| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Thrombin; Trypsin (Kd = 0.06 pM); kallikrein (Kd = 0.8 nM); chymotrypsin (Kd = 9.5 nM); trypsinogen (Kd = 2 μM)
Aprotinin is an irreversible inhibitor of serine proteases, including trypsin (Ki = 0.06 nM), plasmin (Ki = 0.15 nM), and kallikrein (Ki = 0.08 nM) [1] - Aprotinin inhibits factor XIIa (Ki = 0.2 nM) and factor XIa (Ki = 0.5 nM), key enzymes in the intrinsic coagulation pathway [2] - Aprotinin blocks serine proteases involved in embryonic tissue remodeling during chick limb development [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
抑肽酶是一种抗纤维蛋白溶解分子,可抑制胰蛋白酶和相关蛋白水解酶。在细胞生物学中,抑肽酶用作酶抑制剂,以防止细胞和组织裂解或匀浆过程中蛋白质降解。在抑肽酶存在下,纤溶活性受到浓度依赖性抑制,并且凝血时间延长。抑肽酶是体外接触(内在)凝血途径的有效抑制剂。细胞测定:将小鼠 G8-1 成肌细胞置于 DMEM + 20% FBS(维持培养基)中,在其中它们保持未分化。当细胞达到大约 40-50% 汇合时,将不同的蛋白酶抑制剂添加到培养基中并将细胞孵育过夜。然后将细胞转移至分化促进培养基(DMEM + 10%马血清±蛋白酶抑制剂)并孵育7天。
在无细胞酶活实验中,Aprotinin 以剂量依赖性方式抑制胰蛋白酶、纤溶酶和激肽释放酶:浓度为1 nM时,胰蛋白酶活性降低约98%,纤溶酶降低约95%,激肽释放酶降低约97% [1] - 在人血浆凝血实验中,100 IU/mL Aprotinin 可使活化部分凝血活酶时间(APTT)延长约40%,并使纤溶酶介导的纤维蛋白降解减少约85%(通过纤维蛋白平板实验检测)[2] - 在鸡胚肢芽间充质细胞原代培养中,50 IU/mL Aprotinin 处理48小时可抑制细胞迁移约60%(transwell实验),并使胶原酶活性降低约55%(明胶酶谱法检测)[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
抑肽酶在体外抑制血块溶解,在体内抑制鼠尾出血时间,并延长人血浆中的凝血时间。在大鼠动静脉分流模型中,抑肽酶可减少血栓重量。
在大鼠动脉血栓模型(通过FeCl₃诱导颈动脉损伤建立)中,以20,000 IU/kg/h的剂量静脉输注Aprotinin 2小时,血栓重量较溶剂对照组减少约55%;未观察到出血时间显著延长[2] - 在鸡胚肢体发育模型(卵内注射)中,胚胎发育第3天(E3)向羊膜腔注射100 IU Aprotinin 可干扰指(趾)形成:E10时,完全发育的指(趾)数量从对照组的4-5个减少至2-3个,指间组织退化延迟约48小时[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
抑肽酶(IC(50),0.16+/-0.02微摩尔L(-1))和氨甲环酸(IC(50,24.1+/-1.1微摩尔L))可抑制纤维蛋白溶解。在体内,抑肽酶剂量依赖性地减少大鼠尾部出血时间(最小有效剂量,3 mg kg(-1)推注加6 mg kg(-1h)输注);氨甲环酸减少出血时间(最小有效剂量,100 mg/kg(-1)h(-1))。在体外,抑肽酶在3.2+/-0.2微摩尔L(-1)的浓度下使凝血时间增加了一倍,而氨甲环酸在浓度高达3毫摩尔L(-1)时没有表现出任何影响。抑肽酶以剂量依赖的方式抑制体内血栓形成(最小有效剂量,3 mg kg(-1)推注加6 mg kg(-1h)输注)。相反,氨甲环酸剂量依赖性地增加血栓形成和血栓重量(最低有效剂量,100 mg kg(-1)h(-1)输注)[2]。
