5-6-25)15-3-4-20-21(9-15)37-26(28,29)36-20/h3-4,7-10,16,32-34H,5-6,11-13H2,1-2H3,(H,30,35)
|
| 化学名 |
1-(2,2-difluoro-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-[1-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-6-fluoro-2-(1-hydroxy-2-methylpropan-2-yl)indol-5-yl]cyclopropane-1-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
(Rac)-Tezacaftor; 1226709-85-8; 1-(2,2-difluorobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-N-(1-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-6-fluoro-2-(1-hydroxy-2-Methylpropan-2-yl)-1H-indol-5-yl)cyclopropanecarboxaMide; Tezacaftor (Racemate); SCHEMBL322363; MJUVRTYWUMPBTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N; HMS3652D20; HMS3748O05;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9212 mL | 9.6061 mL | 19.2123 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3842 mL | 1.9212 mL | 3.8425 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1921 mL | 0.9606 mL | 1.9212 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。