| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
VEGFR2 (IC50 = 1 nM); RET (IC50 = 13 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:阿帕替尼是一种有效的、口服生物可利用的选择性 VEGF(血管内皮生长因子受体)信号通路抑制剂,对 VEGFR2 的 IC50 为 1 nM。它具有潜在的抗血管生成和抗肿瘤活性。阿帕替尼有效抑制 VEGFR-2、c-kit 和 c-src 的激酶活性,并抑制 VEGFR-2、c-kit 和 PDGFRβ 的细胞磷酸化。阿帕替尼有效抑制FBS诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和管形成,并阻断大鼠主动脉环的出芽。阿帕替尼的 I 期研究显示出令人鼓舞的抗肿瘤活性和可控的毒性特征。这些发现表明阿帕替尼有望成为一种抗肿瘤药物,并可能具有临床益处。阿帕替尼有效抑制FBS诱导的人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖、迁移和管形成,并阻断大鼠主动脉环的出芽。阿帕替尼通过抑制 ABCB1 和 ABCG2 的转运功能来逆转 ABCB1 和 ABCG2 介导的 MDR,但不是通过阻断 AKT 或 ERK1/2 通路或下调 ABCB1 或 ABCG2 表达来逆转。阿帕替尼显着增强已建立的 ABCB1 和 ABCG2 底物的细胞毒性,并增加 ABCB1 或 ABCG2 过表达细胞中 DOX 和 Rho 123 的积累。此外,阿帕替尼以浓度依赖性方式显着抑制[125I]碘芳基叠氮哌唑嗪对ABCB1和ABCG2的光亲和标记。激酶测定:阿帕替尼 (YN968D1) 是一种新型口服生物可利用的选择性抑制剂,具有潜在的抗血管生成和抗肿瘤活性。阿帕替尼选择性结合并抑制 VEGFR2。 Apatinib 还可以有效抑制 Ret、c-kit 和 c-src 的活性,IC50 分别为 0.013 μM、0.429 μM 和 0.53 μM。阿帕替尼抑制 VEGFR-2、c-kit 和 PDGFRβ 的细胞磷酸化。阿帕替尼显着抑制 20 ng/mL VEGF 刺激的增殖(IC50 = 0.17μM)。细胞测定:在 HUVEC 中,阿帕替尼以浓度依赖性方式降低 VEGF 刺激的 VEGFR-2 KDR 磷酸化。它还在 0.1 μM 浓度下完全抑制 VEGFR-2 激活。此外,阿帕替尼以浓度依赖性方式分别消除用相关配体刺激的 Mo7e 和 NIH-3T3 细胞中 c-kit 和 PDGFRb 的磷酸化。此外,阿帕替尼在体外抑制 HUVEC 的增殖、迁移和管形成,并阻断大鼠主动脉环出芽。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在体内,阿帕替尼单独使用以及与化疗药物联合使用可有效抑制多种已建立的人类肿瘤异种移植模型的生长,且毒性很小。阿帕替尼以显着的剂量依赖性方式抑制多种人类肿瘤异种移植物的生长。阿帕替尼在裸鼠异种移植模型中逆转 ABCB1 介导的 MDR。阿帕替尼显着增强多柔比星在携带 K562/ADR 异种移植物的裸鼠中的抗肿瘤活性。
阿帕替尼在体内具有有效的肿瘤生长抑制作用。与对照组相比,肿瘤体积减小(图7a和b)。根据体外实验,图7c显示阿帕替尼治疗增加了LC3-II和Bax的水平,而体内BCL-2和VEGFR2的水平降低。免疫组织化学显示,阿帕替尼降低了KHOS细胞形成的肿瘤中VEGFR2、p-STAT3和BCL-2的表达(图7d)。所有结果均表明,阿帕替尼在体内抑制骨肉瘤的生长[2]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
酶联免疫吸附试验。[1]
YN968D1对酪氨酸激酶的抑制活性使用之前描述的ELISA方法测定。VEGFR-2和PDGFR是商业购买的;Her-2、c-kit和c-src是由巴氏杆菌杆状病毒表达载体系统表达并经Ni-NTA旋转柱纯化的活化细胞内蛋白酪氨酸激酶。使用VERSAmax在490nm处测量光密度。抑制活性以IC50表示,IC50是通过Logit方法从三个独立的实验中计算出来的。[1] 阿帕替尼(Apatinib)又名YN968D1,是一种新开发的选择性抑制剂,可口服,可能具有抗血管生成和抗肿瘤特性。阿帕替尼通过特异性结合 VEGFR2 来抑制 VEGFR2。阿帕替尼还对 Ret、c-kit 和 c-src 活性具有有效的抑制作用,IC50 值分别为 0.013 M、0.429 M 和 0.53 M。阿帕替尼可防止 PDGFRβ、c-kit 和 VEGFR-2 在细胞中磷酸化。 atainib 显着抑制 20 ng/mL VEGF 诱导的增殖(IC50 = 0.17μM)。 |
| 细胞实验 |
将 HUVEC 接种到 96 孔板中。孵育 24 小时后,将测试剂(作为对照的载体)与 20 ng ⁄mL VEGF 或 20% FBS 一起添加到细胞中,并再放置 72 小时。首先用10%三氯乙酸固定细胞,然后用0.4%磺基罗丹明B在37°C染色30分钟。然后用1%乙酸清洗。添加 Tris 溶解复合物后,测量 520 nm 光密度。1]
如前所述,CCK8测定用于评估细胞存活率。40实验前一天,在96孔板上每孔接种5000个细胞。在指定条件下用阿帕替尼孵育细胞。[2] 细胞凋亡分析和细胞周期:对于细胞周期分析,细胞在-20°C下用70%乙醇固定过夜,并用碘化丙啶染色。对于细胞凋亡分析,根据制造商的解释,用Annexin V/FITC试剂盒对细胞进行染色,并在阿帕替尼治疗后通过流式细胞术进行分析。[2] |
| 动物实验 |
tumor xenograft model (NCI-H460 human lung tumors, HCT 116 human colon tumors, or SGC-7901 human gastric tumors; BALB⁄cA nude mice)
