| 规格 | 价格 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
TACC3/transforming acidic coiled-coil-containing protein 3
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
贴壁培养中的 NPC 神经元可以剂量依赖性方式吸附 KHS101 (EC50 ~ 1 μM)[1]。 KHS101 (5 μM) 刺激 NPC 星形胶质细胞的产生 [1]。 KHS101 (5 μM) 和 KHS101 (0-15 μM; 24 h) 对 NPC 细胞周期的负荷和进展的影响是不利的 [1]。 KHS101 和 TACC3 的蛋白质电位反应 [1]。 KHS101(0-15 μM;24 小时)调节器 ARNT2 核定位 [RT-PCR[1]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
KHS101(6 mg/kg;皮下注射;BID 14 天)在体内分布于大脑中,显着促进神经元分泌[1]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
基于亲和力的目标识别。[1]
通过在PBS中超声处理制备NPC裂解物,并以2 mg/mL的浓度制备蛋白质样品。将二苯甲酮-KHS101化合物(KHS101-BP,5μM;SI Text)加入到50μL的蛋白质组反应中,有和没有未标记的化合物(250μM)。使用长波长(365nm)的手持紫外灯照射1小时,随后进行铜催化的叠氮-炔烃环加成反应(SI Text)。在室温下孵育1小时后,使用三氯乙酸沉淀蛋白质,并将其重新悬浮在等电聚焦样品缓冲液中。按照制造商的方案,使用ReadyStripe IPG条进行2D SDS-PAGE。 基于亲和力的目标识别[2] GBM1细胞在有或没有未标记的KHS101(250μM)的情况下与KHS101-BP(5μM)一起孵育30分钟,并用紫外光(365nm)照射30分钟。使用0.5%Triton X-100和蛋白酶抑制剂混合物裂解细胞。细胞裂解物与25μM叠氮化生物素、1 mM TCEP、100 mM配体(TBTA)和1 mM硫酸铜水溶液在4°C下孵育过夜。随后,使用硫酸铵对蛋白质进行分级,并对20-40%的级分进行2D SDS-PAGE。使用Abcam通过蛋白质印迹检测生物素标记的蛋白质;ab1227)。在平行凝胶上用银染色显示与特定生物素标记的蛋白质相对应的蛋白质斑点。切除一个明显的斑点,并使用液相色谱-串联质谱法鉴定蛋白质。对于HSPD1相互作用确认试验,将总共1μg重组HSPD1稀释在1 mL PBS(含2 mM MgCl2、2 mM DDT和0.1%吐温20)中,并在有或没有未标记的KHS101的情况下,在4°C下与5μM生物素化的KHS101一起孵育过夜。将链霉抗生物素蛋白琼脂糖珠加入孵育混合物中,并在4°C下旋转2小时。然后沉淀珠粒,在PBS中洗涤三次。用2x SDS样品缓冲液洗脱结合的蛋白质,用SDS-PAGE分析,然后进行银染和蛋白质印迹。 |
| 细胞实验 |
RT-PCR[1]
细胞类型:大鼠 NPC 测试浓度: 0.6、1.7 和 5 μM 孵育时间: 24 小时 实验结果: 显示 Cdkn1 mRNA 表达的剂量依赖性诱导。 1]。 细胞增殖测定 [1] 细胞类型:大鼠 NPC 测试浓度: 5 μM 孵育时间:24、48和72小时 实验结果:绝大多数NPC在72小时内停止增殖并变为非有丝分裂。 对于分化试验,将细胞以每孔5000个细胞的密度接种到96孔板中,并用100ng/mL的重组人BMP4处理4天。随后,在100μL培养基中用DMSO(0.1%)或KHS101(1-20μM)处理细胞48小时,并根据制造商的说明进行CellTiter-Glo测定。2. 对于集落形成试验,以125个细胞/孔的密度(在24孔板中)接种细胞并使其粘附。第二天,计数每孔的单细胞,并用DMSO或KHS101处理。10天后计数由>6个细胞组成的集落,并确定能够形成集落的细胞百分比。2. 对于活细胞分析,在加入KHS101(7.5μM)或DMSO(0.1%)之前,让细胞生长2天,随后监测3天。使用IncuCyte ZOOM活细胞成像系统以45分钟的间隔采集图像。2. 为了分析细胞活力和半胱天冬酶3/7活化,将细胞分别以10000和2500个细胞的密度接种到96孔板中。第二天,用载体(DMSO)、KHS101、KHS101/Z-VAD-FMK(20μM)或Staurosporine在100μL培养基中以指定浓度处理细胞。CellTiter Glo和Caspase Glo 3/7测定 根据制造商的说明在指定时间点进行。2. 为了使用膜联蛋白V和碘化丙啶定量凋亡,GBM1细胞用KHS101(7.5μM)、巴非霉素A1(10 nM)或载体(DMSO,0.1%)处理48小时,然后用胰蛋白酶收获,用PBS洗涤,并根据制造商的方案在37°C下用膜联蛋白V-荧光素染色试剂盒用膜联素V和碘化丙啶染色15分钟。使用NC3000细胞仪通过象限门控定量标记的早期凋亡和晚期凋亡/坏死细胞[2]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Adult Fisher 344 rats (∼10 weeks old) [1] Usage and
Doses: 6 mg/kg Route of Administration: SC, BID, for 14 days Experimental Results: Increased neuronal differentiation. NPC proliferation diminished. Animal Experiments.[1] To investigate the pharmacokinetic properties of KHS101, male Sprague–Dawley rats were administered 3 mg/kg KHS101 i.v. or s.c. One rat was killed per time point at 5 min, 40 min, 1 h, and 3 h after dosing, and samples of blood (100 μL) and whole brains were collected. In a separate study, rats were administered 6 mg/kg KHS101 i.v. or s.c. Five blood samples of 100 μL each were collected serially via a jugular vein catheter at 2 min (i.v. only), 0.5 h (s.c. only), and 1, 3, 7 and 24 h after dosing. Plasma and homogenized whole brain samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). To study neuronal differentiation upon KHS101 administration in vivo, adult Fisher 344 rats (∼10 wk old) received s.c. injections of 6 mg/kg KHS101 or vehicle control (5% ethanol in 15% Captisol). All rats received one daily i.p. injection of 200 mg/kg BrdU for 6 consecutive days after the first day. After 14 d, the animals were killed and perfusion fixed, and the brains were removed and subjected to immunohistochemical