丝氨酸蛋白酶活性检测流程(基于[1]摘要描述):将纯化的胰蛋白酶、纤溶酶或激肽释放酶稀释于Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH 8.0,含0.15 M NaCl)中。加入各酶特异性显色底物(胰蛋白酶用S-2222,纤溶酶用S-2251,激肽释放酶用S-2302)至终浓度0.5 mM,再加入0.01 nM~10 nM的Aprotinin。混合物在37°C孵育30分钟后,检测405 nm处的吸光度以计算酶活性。通过与溶剂对照组比较确定抑制率,并采用Lineweaver-Burk双倒数作图法计算Ki值[1] - XIIa/XIa因子活性检测流程(基于[2]摘要描述):将重组人XIIa因子或XIa因子与各自的显色底物(XIIa因子用S-2337,XIa因子用S-2366)混合于HEPES缓冲液(pH 7.4,含5 mM CaCl₂)中。加入0.05 nM~5 nM的Aprotinin,在37°C孵育45分钟后检测405 nm处的吸光度,相对于无药对照组定量酶抑制率[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
小鼠 G8-1 成肌细胞在维持培养基 (DMEM + 20% FBS) 中培养,不分化。当细胞达到约 40-50% 汇合时,将不同的蛋白酶抑制剂添加到培养基中,然后将细胞再孵育一晚。之后,使用分化促进培养基(DMEM + 10%马血清±蛋白酶抑制剂)将细胞置于7天的孵育期。
鸡胚肢芽间充质细胞实验流程(基于[3]摘要描述):从E3鸡胚中分离肢芽,用胶原酶消化获得间充质细胞。将细胞以5×10⁴细胞/孔的密度接种于含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基中,向培养基中加入10 IU/mL~100 IU/mL的Aprotinin,孵育48小时。迁移实验中,将细胞接种于transwell小室(8 μm孔径)上室,对下室膜上的迁移细胞进行染色并计数;胶原酶活性检测时,将培养上清液通过含明胶的SDS-PAGE凝胶分离,孵育后用考马斯亮蓝染色,以透明带面积量化胶原酶活性[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Rats: In the study, male Wistar rats weighing 180–220 g are employed. Physiological saline dissolves aprotinin. A maintenance infusion is given after a bolus injection of aprotinin. 1.5 mg kg -1 and 3 mg kg -1 h -1 , 3 mg kg -1 and 6 mg kg -1 h -1 , up to 5 mg kg -1 and 10 mg kg -1 h -1 , are the doses that are administered. Pharmacokinetic studies in rats are used to determine the plasma concentrations of the two agents[4].
Mice: The study employed an intact mouse model of ischemia/reperfusion (30 min-I/60 min-R), and the mice were divided into four groups: wild type (WT, C57BL/6; n = 10), WT mice with aprotinin (4mL/kg; n = 10), transgenic mice lacking the TNFRI (TNFRInull; n = 10), and TNFRInull with aprotinin (n = 10)[6].
