| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
VEGFR2 (IC50 = 20 nM); FGFR1 (IC50 = 30 nM); PDGFRβ (IC50 = 510 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:SU5402 抑制 VEGF、FGF、PDGF 依赖性细胞增殖,IC50 分别为 0.05 μM、2.80μM、28.4 μM。在 HUVEC 中,SU5416 以剂量依赖性方式选择性抑制 VEGF 驱动的有丝分裂,IC50 为 0.04 μM。在鼻咽上皮细胞中,SU5402 减弱 LMP1 介导的有氧糖酵解、细胞转化、细胞迁移和侵袭。在小鼠 C3H10T1/2 细胞中,SU 5402 减弱 FGF23 对细胞分化的影响 激酶测定:用工程基因感染草地贪夜蛾 (sf9) 细胞后,FGF-R1 和 Flk-1/KDR 的催化部分表达为 GST 融合蛋白杆状病毒。通过谷胱甘肽琼脂糖层析将受感染的 sf9 细胞裂解物中的 GST-FGFR1 和 GST-Flk1 纯化至同质。测定在 96 孔微量滴定板中进行,该板每孔用 2.0 μg 聚 Glu-Tyr 肽 (4:1) 的 0.1 mL PBS 包被过夜。将纯化的激酶在激酶测定缓冲液(100 mM Hepes pH 7.5、100 mM NaCl 和 0.1 mM 原钒酸钠)中稀释,并以每 0.05 mL 体积缓冲液 5 ng GST 融合蛋白添加到所有测试孔中。测试化合物用 4% DMSO 稀释并添加到测试孔中(0.025 mL/孔)。通过添加 0.025 mL 40 μM ATP/40 mM MnCl2 启动激酶反应,将板摇动 10 分钟,然后添加 0.025 mL 0.5 M EDTA 停止反应。最终 ATP 浓度为 10 μM,是实验确定的 ATP Km 值的两倍。阴性对照孔仅接受 MnCl2,不含 ATP。将板用 10 mM Tris pH 7.4、150 mM NaCl 和 0.05% Tween-20 (TBST) 洗涤三次。将兔多克隆抗磷酸酪氨酸抗血清以 1:10000 稀释度加入 TBST 中,孵育 1 小时。然后用TBST洗涤板3次。然后将与辣根过氧化物酶缀合的山羊抗兔抗血清添加至所有孔中1小时。用TBST洗涤板3次,并通过添加2,2'-偶氮双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)(ABTS)来检测过氧化物酶反应。检测的颜色读数允许进行 20−30 分钟,并使用 410 nM 测试过滤器在 Dynatech MR5000 ELISA 板读取器上读取。细胞测定:用于体外生长的肿瘤细胞系(SF767T、SF763、EPH4-VEGF、C6、A375、A431、LNCAP、Calu-6、3T3Her2 和 488G2M2 细胞)在 37°C 的培养基中培养 5-10 小时。 %二氧化碳。 SU5416 在含有 DMSO (<0.5%) 的培养基中连续稀释,并在开始培养 1 天后添加到肿瘤细胞培养物中。 96 小时后使用磺基罗丹明 B 法测量细胞生长。使用四参数分析通过曲线拟合计算 IC50。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在小鼠中,SU5402(25 mg/kg,腹腔注射)通过抑制与肿瘤生长相关的血管生成过程来抑制一组肿瘤细胞系的皮下生长。
相比之下,在小鼠体内以无毒剂量全身给药SU5402可抑制来自各种组织来源的细胞的皮下肿瘤生长。SU5416的抗肿瘤作用伴随着从药物治疗动物身上切除的淡白色肿瘤的出现,这支持了该药物的抗血管生成特性。这些发现支持,对血管内皮生长因子受体酶活性的药理学抑制代表了一种限制多种肿瘤类型生长的新策略。[2] FGFR1抑制剂SU5402逆转MCT诱导的PH。[5] 为了证实与FGF2-siRNA治疗相关的肺血管改变和PH的减少与FGF2敲低有关,表明FGF2在PH中过量产生的关键作用,我们研究了选择性FGFR1抑制剂SU5402是否可以预防和/或逆转MCT在大鼠中诱导的PH。在MCT注射后第21至42天用SU5402治疗的大鼠中,第42天的评估显示,与用载体(生理盐水)治疗的大白鼠相比,PAP、RV/(LV+S)和远端动脉肌肉化明显降低(图8)。 |
| 酶活实验 |
基因组改变的杆状病毒感染草地贪夜蛾 (sf9) 细胞后,FGF-R1 和 Flk-1/KDR 的催化结构域表达为 GST 融合蛋白。使用谷胱甘肽琼脂糖层析,将感染的 sf9 细胞裂解物纯化至 GST-FGFR1 和 GST-Flk1 的同质性。在 96 孔微量滴定板中,每孔 0.1 mL PBS 中的 2.0 μg 聚谷氨酸-Tyr 肽 (4:1) 包被过夜,然后进行测定。使用激酶测定缓冲液(100 mM Hepes pH 7.5、100 mM NaCl 和 0.1 mM 原钒酸钠),以每 0.05 mL 体积缓冲液 5 ng GST 融合蛋白的比例将稀释的纯化激酶引入每个测试孔。将测试化合物用 4% DMSO 稀释后添加到测试孔中(0.025 mL/孔)。要启动激酶反应,请添加 0.025 mL 的 40 μM ATP/40 mM MnCl2。