| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv( MIC50=2.7 nM )
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Q203 是一种咪唑并吡啶酰胺 (IAP) 化合物,通过靶向呼吸道细胞色素 bc1 复合物来阻断结核分枝杆菌的生长。它具有治疗结核病的潜力。 Q203 在低纳摩尔范围内抑制肉汤培养基中 MDR 和 XDR 结核分枝杆菌临床分离株的生长,并且在小鼠结核病模型中以低于 1 mg/kg 体重的剂量有效,这凸显了 Q203 的效力。 Q203 对参考菌株结核分枝杆菌 H37Rv 有活性,在肉汤培养基中的 MIC50 为 2.7 nM,在巨噬细胞内的 MIC50 为 0.28 nM。此外,Q203 显示出与每日一次给药兼容的药代动力学和安全性特征。总之,这些数据表明 Q203 是治疗结核病的有前途的新临床候选药物。激酶测定:Q203 对参考菌株结核分枝杆菌 H37Rv 有活性,在培养基中的 MIC50 为 2.7 nM,在巨噬细胞内的 MIC50 为 0.28 nM。细胞测定:
Telacebec (Q203; IAP6)对参考菌株结核分枝杆菌H37Rv有活性,最低浓度为抑制培养液中50%生物体(MIC50) 2.7 nM,巨噬细胞内MIC50为0.28 nM(图1b,c)。在三个中心采用四种不同的技术(见在线方法)测定培养液培养基中的MIC50,结果具有可比性。此外,我们通过琼脂板的CFU测定,证实了Q203在液体肉汤培养基中的活性。[1] 深入了解Telacebec (Q203; IAP6)并确定其分子靶点,我们选择了两种不同的IPA衍生物IPA04和IPA05的自发抗性突变体(Supplementary Fig. 5)。在确认了对Q203的稳定基因型抗性后(图3a),我们对来自独立生物重复的6个自发抗性突变体进行了全基因组测序。突变体显示Q203的MIC50持续增加了几个数量级,但仍然对标准抗结核药物敏感。我们在所有六个突变体中发现了细胞色素b亚基(qcrB,也称为细胞色素bc1复合体的Rv2196)中的单个氨基酸取代(图3b)。对另外18株独立的自发性耐药突变体(全部受试的18株)进行qcrB序列分析证实:Thr313突变为丙氨酸或异亮氨酸(图3b)与特拉西贝克(Q203;IAP6)耐药性相关。此外,通过同源重组在亲本结核分枝杆菌H37Rv中重新引入突变Ala313,获得了对Q203的抗性(图3a),表明这种取代直接和特异性地参与了对该化合物的抗性机制。在1 μM浓度下,对IPA04和IPA05的6个独立突变选择实验进行综合分析,结果表明,IPA04和IPA05的自发突变率为2.4 × 10−8,抗性突变体出现的概率较低。直接在Q203上选择的自发抗性突变体也对Q203具有高度抗性(补充图6),并且在qcrB中含有多态性T313A,而我们在两个泛易感和三个XDR临床分离株中未发现qcrB突变(补充图7)。最近,在由相关IPA衍生物选择的牛分枝杆菌卡介苗(BCG)突变体中发现了类似的qcrB多态性,该突变体在体外抑制结核分枝杆菌生长的活性低于Q203,且未优化用于临床。[1] 值得注意的是,在QP位点抑制剂的结合中起关键作用的几个残基(例如,stigmatellin)或涉及对此类抑制剂的抗性,或两者都位于ef区(补充图8),这表明Telacebec (Q203;IAP6)类似于作用于QP位点的非选择性抑制剂。考虑到细胞色素bc1在呼吸电子传递链中的关键作用,我们测试了Telacebec (Q203;IAP6 可能干扰结核分枝杆菌ATP合成。我们发现Telacebec (Q203; IAP6)触发了细胞内ATP的快速减少,IC50为1.1 nM(图3c)。在类似的实验条件下(见在线方法),莫西沙星或链霉素没有减少ATP池大小,而贝达喹啉有(IC50为27.7 nM)。最后,Q203能够在小于10 nM的IC50下干扰缺氧非复制结核中的ATP稳态(图3d)。在低浓度下快速抑制ATP合成强烈提示抑制细胞色素bc1活性是Q203[1]的主要作用方式。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Q203 显示出与每日一次给药兼容的药代动力学和安全性特征。 Q203的生物利用度为90%,终末半衰期为23.4小时。分布容积适中(5.27 l/kg体重),全身清除率低(4.03 mL/min/kg)。治疗 4 周后,在按每公斤体重 0.4、2 和 10 毫克 Q203 治疗的组中,观察到结核分枝杆菌 H37Rv 细菌载量分别减少了 90%、99% 和 99.9%
|
| 酶活实验 |
肝微粒体稳定性测定。[1]
将化合物(终浓度为2μM,溶于0.2%DMSO中)与0.5 mg mL-1人(200只,混合性别)、雄性狗、雄性大鼠或雄性小鼠肝微粒体在磷酸钾缓冲液中孵育。通过加入NADPH引发反应,并立即或在10、20、30或60分钟时停止,以精确估计清除率。采用带有电喷雾电离(ESI)的三重四极杆Quattro Premier质谱仪进行样品分析。样品通过捕集筒(Acquity BEH RP18 50 mm×2.1 mm,1.7μm,Waters,Milford,MA),然后通过分析柱。通过与0分钟时的初始量进行比较来计算剩余化合物的百分比。然后使用一级反应动力学计算半衰期。
CYP450抑制试验。[1] 该测定使用具有单个重组人细胞色素P450(rhCYP)同工酶的单个荧光探针底物,并根据先前发表的方法进行荧光检测36。用于每种同工酶的探针底物(在0.5%DMSO中)如下:CYP3A4为7-苄氧基-4-(三氟甲基)-香豆素,CYP2D6为3-[2-(N,N-二乙基-N-甲基铵)乙基]-7-甲氧基-4-甲基香豆素(AMMC),1A2和2C19为3-氰基-7-乙氧基香豆素(CEC),2C9为7-甲氧基-4-(三氟甲基)香豆素(MFC)。使用Victor3 V多标记板阅读器测量荧光。使用三倍连续稀释的八点浓度曲线测定IC50。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞毒性。[1]
如前所述,使用MTT(3-(4,5-二甲基噻唑-2-基)-2,5-二苯基溴化四唑)存活率测定法对人细胞系SH-SY5Y(脑)、HEK293(肾)和HepG2(肝)进行了细胞毒性测试。
结核分枝杆菌H37Rv ATP耗竭试验。[1] 将结核分枝杆菌H37Rv暴露于受试化合物24小时(需氧)或5天(厌氧),与等体积的BacTiter-Glo试剂混合,在黑暗中孵育10分钟。在Victor3 V多标签平板阅读器上记录发光。 |
| 动物实验 |
Rats: Sprague Dawley rats are used for pharmacokinetic studies. Compounds (Q203) are given at a dose of 2 mg per kg body weight intravenously or 10 mg per kg body weight orally. The compounds (Telacebec (Q203; IAP6)) are formulated in 20% TPGS (d-α tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate) for repeated-dose studies and in 40% PEG400, pH4 for single-dose studies. Blood samples are taken through the caudal vena cava using 1-mL syringes before perfusion. Samples are collected from three mice or rats at 0.5, 1, 2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h post-dose. Blood samples are centrifuged at 3,200g for 10 min at 4 °C. Following centrifugation, plasma is collected and frozen until further analysis. Compound concentrations are determined by LC-MS;