Rat arterial thrombosis model (from [2] abstract description): Male Sprague-Dawley rats (300-350 g) were anesthetized with isoflurane. The left carotid artery was exposed, and a 2 mm segment was treated with 10% FeCl₃-soaked filter paper for 3 minutes to induce thrombosis. Aprotinin was dissolved in 0.9% physiological saline and administered via intravenous infusion at 20,000 IU/kg/h for 2 hours (starting 10 minutes before FeCl₃ treatment). Vehicle controls received saline infusion. After 2 hours, the carotid artery was excised, and thrombus weight was measured; bleeding time was assessed via tail transection assay [2] - Chick embryo in ovo assay (from [3] abstract description): Fertilized chick eggs were incubated at 37°C with 60% humidity until E3. A small window was opened in the eggshell, and 100 IU Aprotinin (dissolved in 50 μL sterile PBS) was injected into the amniotic cavity. Control eggs received 50 μL PBS. Eggs were re-sealed and incubated until E10, when embryos were harvested. Limb development was evaluated by counting fully formed digits and measuring interdigital tissue area via image analysis [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
100% (IV) Following a single IV dose of radiolabelled aprotinin, approximately 25-40% of the radioactivity is excreted in the urine over 48 hours. After a 30 minute infusion of 1 million KIU, about 2% is excreted as unchanged drug. After a larger dose of 2 million KIU infused over 30 minutes, urinary excretion of unchanged aprotinin accounts for approximately 9% of the dose. After intravenous (iv) injection, rapid distribution of aprotinin occurs into the total extracellular space, leading to a rapid initial decrease in plasma aprotinin concentration. Following a single iv dose of radiolabelled aprotinin, approximately 25-40% of the radioactivity is excreted in the urine over 48 hours. After a 30 minute infusion of 1 million KIU, about 2% is excreted as unchanged drug. After a larger dose of 2 million KIU infused over 30 minutes, urinary excretion of unchanged aprotinin accounts for approximately 9% of the dose. Animal studies have shown that aprotinin is accumulated primarily in the kidney. Aprotinin, after being filtered by the glomeruli, is actively reabsorbed by the proximal tubules in which it is stored in phagolysosomes. There are no available studies on the distribution of aprotinin into breast milk. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for APROTININ (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Aprotinin is slowly degraded by lysosomal enzymes. Aprotinin is slowly degraded by lysosomal enzymes. The physiological renal handling of aprotinin is similar to that of other small proteins, e.g., insulin. Biological Half-Life Following this distribution phase, a plasma half-life of about 150 minutes is observed. At later time points, (i.e., beyond 5 hours after dosing) there is a terminal elimination phase with a half-life of about 10 hours. Following this distribution phase, a plasma half-life of about 150 minutes is observed. At later time points, (i.e., beyond 5 hours after dosing) there is a terminal elimination phase with a half-life of about 10 hours. In male beagle dogs (10-12 kg) administered intravenous Aprotinin at 50,000 IU/kg, the plasma elimination half-life (t₁/₂β) was ~2.5 hours, and the volume of distribution (Vd) was ~0.3 L/kg [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In the rat arterial thrombosis model, intravenous infusion of Aprotinin at 40,000 IU/kg/h (twice the therapeutic dose) caused transient hypotension in 2 out of 5 rats (mean arterial pressure decreased by ~15% for 10 minutes), which recovered spontaneously; no mortality or organ damage was observed [2]
- In chick embryos, repeated in ovo injection of Aprotinin (100 IU at E3 and E5) resulted in 30% embryo mortality by E10, compared to 5% in control groups [3] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Aprotinin is a protein-based drug that is also known as bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI). Since it demonstrates the capacity to slow fibrinolysis, it has been employed to reduce bleeding during complex surgery such as heart and liver surgery. For this use, it is typically administered by injection. The goal of using of aprotinin was subsequently to minimize end-organ damage resulting from hypotension due to blood loss in surgery and to reduce the necessity for blood transfusions during surgery. Nevertheless, the drug was formally withdrawn worldwide in May of 2008 after studies confirmed that its use enhanced the risk of complications or death. The substance is consequently made available only for very restricted research use.
