| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The Cmax of amiodarone in the plasma is achieved about 3 to 7 hours after administration. The general time to onset of action of amiodarone after one dose given by the intravenous route is between 1 and 30 minutes, with therapeutic effects lasting from 1-3 hours. Steady-state concentrations of amiodarone in the plasma ranges between 0.4 to 11.99 μg/ml; it is advisable that steady-state levels are generally maintained between 1.0 and 2.5 μg/ml in patients with arrhythmias. Interestingly, its onset of action may sometimes begin after 2 to 3 days, but frequently takes 1 to 3 weeks, despite the administration of higher loading doses. The bioavailability of amiodarone varies in clinical studies, averaging between 35 and 65%. Effect of food In healthy subjects who were given a single 600-mg dose immediately after consuming a meal high in fat, the AUC of amiodarone increased by 2.3 and the Cmax by 3.8 times. Food also enhances absorption, reducing the Tmax by about 37%. Amiodarone is eliminated primarily by hepatic metabolism and biliary excretion. A small amount of desethylamiodarone (DEA) is found in the urine. In a pharmacokinetic study of 3 healthy individuals and 3 patients diagnosed with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), the volume of distribution was found to be 9.26-17.17 L/kg in healthy volunteers and 6.88-21.05 L/kg in the SVT patients. Prescribing information mentions that the volume of distribution of amiodarone varies greatly, with a mean distribution of approximately 60 L/kg. It accumulates throughout the body, especially in adipose tissue and highly vascular organs including the lung, liver, and spleen. One major metabolite of amiodarone, desethylamiodarone (DEA), is found in even higher proportions in the same tissues as amiodarone. The clearance of amiodarone after intravenous administration in patients with ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia ranged from 220 to 440 ml/hr/kg in one clinically study. Another study determined that the total body clearance of amiodarone varies from 0.10 to 0.77 L/min after one intravenous dose. Renal impairment does not appear to affect the clearance of amiodarone, but hepatic impairment may reduce clearance. Patients with liver cirrhosis exhibited significantly lower Cmax and mean amiodarone concentration for DEA, but not for amiodarone. Severe left ventricular dysfunction prolongs the half-life of DEA. A note on monitoring No guidelines have been developed for adjusting the dose of amiodarone in renal, hepatic, or cardiac abnormalities. In patients on chronic amiodarone treatment, close clinical monitoring is advisable, especially for elderly patients and those with severe left ventricular dysfunction. Metabolism / Metabolites This drug is metabolized to the main metabolite desethylamiodarone (DEA) by the CYP3A4 and CYP2C8 enzymes. The CYP3A4 enzyme is found in the liver and intestines. A hydroxyl metabolite of DEA has been identified in mammals, but its clinical significance is unknown. Amiodarone has known human metabolites that include N-Desethylamiodarone. Amiodarone is extensively metabolized in the liver via CYP2C8 (under 1% unchanged in urine), and can effect the metabolism of numerous other drugs. The major metabolite of amiodarone is desethylamiodarone (DEA), which also has antiarrhythmic properties. The metabolism of amiodarone is inhibited by grapefruit juice, leading to elevated serum levels of amiodarone. Route of Elimination: Amiodarone is eliminated primarily by hepatic metabolism and biliary excretion and there is negligible excretion of amiodarone or DEA in urine. Half Life: 58 days (range 15-142 days) Biological Half-Life The terminal half-life of amiodarone varies according to the patient, but is long nonetheless, and ranges from about 9-100 days. The half-life duration varies according to different sources. According to the prescribing information for amiodarone, the average apparent plasma terminal elimination half-life of amiodarone is of 58 days (ranging from 15 to 142 days). The terminal half-life range was between 14 to 75 days for the active metabolite, (DEA). The plasma half-life of amiodarone after one dose ranges from 3.2 to 79.7 hours, according to one source. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The antiarrhythmic effect of amiodarone may be due to at least two major actions. It prolongs the myocardial cell-action potential (phase 3) duration and refractory period and acts as a noncompetitive a- and b-adrenergic inhibitor. Toxicity Data Intravenous, mouse: LD50 = 178 mg/kg. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
After intravenous administration, amiodarone acts to relax smooth muscles that line vascular walls, decreases peripheral vascular resistance (afterload), and increases the cardiac index by a small amount. Administration by this route also decreases cardiac conduction, preventing and treating arrhythmias. When it is given orally, however, amiodarone does not lead to significant changes in the left ventricular ejection fraction. Similar to other anti-arrhythmic agents, controlled clinical trials do not confirm that oral amiodarone increases survival. Amiodarone prolongs the QRS duration and QT interval. In addition, a decreased SA (sinoatrial) node automaticity occurs with a decrease in AV node conduction velocity. Ectopic pacemaker automaticity is also inhibited. Thyrotoxicosis or hypothyroidism may also result from the administration of amiodarone, which contains high levels of iodine, and interferes with normal thyroid function. |
| 分子式 |
C25H29I2NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
645.31
|
| 精确质量 |
645.024
|
| CAS号 |
1951-25-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Amiodarone-d10 hydrochloride;1261393-77-4;Amiodarone hydrochloride;19774-82-4;Amiodarone-d4 hydrochloride;1216715-80-8
|
| PubChem CID |
2157
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow oil
|
| 密度 |
1.58 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
635.1ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
156ºC
|
| 闪点 |
337.9ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
4.95E-16mmHg at 25°C
|
| LogP |
6.936
|
| tPSA |
42.68
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
547
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
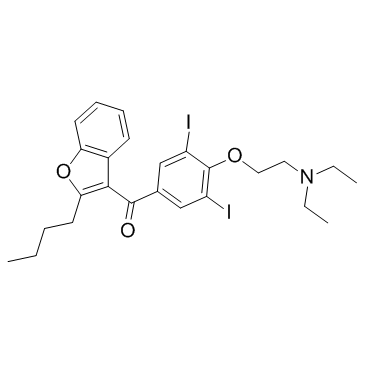
CCCCC1=C(C(C2=CC(I)=C(OCCN(CC)CC)C(I)=C2)=O)C3=C(O1)C=CC=C3
|
| InChi Key |
IYIKLHRQXLHMJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H29I2NO3/c1-4-7-11-22-23(18-10-8-9-12-21(18)31-22)24(29)17-15-19(26)25(20(27)16-17)30-14-13-28(5-2)6-3/h8-10,12,15-16H,4-7,11,13-14H2,1-3H3
|
| 化学名 |
(2-butyl-1-benzofuran-3-yl)-[4-[2-(diethylamino)ethoxy]-3,5-diiodophenyl]methanone
|
| 别名 |
Amiodaronum AratacCordarone Amiodarona Nexterone
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5496 mL | 7.7482 mL | 15.4964 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3099 mL | 1.5496 mL | 3.0993 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1550 mL | 0.7748 mL | 1.5496 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
MAGNAM Trial, Magnesium Versus Amiodarone in Atrial Fibrillation in Critical Care
CTID: NCT05287191
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-04-25