摇动板 10 分钟,然后添加 0.025 mL 0.5 M EDTA 以终止反应。 ATP 的终浓度为 10 μM,是实验测定的 ATP Km 值的两倍。阴性对照孔中添加 MnCl2 且不添加 ATP。使用 10 mM Tris pH 7.4、150 mM NaCl 和 0.05% Tween-20 (TBST) 对板进行三轮洗涤。将兔多克隆抗磷酸酪氨酸抗血清在 TBST 中的 1:10000 稀释液充满孔,持续一小时。然后用TBST洗板3次。然后,在一小时内,每个孔接受山羊抗兔抗血清和辣根过氧化物酶的缀合物。板的 3 次 TBST 洗涤后,添加 2,2'-azinobis(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸) (ABTS) 以检测过氧化物酶反应。待测定的颜色读数显色 20 至 30 分钟后,使用 Dynatech MR5000 ELISA 酶标仪上的 410 nM 测试过滤器进行读取。
|
| 细胞实验 |
用于体外生长的肿瘤细胞系在 37°C、5–10% CO2 的培养基中生长。培养开始一天后,SU5402在含有 DMSO (<0.5%) 的培养基中连续稀释并添加到肿瘤细胞培养物中。采用磺基罗丹明B法测定96小时后细胞的生长情况。使用四参数分析和曲线拟合,确定 IC50。
蛋白质印迹分析: 总细胞裂解物(5-50µg蛋白质)通过10%或4-12%SDS-PAGE分离,并在免疫印迹前转移到PVDF膜上。 免疫荧光和免疫组织化学染色: 如前所述进行免疫荧光染色和免疫组织化学染色[3]。 细胞增殖试验: 用细胞增殖试剂CCK-8[3]进行细胞增殖试验。 软琼脂克隆试验: 软琼脂菌落形成试验如前所述[3]。 迁移和入侵检测: 分别使用CytoSelect 24孔伤口愈合检测试剂盒和CytoSelect24孔细胞侵袭检测试剂盒进行细胞迁移检测和Boyden腔侵袭检测。对于胶原凝胶侵袭试验,用I型胶原溶液制备胶原混合物[3]。 通过[3H]胸腺嘧啶掺入法评估SMC增殖。[5] 将PA-SMCs在含有15% FCS的DMEM中接种到24孔板中,密度为5 × 10^4细胞/孔,并使其贴壁。细胞在无血清培养基中进行48小时的生长停滞,然后用1 ml条件化的P-EC培养基处理。我们还测试了外源性PDGF(10 ng/ml)和FGF2(10 ng/ml)在有或无伊马替尼(10^-5 M)、EGF拮抗剂(10^-5 M)和SU5402(10^-5 M)的情况下对PA-SMC增殖的影响。在每种条件下,向每孔加入[3H]胸腺嘧啶(1 μCi/ml)。孵育24小时后,用PBS洗涤细胞两次,用冰冷的10%三氯乙酸处理,并溶解在0.1 N NaOH中(0.5 ml/孔)。对掺入的放射性进行计数,并以cpm/孔报告。 |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: For one week, intraperitoneal injections of DMSO or SU 5402 (dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 6 mg/mL) at 25 mg/kg body weight are given to male ΔF508 mice (CFTRtm1Eur on a 129/FVB background) and their wild-type littermates, aged 9–12 weeks. Every day, the dosages are modified based on the mice's weight. Afterwards, isoflurane is breathed into the mice to induce anesthesia until the procedure is completed. To prevent potential cholinergic stimulation of the salivary gland, 50 μL of the cholinergic antagonist atropine (1 mM) is subcutaneously injected into the right cheek. For four minutes, the injected cheek is pressed up against a tiny strip of filter paper. The same location is then subinjected with isoprenaline (10 mM, 37.5 μL) to elicit an adrenergic secretion of saliva (time 0). For thirty minutes, replace the filter strips (pre-weighed in an Eppendorf tube) every five minutes. After the collection is complete, the weight of all six filter strips is measured, and the results are normalized to mg/g body weight.