Aprotinin is a single chain polypeptide isolated from bovine lung with antifibrinolytic and anti-inflammatory activities. As a broad-spectrum serine protease inhibitor, aprotinin bovine competitively and reversibly inhibits the activity of a number of different esterases and proteases, including trypsin, chymotrypsin, kallikrein, plasmin, tissue plasminogen activator, and tissue and leukocytic proteinases, resulting in attenuation of the systemic inflammatory response (SIR), fibrinolysis, and thrombin generation. This agent also inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine release and maintains glycoprotein homeostasis. A single-chain polypeptide derived from bovine tissues consisting of 58 amino-acid residues. It is an inhibitor of proteolytic enzymes including CHYMOTRYPSIN; KALLIKREIN; PLASMIN; and TRYPSIN. It is used in the treatment of HEMORRHAGE associated with raised plasma concentrations of plasmin. It is also used to reduce blood loss and transfusion requirements in patients at high risk of major blood loss during and following open heart surgery with EXTRACORPOREAL CIRCULATION. (Reynolds JEF(Ed): Martindale: The Extra Pharmacopoeia (electronic version). Micromedex, Inc, Englewood, CO, 1995) See also: Aprotinin (annotation moved to). Drug Indication For prophylactic use to reduce perioperative blood loss and the need for blood transfusion in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass in the course of coronary artery bypass graft surgery who are at an increased risk for blood loss and blood transfusion. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Aprotinin inhibits serine proteases including trypsin, chymotrypsin and plasmin at a concentration of about 125,000 IU/mL, and kallikrein at 300,000 IU/mL. The inhibition of kallikrein inhibits formation of factor XIIa. This inhibits the intrinsic pathway of coagulation and fibrinolysis. Inhibition of plasmin also slows fibrinolysis. Aprotinin is a broad spectrum protease inhibitor which modulates the systemic inflammatory response (SIR) associated with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) surgery. SIR results in the interrelated activation of the hemostatic, fibrinolytic, cellular and humoral inflammatory systems. Aprotinin, through its inhibition of multiple mediators (e.g., kallikrein, plasmin) results in the attenuation of inflammatory responses, fibrinolysis, and thrombin generation. Aprotinin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine release and maintains glycoprotein homeostasis. In platelets, aprotinin reduces glycoprotein loss (e.g., GpIb, GpIIb/IIIa), while in granulocytes it prevents the expression of pro-inflammatory adhesive glycoproteins (e.g., CD11b). The effects of aprotinin use in ... /cardiopulmonary bypass/ involves a reduction in inflammatory response which translates into a decreased need for allogeneic blood transfusions, reduced bleeding, and decreased mediastinal re-exploration for bleeding. Aprotinin is thought to improve hemostasis during and after cardiopulmonary bypass by preserving platelet membrane receptors that maintain the adhesive and aggregative capacity of platelets. In addition, aprotinin inhibits fibrinolysis through inhibition of plasmin and plasma and tissue kallikreins. Because of its effects on kallikrein, aprotinin also inhibits activation of the intrinsic clotting system (i.e., contact phase of coagulation), a process that both initiates coagulation and promotes fibrinolysis. The relative contribution of these effects of aprotinin to the drug's therapeutic action remains to be fully elucidated. For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for APROTININ (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Aprotinin is a naturally occurring polypeptide (58 amino acids) originally isolated from bovine lung, classified as a Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor [1] - Clinically, Aprotinin was historically used to reduce bleeding during cardiac surgery and orthopedic procedures by inhibiting plasmin-mediated fibrinolysis and coagulation cascade proteases; it was withdrawn from some markets due to concerns about hypersensitivity reactions and increased risk of thrombotic events [2] - In developmental biology, Aprotinin is used as a research tool to study the role of serine proteases in tissue remodeling, cell migration, and organogenesis (e.g., limb digit formation) [3] |
