| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
用依泽斯汀极大地抑制 HNEpC 增殖有助于对抗气道重塑 [5]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在糖尿病高脂血症蛋白 B 的大鼠模型中,依泽斯汀(4 mg/kg;口服;每日;持续 8 周)可显着降低血清碱性磷酸酶 (ALP)、骨钙素、血糖和 HbA1c,并下调脂多糖 [2]。在糖尿病高脂血症大鼠模型中,依泽斯汀(4 mg/kg;口服;每日;持续 8 周)可改善血脂状况(增加 HDL-c 并降低 LDL-c)[2]。在糖尿病高脂血症大鼠模型中,依泽斯汀(4 mg/kg;口服;每日;持续 8 周)可减少主动脉钙化和钙沉积 [2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞增殖测定 [5]
细胞类型: 人鼻上皮细胞 (HNEpC) 测试浓度: 100 μM、400 μM 孵化持续时间:21天 实验结果:抑制HNEpC生长。 蛋白质印迹分析[5] 细胞类型: 人鼻上皮细胞 (HNEpC) 测试浓度: 100 μM 孵化时间:7天 实验结果:H1R、M1R和M3R水平显着上调。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male albino Wistar rat (150-170 g), diabetic hyperlipidemia rat model [2]
Doses: 4 mg/kg Route of Administration: Orally, one time/day for 8 weeks Experimental Results: Aortic calcification Improvement, apolipoprotein A expression increased, while apolipoprotein B diminished. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Systemic bioavailability of azelastine hydrochloride following intranasal administration is approximately 40%, reaching Cmax within 2-3 hours. When administered at doses greater than the recommended maximum, greater than proportional increases in both Cmax and AUC were observed. After an oral dose of radio-labeled azelastine hydrochloride, approximately 75% was excreted in the feces, with less than 10% as unchanged azelastine hydrochloride. After intravenous and oral administration, the steady-state volume of distribution is 14.5 L/kg. Based on intravenous and oral administration, azelastine demonstrated a plasma clearance of 0.5 L/h/kg. After intranasal administration, the systemic bioavailability of azelastine hydrochloride is approximately 40%. Maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) are achieved in 2-3 hours. Based on oral, single-dose studies, renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance <50 mL/min) resulted in a 70-75% higher Cmax and AUC compared to normal subjects. Time to maximum concentration was unchanged. Based on intravenous and oral administration, the steady-state volume of distribution, and plasma clearance are 14.5 L/kg, and 0.5 L/hr/kg, respectively. In vitro studies with human plasma indicate that the plasma protein binding of azelastine and desmethylazelastine are approximately 88% and 97%, respectively. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for Azelastine (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Azelastine hydrochloride is oxidatively metabolized to its main, and biologically active, metabolite desmethylazelastine by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Though labels for azelastine state that specific CYP enzyme involvement has not been elucidated, it has been suggested that the N-demethylation of azelastine is primarily catalyzed by CYP3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP1A2. Azelastine is oxidatively metabolized to the principal active metabolite, desmethylazelastine, by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. The specific P450 isoforms responsible for the biotransformation of azelastine have not been identified The major active metabolite, desmethylazelastine, was not measurable (below assay limits) after single-dose intranasal administration of azelastine hydrochloride. After intranasal dosing of azelastine hydrochloride to steady-state, plasma concentrations of desmethylazelastine range from 20-50% of azelastine concentrations. The ... pharmacokinetics of azelastine hydrochloride after single and multiple dosing (4.4 mg as tablet, tau = 12 hr) were investigated in 14 volunteers (6 female, 8 male) older than 65 years (70 +/- 5 years, mean +/- SD). ... The RIA co-detects besides azelastine the pharmacodynamically active metabolite N-demethyl-azelastine and thus, the parameters describe the pharmacokinetic behaviour as a resultant from both compounds, i.e. the "active principle". N-Demethylated metabolites are known to have longer half-lives usually than their parent compounds and thus, accumulate in a higher degree during multiple dosing. Azelastine hydrochloride is oxidatively metabolized to the principal metabolite, N-desmethylazelastine, by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, however the exact cytochrome P450 isoenzyme involved has not been determined. The major metabolite, desmethylazelastine, also has H1-receptor antagonist activity. Route of Elimination: Approximately 75% of an oral dose of radiolabeled azelastine hydrochloride was excreted in the feces with less than 10% as unchanged azelastine. Azelastine hydrochloride is oxidatively metabolized to the principal metabolite, N-desmethylazelastine, by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Half Life: Elimination half-life (based on intravenous and oral administration) is 22 hours. Elimination half-life of the active metabolite, desmethylazelastine, is 54 hours (after oral administration of azelastine). Biological Half-Life Based on intravenous and oral administration, azelastine demonstrated an elimination half-life of 22 hours. Its primary active metabolite, desmethylazelastine, has an elimination half-life of 54 hours. Based on intravenous and oral administration, the elimination half-life is 22 hours ... When azelastine hydrochloride is administered orally, desmethylazelastine has an elimination half-life of 54 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Azelastine competes with histamine for the H1-receptor sites on effector cells and acts as an antagonist by inhibiting the release of histamine and other mediators involved in the allergic response. Interactions Concurrent use of Astelin Nasal Spray with alcohol or other CNS depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of CNS performance may occur. Cimetidine increased the mean Cmax and AUC of orally administered azelastine hydrochloride by approximately 65%. Ranitidine hydrochloride had no effect on azelastine pharmacokinetics. Interaction studies investigating the cardiac effects, as measured by the corrected QT interval (QTc), of concomitantly administered oral azelastine hydrochloride and erythromycin or ketoconazole were conducted. Oral erythromycin had no effect on azelastine pharmacokinetics or QTc based on analyses of serial electrocardiograms. Ketoconazole interfered with the measurement of azelastine plasma concentrations; however, no effects on QTc were observed. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Craig La Force. Review of the pharmacology, clinical efficacy, and safety of azelastine hydrochloridel. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2005 Jul;1(2):191-201.