Mice: Efficacy of Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) in a mouse model of established tuberculosis is studied. Bacterial loads are enumerated in the lung of infected mice after 14 d and 28 d of treatment. Q203 is used at 0.4, 2 and 10 mg per kg body weight. Bedaquiline and isoniazid (INH) are used as positive controls at 6.5 and 15 mg per kg body weight, respectively. Five mice per group and per time point are used. Pharmacokinetics.[1] BALB/c mice and Sprague Dawley rats were used for pharmacokinetic studies. Compounds were given at a dose of 2 mg per kg body weight intravenously or 10 mg per kg body weight orally. Otherwise stated, the compounds [Telacebec (Q203; IAP6)] were formulated in 20% TPGS (D-α tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate) for repeated-dose studies and in 40% PEG400, pH4 for single-dose studies. Blood samples were taken through the caudal vena cava using 1-mL syringes before perfusion. Samples were collected from three mice or rats at 0.5, 1, 2, 6, 12, 24 and 48 h post-dose. Blood samples were centrifuged at 3,200g for 10 min at 4 °C. Following centrifugation, plasma was collected and frozen until further analysis. Compound concentrations were determined by LC-MS. In vivo efficacy in the mouse model of tuberculosis.[1] The acute model was performed as previously described. Briefly, mice were infected with a high dose of M. tuberculosis H37Rv. Dosing was initiated 6 d after infection. Drugs [Telacebec (Q203; IAP6)] were administered orally for 3 d. Bacterial load in the lungs of infected mice was determined by colony-forming unit (CFU) enumeration. For the established mouse model, BALB/c mice were infected with 2 × 102 to 2 × 103 CFU of M. tuberculosis H37Rv by the intranasal route. Treatment was initiated 3 weeks after infection. Drugs were formulated in 20% TPGS and administered by oral gavage for 28 d, five times per week. Bacterial load in the lungs of infected mice was determined by CFU enumeration. For histopathology analysis, segments of the lungs were fixed with 10% neutral formalin, embedded in paraffin and processed for histology. Sections (5 μm) were stained with H&E. Histologic sections were used for morphologic analysis of the size and number of granulomas using an image analyzer. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The metabolic stability of Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) in microsomes and cryopreserved hepatocytes from human, monkey, rat and dog origin was high (Supplementary Table 5), suggesting that Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) may achieve good blood exposure in humans. Because any new antitubercular drug will be given clinically in combination with other medications, the absence of drug-drug interactions is crucial. Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) did not inhibit any of the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) isoenzymes tested, nor did it induce human pregnane X receptor (hPXR) activation (Supplementary Table 5). In addition, it was not a substrate or an inhibitor for the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (Supplementary Table 5), indicating that it has low potential for drug-drug interaction.[1]