| 分子式 |
C284H432N84O79S7
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
6511.51
|
|
| 精确质量 |
6507
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 52.44; H, 6.59; N, 18.09; O, 19.43; S, 3.45
|
|
| CAS号 |
9087-70-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
16130295
|
|
| 序列 |
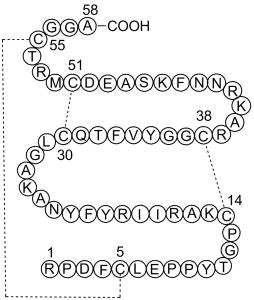
Arg-Pro-Asp-Phe-Cys-Leu-Glu-Pro-Pro-Tyr-Thr-Gly-Pro-Cys-Lys-Ala-Arg-Ile-Ile-Arg-Tyr-Phe-Tyr-Asn-Ala-Lys-Ala-Gly-Leu-Cys-Gln-Thr-Phe-Val-Tyr-Gly-Gly-Cys-Arg-Ala-Lys-Arg-Asn-Asn-Phe-Lys-Ser-Ala-Glu-Asp-Cys-Met-Arg-Thr-Cys-Gly-Gly-Ala(Disulfide bridge: Cys5-Cys55,Cys14-Cys38,Cys30-Cys51)
|
|
| 短序列 |
RPDFCLEPPYTGPCKARIIRYFYNAKAGLCQTFVYGGCRAKRNNFKSAEDCMRTCGGA(Disulfide bridge: Cys5-Cys55,Cys14-Cys38,Cys30-Cys51)
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light brown solid powder
|
|
| 熔点 |
>100 °C
|
|
| LogP |
-25.4
|
|
| tPSA |
2820Ų
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
93
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
97
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
111
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
454
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
16700
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
57
|
|
| SMILES |
NC(=N)NCCC[C@@H](N)C(=O)N1[C@H](CCC1)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)N[C@H]3C(=O)N[C@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(=O)N4[C@H](CCC4)C(=O)N5[C@@H](CCC5)C(=O)N[C@H](CC6=CC=C(O)C=C6)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@H](C)O)C(=O)NCC(=O)N7[C@@H](CCC7)C(=O)N[C@H]8C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@H]([C@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC9=CC=C(O)C=C9)C(=O)N[C@H](CC%10=CC=CC=C%10)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC%11=CC=C(O)C=C%11)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H]%12C(=O)N[C@H](CCC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)O)C(=O)N[C@H](CC%13=CC=CC=C%13)C(=O)N[C@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](CC%14=CC=C(O)C=C%14)C(=O)NCC(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H](CSSC8)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(=O)N[C@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC%15=CC=CC=C%15)C(=O)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@H](CSSC%12)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(=O)N[C@H](CCCNC(N)=N)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@H](C)O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CSSC3)C(=O)NCC(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@H](C)C(O)=O
|
|
| InChi Key |
ZPNFWUPYTFPOJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C284H432N84O79S7/c1-21-144(9)222-271(439)337-174(68-46-105-309-282(300)301)239(407)340-187(120-160-77-85-164(374)86-78-160)251(419)341-185(116-156-55-29-24-30-56-156)250(418)342-188(121-161-79-87-165(375)88-80-161)252(420)346-191(123-208(291)378)246(414)322-149(14)230(398)326-168(62-35-39-98-285)234(402)319-146(11)227(395)314-132-215(385)324-181(113-141(3)4)247(415)354-199-137-452-453-138-200-263(431)336-179(97-112-448-20)242(410)331-176(70-48-107-311-284(304)305)244(412)363-226(154(19)372)274(442)358-197(233(401)316-129-212(382)312-130-213(383)318-151(16)278(446)447)135-449-451-139-201(355-253(421)186(117-157-57-31-25-32-58-157)344-256(424)195(127-220(393)394)350-267(435)204-72-50-109-366(204)275(443)167(289)61-43-102-306-279(294)295)265(433)339-182(114-142(5)6)248(416)338-180(93-96-218(389)390)276(444)368-111-52-74-206(368)277(445)367-110-51-73-205(367)268(436)349-189(122-162-81-89-166(376)90-82-162)259(427)362-224(152(17)370)269(437)317-133-216(386)365-108-49-71-203(365)266