analysis. Xenograft tumor experiments [2] Animal experiments were carried out under UK project license approval and institutional guidelines. Animals were maintained under standard conditions (12 hour day/night cycle with food and water ad libitum). Experiments were carried out using 6 to 8-week-old NOD scid gamma (NSG) and BALB/c Nude mice for the GBM1 and GBMX1 models, respectively. Mice were stereotactically injected with 2 x 105 GBM1 cells or 8 x 104 GBMX1 cells in a volume of 2 μL (containing 30% Matrigel) into the right striatum (2.5 mm from the midline, 2.5 mm anterior from bregma, 3 mm deep). Surgery was performed under general anaesthesia using aseptic techniques. Mice were monitored daily for signs of sickness, pain or weight loss. After the indicated tumor-establishing period, 6 mg/kg KHS101 or vehicle control (5% (v/v) ethanol, 15% (w/v) (2-Hydroxypropyl)-β-cyclo-dextrin) was administered subcutaneously (s.c.) twice daily with bi-weekly alteration of 5 and 3 treatment days per week. Experiments were concluded at indicated endpoints and tissue was subjected to immunohistological and image analysis. Affinity-Based Target Identification.[1] NPC lysate was prepared by sonication in PBS and protein samples were prepared at a concentration of 2 mg/mL. The benzophenone-KHS101 compound (KHS101-BP, 5 μM; SI Text) was added to 50 μL of the proteome reaction with and without unlabeled compound (250 μM). Irradiation was for 1 h using a hand-held UV lamp at long wavelength (365 nm), and subsequently a copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition reaction was performed (SI Text). After incubation for 1 h at RT, proteins were precipitated using trichloroacetic acid and resuspended in isoelectric focusing sample buffer. 2D SDS/PAGE was performed using ReadyStripe IPG stripes following the manufacturer's protocol. Affinity-based target identification [2] GBM1 cells were incubated with KHS101-BP (5 μM) in the presence or absence of unlabeled KHS101 (250 μM) for 30 minutes, and irradiated with UV light (365nm) for 30 minutes. Cells were lysed using 0.5% Triton X-100 and protease inhibitor cocktail. Cell lysates were incubated with 25 μM biotin azide, 1 mM TCEP, 100 mM ligand (TBTA), and 1 mM aqueous copper sulfate at 4°C overnight. Subsequently, proteins were fractionated using ammonium sulfate and the 20-40% fractions were subject to 2D SDS/PAGE. Biotin-labeled proteins were detected through Western blotting using Abcam; ab1227). Protein spots corresponding to the specific biotin-labeled proteins were visualized with silver staining on parallel gels. A distinct spot was excised and protein identified using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. For HSPD1 interaction confirmation assays, a total of 1 μg recombinant HSPD1 was diluted in 1 mL PBS (with 2 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DDT, and 0.1% tween 20) and incubated with 5 μM biotinylated KHS101 at 4°C overnight in the presence or the absence of non-labeled KHS101. Streptavidin agarose beads were added to the incubation mixture and rotated at 4°C for 2 hours. The beads were then precipitated and washed three times in PBS. Bound proteins were eluted with 2x SDS sample buffer and analyzed with SDS/PAGE followed by silver staining and Western blotting. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Adult neurogenesis occurs in mammals and provides a mechanism for continuous neural plasticity in the brain. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms regulating hippocampal neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and whether their fate can be pharmacologically modulated to improve neural plasticity and regeneration. Here, we report the characterization of a small molecule (KHS101) that selectively induces a neuronal differentiation phenotype. Mechanism of action studies revealed a link of KHS101 to cell cycle exit and specific binding to the TACC3 protein, whose knockdown in NPCs recapitulates the KHS101-induced phenotype. Upon systemic administration, KHS101 distributed to the brain and resulted in a significant increase in neuronal differentiation in vivo. Our findings indicate that KHS101 accelerates neuronal differentiation by interaction with TACC3 and may provide a basis for pharmacological intervention directed at endogenous NPCs.[1]
Pharmacological inhibition of uncontrolled cell growth with small-molecule inhibitors is a potential strategy for treating glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most malignant primary brain cancer. We showed that the synthetic small-molecule KHS101 promoted tumor cell death in diverse GBM cell models, independent of their tumor subtype, and without affecting the viability of noncancerous brain cell lines. KHS101 exerted cytotoxic effects by disrupting the mitochondrial chaperone heat shock protein family D member 1 (HSPD1). In GBM cells, KHS101 promoted aggregation of proteins regulating mitochondrial integrity and energy metabolism. Mitochondrial bioenergetic capacity and glycolytic activity were selectively impaired in KHS101-treated GBM cells. In two intracranial patient-derived xenograft tumor models in mice, systemic administration of KHS101 reduced tumor growth and increased survival without discernible side effects. These findings suggest that targeting of HSPD1-dependent metabolic pathways might be an effective strategy for treating GBM.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C18H21N5S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
339.461
|
| 精确质量 |
339.152
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 63.69; H, 6.24; N, 20.63; S, 9.44
|
| CAS号 |
1262770-73-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
KHS101 hydrochloride;1784282-12-7
|
| PubChem CID |
71304818
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.775
|
| tPSA |
94.2
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
361
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
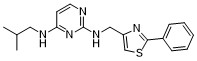
CC(C)CN=C1C=CN=C(NCC2=CSC(=N2)C3=CC=CC=C3)N1
|
| InChi Key |
DGRJOOOHPBSAHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H21N5S/c1-13(2)10-20-16-8-9-19-18(23-16)21-11-15-12-24-17(22-15)14-6-4-3-5-7-14/h3-9,12-13H,10-11H2,1-2H3,(H2,19,20,21,23)
|
| 化学名 |
N4-isobutyl-N2-((2-phenylthiazol-4-yl)methyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine
|
| 别名 |
KHS-101; KHS 101; N4-isobutyl-N2-((2-phenylthiazol-4-yl)methyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine; KHS-101; N4-(2-Methylpropyl)-N2-[(2-phenyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl]pyrimidine-2,4-diamine; 4-N-(2-methylpropyl)-2-N-[(2-phenyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl]pyrimidine-2,4-diamine; MLS006010727; CHEMBL3186037; KHS101;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9459 mL | 14.7293 mL | 29.4586 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5892 mL | 2.9459 mL | 5.8917 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2946 mL | 1.4729 mL | 2.9459 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。