50, 100 and 200 mg/kg by oral gavage[1] Nude mouse human tumor xenograft model. The effects of Apatinib (YN968D1) on tumor growth were tested against various human tumors grown subcutaneously in BALB/cA nude mice. Tumor growth was initiated by subcutaneous inoculation of cells into mice. Tumors were allowed to establish and grow to 100–300 mm3, at which time the mice were randomized into experimental groups. YN968D1 was administered once daily by oral gavage for the indicated periods (Table 1). In combination treatment experiments, mice were administered YN968D1 alone by oral gavage; 5‐FU, oxaliplatin, docetaxel and doxorubicin alone by intravenous injection; or YN968D1 in combination with each cytotoxic drug at the indicated dose and schedule (Table 2). Tumor volume and bodyweight were monitored every other day or every 3 days, with the means indicated for groups of six (treated) or 12 (vehicle control) animals. Tumor volumes were determined by measuring the largest diameter (a) and its perpendicular (b) according to the formula (a × b2)/2. The evaluation index for inhibition was the relative tumor growth ratio according to the equation: T/C (%) = mean increase of tumor volumes of treated groups/mean increase of tumor volumes of control groups × 100%.[1] A 4- to 6-week-old BALB/c nude mice were subcutaneously injected in the right flank with 2 × 106 KHOS cells. The mice were fed in specific pathogen-free conditions, and when a palpable mass developed, the mice were randomly divided into two sets and were administered DMSO or Apatinib 50 mg/kg orally daily for 30 days. The tumor was scaled every other day for 4 days. The tumor volume was counted by (length × width2/2). The mice were killed on the 13th day after the treatment. Tumor samples were prepared for western blot and IHC.[2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Pharmacokinetic evaluation revealed GNE-3511 exhibited moderate (mouse, rat, and cynomolgus) to high (dog) in vivo plasma clearances, moderate volumes of distribution, short half-lives, and brain penetration sufficient to enable examination in animal models of neurodegeneration (Table 6). DLK inhibitor GNE-3511 was then tested in the mouse optic nerve crush model of axonal injury, which mimics the degeneration that occurs in glaucoma or optic neuropathy. Our previous studies demonstrated that loss of DLK expression resulted in protection of retinal ganglion cell neurons from degeneration as well as an attenuation of downstream signaling following injury. In this and other neuronal injury models, phosphorylation of c-Jun (p-c-Jun) is strongly induced by injury in a DLK/JNK dependent fashion and could thus be used as a pharmacodynamic readout of DLK inhibition in vivo. Animals were dosed orally with either inhibitor GNE-3511 at two dose levels or vehicle control 30 min prior to nerve crush injury. Six hours after insult, levels of p-c-Jun in retina were measured using a MSD assay. Treatment with inhibitor GNE-3511 resulted in a dose-dependent reduction of p-c-Jun present in retina (Figure 5).
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Rivoceranib is under investigation in clinical trial NCT02726854 (Apatinib as Second-line Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer).