(434)357-202(264(432)333-169(63-36-40-99-286)235(403)320-148(13)229(397)328-175(69-47-106-310-283(302)303)243(411)360-223(145(10)22-2)272(440)361-222)140-454-450-136-198(325-214(384)131-313-211(381)128-315-232(400)183(119-159-75-83-163(373)84-76-159)351-270(438)221(143(7)8)359-258(426)190(118-158-59-33-26-34-60-158)352-273(441)225(153(18)371)364-245(413)177(335-262(199)430)91-94-207(290)377)261(429)334-172(66-44-103-307-280(296)297)236(404)321-147(12)228(396)327-170(64-37-41-100-287)237(405)330-173(67-45-104-308-281(298)299)238(406)345-192(124-209(292)379)255(423)347-193(125-210(293)380)254(422)343-184(115-155-53-27-23-28-54-155)249(417)332-171(65-38-42-101-288)240(408)353-196(134-369)260(428)323-150(15)231(399)329-178(92-95-217(387)388)241(409)348-194(126-219(391)392)257(425)356-200/h23-34,53-60,75-90,141-154,167-206,221-226,369-376H,21-22,35-52,61-74,91-140,285-289H2,1-20H3,(H2,290,377)(H2,291,378)(H2,292,379)(H2,293,380)(H,312,382)(H,313,381)(H,314,395)(H,315,400)(H,316,401)(H,317,437)(H,318,383)(H,319,402)(H,320,403)(H,321,404)(H,322,414)(H,323,428)(H,324,385)(H,325,384)(H,326,398)(H,327,396)(H,328,397)(H,329,399)(H,330,405)(H,331,410)(H,332,417)(H,333,432)(H,334,429)(H,335,430)(H,336,431)(H,337,439)(H,338,416)(H,339,433)(H,340,407)(H,341,419)(H,342,418)(H,343,422)(H,344,424)(H,345,406)(H,346,420)(H,347,423)(H,348,409)(H,349,436)(H,350,435)(H,351,438)(H,352,441)(H,353,408)(H,354,415)(H,355,421)(H,356,425)(H,357,434)(H,358,442)(H,359,426)(H,360,411)(H,361,440)(H,362,427)(H,363,412)(H,364,413)(H,387,388)(H,389,390)(H,391,392)(H,393,394)(H,446,447)(H4,294,295,306)(H4,296,297,307)(H4,298,299,308)(H4,300,301,309)(H4,302,303,310)(H4,304,305,311)
|
|
| 化学名 |
4-[[1-[[29a,62a,69,84-tetrakis(4-aminobutyl)-35a,75,78-tris(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-14a-(3-amino-3-oxopropyl)-8a,41a,72-tribenzyl-50a,53a-di(butan-2-yl)-47a,48,56a,81,90-pentakis(3-carbamimidamidopropyl)-31,60-bis(2-carboxyethyl)-42-[[2-[[2-(1-carboxyethylamino)-2-oxoethyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]carbamoyl]-57-(carboxymethyl)-11a,13,45-tris(1-hydroxyethyl)-66-(hydroxymethyl)-2a,16,38a,44a-tetrakis[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-26a,32a,59a,63,87-pentamethyl-20a,34-bis(2-methylpropyl)-51-(2-methylsulfanylethyl)-1a,3,4a,7a,9,10a,12,13a,15,16a,18,19a,22a,24,25a,28a,30,31a,33,34a,36,37a,40a,43a,44,46a,47,49a,50,52a,53,55a,56,58a,59,61a,62,64a,65,68,71,74,77,80,83,86,89,92,95,98-pentacontaoxo-5a-propan-2-yl-39,40,66a,67a,70a,71a-hexathia-a,2,3a,6a,8,9a,11,12a,14,15a,17,18a,21a,23,24a,27a,29,30a,32,33a,35,36a,39a,42a,43,45a,46,48a,49,51a,52,54a,55,57a,58,60a,61,63a,64,67,70,73,76,79,82,85,88,91,94,97-pentacontazahexacyclo[91.71.4.454,117.04,8.019,23.025,29]doheptacontahectan-37-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-3-[[1-(2-amino-5-carbamimidamidopentanoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
Note: 如何溶解多肽产品?请参考本产品网页右上角“产品说明书“文件,第4页。 注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。 注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.1536 mL | 0.7679 mL | 1.5357 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.0307 mL | 0.1536 mL | 0.3071 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0154 mL | 0.0768 mL | 0.1536 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00357851 | Completed | Drug: Aprotinin | Pancreatitis | Nemours Children's Clinic | March 2005 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00257751 | Completed | Procedure: Aprotinine | Coronary Artery Disease | Oslo University Hospital | March 2004 | Not Applicable |
| NCT00668031 | Completed | Drug: Trasylol (Aprotinin, BAYA0128) Drug: dolutegravir |
Blood Loss, Surgical | Bayer | February 2005 | Phase 3 |
| NCT00617955 | Completed | Drug: Aprotinin Drug: Amicar |
Cardiac Surgery | State University of New York - Upstate Medical University |
September 2007 | |
| NCT00131040 | Completed | Drug: Aprotinin | Ischemic Heart Disease Angina Pectoris |
Imperial College London | January 2003 | Not Applicable |
 |
|---|
 |
 |
 |
|---|
 |