Next, we determined the pharmacokinetic profile of Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) in mice (Supplementary Table 6). Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) had a bioavailability of 90% and a terminal half-life of 23.4 h. The volume of distribution was moderate (5.27 l per kg body weight), and the systemic clearance was low (4.03 ml min−1 kg−1). The drug concentration in lungs was two- to threefold higher than in the serum (Supplementary Table 7), which is a desirable property for an antitubercular drug15. Given its desirable pharmacokinetic and safety profile, we assessed Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) for in vivo efficacy. We initially evaluated Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) in an acute mouse model of tuberculosis16. It promoted a reduction in bacterial load of more than 90% at a dose of 10 mg per kg body weight, an effect comparable to that of bedaquiline or isoniazid (Fig. 2a). We further evaluated Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) in a mouse model of established tuberculosis. After 4 weeks of treatment, we observed reductions of 90%, 99% and 99.9% in M. tuberculosis H37Rv bacterial load in the groups treated with v at 0.4, 2 and 10 mg per kg body weight, respectively (Fig. 2b). Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) was slow acting compared to isoniazid; the reduction in bacterial number was less than one order of magnitude in the first 2 weeks of treatment, but it was more than two orders of magnitude in the following 2 weeks. This profile might be explained by its pharmacokinetic properties or by its mode of action. Of note, bedaquiline displayed a similar time-dependent efficacy (Fig. 2b). We also observed that Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) reduced the formation of lung granulomatous lesions (Fig. 2 c–i). In untreated mice, the lung sections contained multiple tuberculosis granulomatous foci (Fig. 2c), consisting predominantly of lymphocytes surrounding intra-alveolar macrophages (Fig. 2f). In isoniazid-treated groups, we observed a reduction in the size of the granulomatous foci; however, the number of the inflammatory lesions was comparable to that in the untreated control group (Fig. 2d,g,i). In contrast, we observed only a limited number of small granulomatous foci in the lungs of the mice treated with Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) (Fig. 2e–i). Notably, other very effective drugs, such as bedaquiline, also have a strong beneficial effect on lung pathology [1]. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Given that successful treatment of tuberculosis lasts at least six months, the safety profile of a clinical candidate is of utmost importance. To evaluate the cytotoxicity of Telacebec (Q203; IAP6), we measured the minimum concentration that induces cell death in three eukaryotic cell lines. We did not observe cytotoxicity in any of the cell lines up to a concentration of 10 μM (Fig. 1d), which gives Telacebec (Q203; IAP6) a selectivity index of >3,700. We used a hERG potassium channel patch-clamp assay to test whether Q203 would cause QT interval prolongation as a result of hERG potassium channel inhibition. Q203 did not inhibit hERG, suggesting a low risk for cardiotoxicity (Supplementary Table 5). In addition, Q203 had no genetic toxicity in a mini-Ames mutagenicity test and in micronucleus formation assays (Supplementary Table 5). To test for acute toxicity in mice, we administered a high dose of Q203 and observed the mice for 2 weeks. The mice tolerated, without clinical signs of toxicity, a single oral administration of 1,000 mg per kg body weight of Q203, a dose that resulted in a maximum serum concentration of 14.8 μg ml−1 at 24 h and serum concentrations of >3 μg ml−1 for at least 10 d (Supplementary Fig. 3). Furthermore, in a rat long-term administration study, Q203 was well tolerated without body weight loss (Supplementary Fig. 4) or clinical signs of toxicity when administered daily at a dose of 10 mg per kg body weight for 20 d. These data showed that Q203 was well tolerated at a prolonged exposure level.[1]
|
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Nat Med.2013 Sep;19(9):1157-60.