Rats: Adult male Wistar rats (200–250 g) are given MCT (60 mg/kg s.c.) and left untreated for 21 dayIn order to evaluate the possible impact of the FGFR1 inhibitor SU 5402 on established PH, adult male Wistar rats weighing 200–250 g are administered MCT (60 mg/kg s.c.), allowed to go untreated for 21 days, and then split into two groups at random (10 animals per group): one group receives treatment with SU 5402 (25 mg/kg/day), while the other group receives no treatment from day 21 to day 42. Every treatment is administered intravenously (s.c.) once daily. Effect of treatment with SU5402 on established MCT PH. [5] To assess the potential effects of the FGFR1 inhibitor SU5402 on established PH, adult male Wistar rats (200–250 g) were given MCT (60 mg/kg s.c.), left untreated for 21 days, then randomly divided into 2 groups (10 animals in each group), of which one was treated with SU5402 (25 mg/kg/day) and the other given the vehicle, from day 21 to day 42. All treatments were given once a day by s.c. injection |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
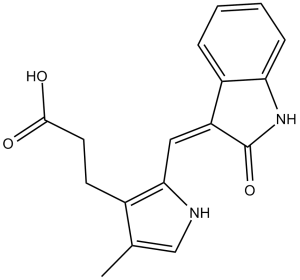
SU5402 is an oxindole that is 3-methyleneoxindole in which one of the hydrogens of the methylene group is substituted by a 3-(2-carboxyethyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl group. It is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase activity of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1. It has a role as a fibroblast growth factor receptor antagonist. It is a monocarboxylic acid, a member of pyrroles and a member of oxindoles. It is functionally related to a 3-methyleneoxindole.
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) have been implicated as therapeutic targets for the treatment of human diseases including cancers, inflammatory diseases, cardiovascular diseases including arterial restenosis, and fibrotic diseases of the lung, liver, and kidney. Three classes of 3-substituted indolin-2-ones containing propionic acid functionality attached to the pyrrole ring at the C-3 position of the core have been identified as catalytic inhibitors of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF), and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) RTKs. Some of the compounds were found to inhibit the tyrosine kinase activity associated with isolated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGF-R2) [fetal liver tyrosine kinase 1 (Flk-1)/kinase insert domain-containing receptor (KDR)], fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGF-R), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGF-R) tyrosine kinase with IC(50) values at nanomolar level. Thus, compound 1 showed inhibition against VEGF-R2 (Flk-1/KDR) and FGF-R1 tyrosine kinase activity with IC(50) values of 20 and 30 nM, respectively, while compound 16f inhibited the PDGF-R tyrosine kinase activity with IC(50) value of 10 nM. Structural models and structure-activity relationship analysis of these compounds for the target receptors are discussed. The cellular activities of these compounds were profiled using cellular proliferation assays as measured by bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation. Specific and potent inhibition of cell growth was observed for some of these compounds. These data provide evidence that these compounds can be used to inhibit the function of these target receptors. [1] Non-keratinizing nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is closely associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. The EBV-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is believed to play an important role in NPC pathogenesis by virtue of its ability to activate multiple cell signalling pathways which collectively promote cell proliferation, transformation, angiogenesis, and invasiveness, as well as modulation of energy metabolism. In this study, we report that LMP1 increases cellular uptake of glucose and glutamine, enhances LDHA activity and lactate production, but reduces pyruvate kinase activity and pyruvate concentrations. LMP1 also increases the phosphorylation of PKM2, LDHA, and FGFR1, as well as the expression of PDHK1, FGFR1, c-Myc, and HIF-1α, regardless of oxygen availability. Collectively, these findings suggest that LMP1 promotes aerobic glycolysis. With respect to FGFR1 signalling, LMP1 not only increases FGFR1 expression, but also up-regulates FGF2, leading to constitutive activation of the FGFR1 signalling pathway. Furthermore, two inhibitors of FGFR1 (PD161570 and SU5402) attenuate LMP1-mediated aerobic glycolysis, cellular transformation (proliferation and anchorage-independent growth), cell migration, and invasion in nasopharyngeal epithelial cells, identifying FGFR1 signalling as a key pathway in LMP1-mediated growth transformation. Immunohistochemical staining revealed that high levels of phosphorylated FGFR1 are common in primary NPC specimens and that this correlated with the expression of LMP1. In addition, FGFR1 inhibitors suppress cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of NPC cells. Our current findings demonstrate that LMP1-mediated FGFR1 activation contributes to aerobic