Rivoceranib is an orally bioavailable, small-molecule receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potential antiangiogenic and antineoplastic activities. Upon administration, rivoceranib selectively binds to and inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, which may inhibit VEGF-stimulated endothelial cell migration and proliferation and decrease tumor microvessel density. In addition, this agent mildly inhibits c-Kit and c-SRC tyrosine kinases. Angiogenesis is an important process in cell development, especially in cancer. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling is an important regulator of angiogenesis. Several therapies that act against VEGF signal transduction have been developed, including YN968D1, which is a potent inhibitor of the VEGF signaling pathway. This study investigated the antitumor activity of YN968D1 (apatinib mesylate) in vitro and in vivo. YN968D1 potently suppressed the kinase activities of VEGFR-2, c-kit and c-src, and inhibited cellular phosphorylation of VEGFR-2, c-kit and PDGFRβ. YN968D1 effectively inhibited proliferation, migration and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by FBS, and blocked the budding of rat aortic ring. In vivo, YN968D1 alone and in combination with chemotherapeutic agents effectively inhibited the growth of several established human tumor xenograft models with little toxicity. A phase I study of YN968D1 has shown encouraging antitumor activity and a manageable toxicity profile. These findings suggest that YN968D1 has promise as an antitumor drug and might have clinical benefits.[1] The cure rate of osteosarcoma has not improved in the past 30 years. The search for new treatments and drugs is urgently needed. Apatinib is a high selectivity inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR2) tyrosine kinase, exerting promising antitumoral effect in various tumors. The antitumor effect of Apatinib in human osteosarcoma has never been reported. We investigated the effects of Apatinib in osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Osteosarcoma patients with high levels of VEGFR2 have poor prognosis. Apatinib can inhibit cell growth of osteosarcoma cells. In addition to cycle arrest and apoptosis, Apatinib induces autophagy. Interestingly, inhibition of autophagy increased Apatinib-induced apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells. Immunoprecipitation confirmed direct binding between VEGFR2 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). Downregulation of VEGFR2 by siRNA resulted in STAT3 inhibition in KHOS cells. VEGFR2 and STAT3 are inhibited by Apatinib in KHOS cells, and STAT3 act downstream of VEGFR2. STAT3 and BCL-2 were downregulated by Apatinib. STAT3 knockdown by siRNA reinforced autophagy and apoptosis induced by Apatinib. BCL-2 inhibits autophagy and was apoptosis restrained by Apatinib too. Overexpression of BCL-2 decreased Apatinib-induced apoptosis and autophagy. Apatinib repressed the expression of STAT3 and BCL-2 and suppressed the growth of osteosarcoma in vivo. To sum up, deactivation of VEGFR2/STAT3/BCL-2 signal pathway leads to Apatinib-induced growth inhibition of osteosarcoma.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C24H23N5O.CH4O3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
493.57798
|
| 精确质量 |
397.19
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 72.52; H, 5.83; N, 17.62; O, 4.03
|
| CAS号 |
811803-05-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1218779-89-5 (HCl);1218779-75-9 (mesylate);811803-05-1;
|
| PubChem CID |
11315474
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| LogP |
4.1
|
| tPSA |
90.7Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
608
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
WPEWQEMJFLWMLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H23N5O/c25-17-24(11-1-2-12-24)19-5-7-20(8-6-19)29-23(30)21-4-3-13-27-22(21)28-16-18-9-14-26-15-10-18/h3-10,13-15H,1-2,11-12,16H2,(H,27,28)(H,29,30)
|
| 化学名 |
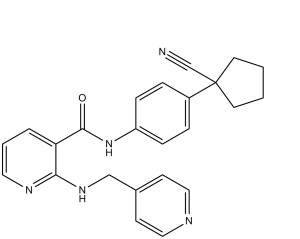
N-[4-(1-cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylamino)pyridine-3-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
YN968D1; YN-968D1; YN 968D1; Rivoceranib; Apatinib; 811803-05-1; rivoceranib; Apatinib free base; Apatinib (free base); YN968D1; N-(4-(1-Cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl)-2-((pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino)nicotinamide; N-[4-(1-cyanocyclopentyl)phenyl]-2-(pyridin-4-ylmethylamino)pyridine-3-carboxamide; Apatinib free base
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0260 mL | 10.1301 mL | 20.2601 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4052 mL | 2.0260 mL | 4.0520 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2026 mL | 1.0130 mL | 2.0260 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03742193 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Apatinib Drug: GD regimen |
Apatinib Osteosarcoma |
Ruijin Hospital | August 11, 2019 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06081595 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Fluzoparib Drug: Apatinib |
Relapsed Ovarian Cancer | Jin Li | October 30, 2023 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04824352 | Recruiting | Drug: apatinib | Effect of Drug Toxicity, Drug |
Peking University People's Hospital | April 1, 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05235100 | Recruiting | Drug: Apatinib Mesylate | Trunk Extremity |
Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences |
September 1, 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04863430 | Recruiting | Drug: Apatinib Drug: Oxaliplatin |
Gastric Cancer | Peking University | May 11, 2021 | Phase 2 |
Effects of YN968D1 on various growth factor‐stimulated receptor phosphorylation at the cellular level detected by western blot analysis.Cancer Sci.2011 Jul;102(7):1374-80. |
Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)‐stimulated HUVEC proliferation, HUVEC tubule formation, HUVEC migration and microvessel outgrowth from rat aortic ring by YN968D1. |
Antitumor activity of YN968D1 against human tumor xenografts in nude mice.Cancer Sci.2011 Jul;102(7):1374-80. |