|
| 其他信息 |
New therapeutic strategies are needed to combat the tuberculosis pandemic and the spread of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) forms of the disease, which remain a serious public health challenge worldwide. The most urgent clinical need is to discover potent agents capable of reducing the duration of MDR and XDR tuberculosis therapy with a success rate comparable to that of current therapies for drug-susceptible tuberculosis. The last decade has seen the discovery of new agent classes for the management of tuberculosis, several of which are currently in clinical trials. However, given the high attrition rate of drug candidates during clinical development and the emergence of drug resistance, the discovery of additional clinical candidates is clearly needed. Here, we report on a promising class of imidazopyridine amide (IPA) compounds that block Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by targeting the respiratory cytochrome bc1 complex. The optimized IPA compound Q203 inhibited the growth of MDR and XDR M. tuberculosis clinical isolates in culture broth medium in the low nanomolar range and was efficacious in a mouse model of tuberculosis at a dose less than 1 mg per kg body weight, which highlights the potency of this compound. In addition, Q203 displays pharmacokinetic and safety profiles compatible with once-daily dosing. Together, our data indicate that Q203 is a promising new clinical candidate for the treatment of tuberculosis. [1]
|
| 分子式 |
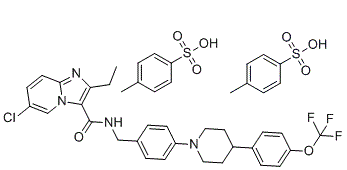
C43H44CLF3N4O8S2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
901.41
|
|
| 精确质量 |
900.224
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 57.30; H, 4.92; Cl, 3.93; F, 6.32; N, 6.22; O, 14.20; S, 7.11
|
|
| CAS号 |
1566517-83-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1334719-95-7;1566517-83-6 (ditosylate);
|
|
| PubChem CID |
91617801
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
|
| tPSA |
184Ų
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
13
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
61
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1000
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C=CC2=NC(CC)=C(C(NCC3C=CC(=CC=3)N3CCC(C4C=CC(=CC=4)OC(F)(F)F)CC3)=O)N2C=1.S(C1C=CC(C)=CC=1)(=O)(=O)O.S(C1C=CC(C)=CC=1)(=O)(=O)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
CCGFTOLSNJBYDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C29H28ClF3N4O2.2C7H8O3S/c1-2-25-27(37-18-22(30)7-12-26(37)35-25)28(38)34-17-19-3-8-23(9-4-19)36-15-13-21(14-16-36)20-5-10-24(11-6-20)39-29(31,32)33;2*1-6-2-4-7(5-3-6)11(8,9)10/h3-12,18,21H,2,13-17H2,1H3,(H,34,38);2*2-5H,1H3,(H,8,9,10)
|
|
| 化学名 |
6-chloro-2-ethyl-N-[[4-[4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]piperidin-1-yl]phenyl]methyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxamide;4-methylbenzenesulfonic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1094 mL | 5.5469 mL | 11.0937 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2219 mL | 1.1094 mL | 2.2187 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1109 mL | 0.5547 mL | 1.1094 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。