glycolysis and transformation of epithelial cells, thereby implicating FGF2/FGFR1 signalling activation in the EBV-driven pathogenesis of NPC. [2] FGF23 is a bone-derived hormone that regulates mineral metabolism by inhibiting renal tubular phosphate reabsorption and suppressing circulating 1,25(OH)2D and PTH levels. These effects are mediated by FGF-receptor binding and activation in the presence of its coreceptor Klotho, which is expressed in the distal tubules of the kidney. Recently, expression of Klotho in skeletal tissues has been reported, indicating a direct, yet unclear, extrarenal effect of FGF23 on cells involved with bone development and remodeling. In the present study, we found that bone marrow stromal cells harvested from Klotho null mice developed fewer osteoblastic but more adipocytic colonies than cells from wild-type mice. The underlying mechanism was explored by experiments on mouse C3H10T1/2 cells. We found that Klotho was weakly expressed and that FGF23 dose-dependently affected the lineage fate determination. The effects of FGF23 on cell differentiation can be diminished by SU5402, a specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor for FGF receptors. Our results indicate that FGF23 directly affects the differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells.[4] Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a progressive, lethal lung disease characterized by pulmonary artery SMC (PA-SMC) hyperplasia leading to right-sided heart failure. Molecular events originating in pulmonary ECs (P-ECs) may contribute to the PA-SMC hyperplasia in PH. Thus, we exposed cultured human PA-SMC to medium conditioned by P-EC from patients with idiopathic PH (IPH) or controls and found that IPH P-EC-conditioned medium increased PA-SMC proliferation more than control P-EC medium. Levels of FGF2 were increased in the medium of IPH P-ECs over controls, while there was no detectable difference in TGF-beta1, PDGF-BB, or EGF levels. No difference in FGF2-induced proliferation or FGF receptor type 1 (FGFR1) mRNA levels was detected between IPH and control PA-SMCs. Knockdown of FGF2 in P-EC using siRNA reduced the PA-SMC growth-stimulating effects of IPH P-EC medium by 60% and control P-EC medium by 10%. In situ hybridization showed FGF2 overproduction predominantly in the remodeled vascular endothelium of lungs from patients with IPH. Repeated intravenous FGF2-siRNA administration abolished lung FGF2 production, both preventing and nearly reversing a rat model of PH. Similarly, pharmacological FGFR1 inhibition with SU5402 reversed established PH in the same model. Thus, endothelial FGF2 is overproduced in IPH and contributes to SMC hyperplasia in IPH, identifying FGF2 as a promising target for new treatments against PH.[5] |
| 分子式 |
C17H16N2O3
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
296.32
|
|
| 精确质量 |
296.116
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 68.91; H, 5.44; N, 9.45; O, 16.20
|
|
| CAS号 |
215543-92-3
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
SU 5402;215543-92-3
|
|
| PubChem CID |
5289418
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Orange solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
592.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
>222ºC (dec.)
|
|
| 闪点 |
312.2±30.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.688
|
|
| LogP |
2.03
|
|
| tPSA |
82.19
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
22
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
488
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C(CCC1=C(NC=C1C)/C=C2C(NC3=C\2C=CC=C3)=O)O
|
|
| InChi Key |
JNDVEAXZWJIOKB-JYRVWZFOSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H16N2O3/c1-10-9-18-15(11(10)6-7-16(20)21)8-13-12-4-2-3-5-14(12)19-17(13)22/h2-5,8-9,18H,6-7H2,1H3,(H,19,22)(H,20,21)/b13-8-
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-[4-methyl-2-[(Z)-(2-oxo-1H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]propanoic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3747 mL | 16.8737 mL | 33.7473 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6749 mL | 3.3747 mL | 6.7495 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3375 mL | 1.6874 mL | 3.3747 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
NIH 3T3 Flk-1 cells (A) or NIH 3T3 platelet-derived growth factor β cells (B) grown to confluency were preincubated with SU5416 at concentrations ranging from 0.05 to 50 μm for 1 h at 37°C. Cancer Res. 1999 Jan 1;59(1):99-106. |
A375 cells (3 × 106) were implanted subcutaneous into the hindflank region of female BALB/c nu/nu mice 8–12 weeks of age. Cancer Res. 1999 Jan 1;59(1):99-106. |
Rat C6 glioma cells were surgically implanted (0.5 × 106 cells/animal) under the serosa of the colon in BALB/c nu/nu mice. Beginning 1 day after implantation, animals were treated once daily with a 50 μl i.p. bolus injection of either SU5416 at 25 mg/kg/day in DMSO or DMSO alone for 16 days. On day 16 after implantation, animals were euthanized, and their local tumors in the colon were first quantitated by measurement using venier calipers and then harvested. Cancer Res. 1999 Jan 1;59(1):99-106. |