[2]. Mohamed M Elseweidy, et al. Azelastine a potent antihistamine agent, as hypolipidemic and modulator for aortic calcification in diabetic hyperlipidemic rats model. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020 Jul 2;1-8. [3]. Carlos D. Zappia, et al. Azelastine potentiates antiasthmatic dexamethasone effect on a murine asthma model. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019 Dec; 7(6): e00531. [4]. Li Yang, et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors among already approved drugs. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 Oct 28 : 1-7. [5]. Shao-Cheng Liu, et al. Effect of budesonide and azelastine on histamine signaling regulation in human nasal epithelial cells. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Feb;274(2):845-853. |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Phthalazines; Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal; Platelet Aggregation Inhibitors; Bronchodilator Agents; Histamine H1 Antagonists, Non-Sedating; Lipoxygenase Inhibitors Oral azelastine has been safely administered to over 1400 asthmatic subjects, supporting the safety of administering Astelin Nasal Spray to allergic rhinitis patients with asthma. Astelin Nasal Spray is indicated for the treatment of the symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis such as rhinorrhea, sneezing, and nasal pruritus in adults and children 5 years and older, and for the treatment of the symptoms of vasomotor rhinitis, such as rhinorrhea, nasal congestion and postnasal drip in adults and children 12 years and older. /Include in US product label/ Azelastine is used for the symptomatic treatment of ocular itching associated with allergic conjunctivitis. This indication is based on environmental studies (duration 2-8 weeks) in which therapy with azelastine ophthalmic solution was more effective than vehicle in providing relief of ocular itching in children and adults with allergic conjunctivitis. THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY: Antihistaminic Drug Warnings Astelin Nasal Spray is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to azelastine hydrochloride or any of its components. ... The occurrence of somnolence has been reported in some patients taking Astelin Nasal Spray; due caution should therefore be exercised when driving a car or operating potentially dangerous machinery while using Astelin Nasal Spray. Concurrent use of Astelin Nasal Spray with alcohol or other CNS depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of CNS performance may occur. The manufacturer states that there was no evidence of an effect on cardiac repolarization in patients who received azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray (548 mcg twice daily for 56 days) in a placebo-controlled study. Although 3- to 7-millisecond increases in mean QTc intervals were observed with higher oral dosages of the drug, such increases were not considered to be clinically important. The principal adverse effects of intranasal azelastine are local (e.g., bitter taste, nasal burning, pharyngitis, paroxysmal sneezing), but adverse systemic effects (e.g., somnolence, headache) also can occur. Anaphylactoid reactions, application site reaction, chest pain, aggravated condition, confusion, diarrhea, dyspnea, facial edema, involuntary muscle contractions, paresthesia, parosmia, pruritus, rash, tolerance, urinary retention, vision abnormality, and xerophthalmia have occurred in patients receiving azelastine nasal spray; a causal relationship between these events and the drug have not been established. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Azelastine (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Azelastine antagonizes the actions of histamine, resulting in the relief of histamine-mediated allergy symptoms. Onset of action occurs within 15 minutes with intranasal formulations and as quickly as 3 minutes with ophthalmic solutions. Intranasal formulations have a relatively long-duration of action, with peak effects observed 4-6 hours after the initial dose and efficacy maintained over the entirety of the standard 12 hour dosing interval. |
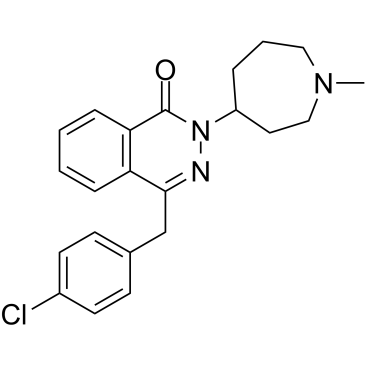
| 分子式 |
C₂₂H₂₄CLN₃O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
381.90
|
| 精确质量 |
381.16
|
| CAS号 |
58581-89-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Azelastine hydrochloride;79307-93-0;Azelastine-13C,d3
|
| PubChem CID |
2267
|
| 外观&性状 |
Oil
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
533.9±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
276.7±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.642
|
| LogP |
3.71
|
| tPSA |
38.13
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
558
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C1N(C2CCN(C)CCC2)N=C(CC3=CC=C(Cl)C=C3)C4=C1C=CC=C4
|
| InChi Key |
MBUVEWMHONZEQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H24ClN3O/c1-25-13-4-5-18(12-14-25)26-22(27)20-7-3-2-6-19(20)21(24-26)15-16-8-10-17(23)11-9-16/h2-3,6-11,18H,4-5,12-15H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
4-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-2-(1-methylazepan-4-yl)phthalazin-1-one
|
| 别名 |
Allergodil Azelastine HCl Astelin Optivar Rhinolast Azeptin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6185 mL | 13.0924 mL | 26.1849 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5237 mL | 2.6185 mL | 5.2370 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2618 mL | 1.3092 mL | 2.6185 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。