| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
nAChR and mAchR receptor (Ki = 10-10000 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
将卡巴胆碱应用于Ussing室中安装的T84细胞单层,会导致短路电流(Isc)立即增加,在5分钟内达到峰值,此后迅速下降,尽管Isc的小幅增加持续了约30分钟。用1微M卡巴胆碱可以检测到Isc的增加;使用10微M卡巴胆碱的半最大值;最大值为100微M卡巴胆碱。单向Na+和Cl-通量测量表明,Isc的增加是由于净Cl-分泌。卡巴胆碱没有改变细胞cAMP,但导致游离细胞质Ca2+([Ca2+]i)从117+/-7nM短暂增加到160+/-15nM。通过增加cAMP起作用的前列腺素E1(PGE1)或血管活性肠多肽(VIP)可增强卡巴胆碱诱导的Isc增加。cAMP和[Ca2+]i的测量表明,增强的反应不是由于这些第二信使的变化。对这些药物对离子转运途径影响的研究表明,卡巴胆碱、PGE1或VIP各自通过激活基底外侧膜上的两种不同的K+转运途径来增加基底外侧K+外流。卡巴胆碱激活的途径对钡不敏感,而PGE1或VIP激活的途径敏感;此外,它们对K+外流的作用是累加的。我们的研究表明,卡巴胆碱会导致Cl-分泌,这种作用可能是由于它能够增加[Ca2+]i和基底外侧K+流出。在VIP或PGE1存在的情况下,卡巴胆碱对Cl-分泌的影响大大增强,这在顶膜上打开了cAMP敏感的Cl-通道,从而增强了反应[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在自由活动的大鼠中,研究了胆碱对睡眠和觉醒的调节作用,这些大鼠在桥脑网状结构中局部注射了不同剂量的卡巴胆碱。当卡巴胆碱被特异性地注入口腔桥脑后网状核(PnO)时,发生了REM睡眠的诱导。用1-10ng卡巴胆碱观察到这种效果,并持续至少6小时。在卡巴胆碱(10ng)前15分钟,将阿托品(100-200ng)注入同一部位可拮抗这种效果,表明REM睡眠诱导是由桥脑毒蕈碱受体的刺激引起的。高剂量卡巴胆碱(500 ng)不会影响REM睡眠,但会增强觉醒。PnO内的胆碱能机制可能在大鼠REM睡眠的调节中发挥关键作用[2]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Topical carbachol penetrates intact corneal epithelium very poorly; combination with wetting agent ... greatly improves corneal penetration by the drug. ... Carbachol /is/ ... absorbed through intact skin. Metabolism / Metabolites Carbachol, which is an unsubstituted carbamyl ester, is totally resistant to hydrolysis by either acetylcholinesterase or nonspecific cholinesterases; its half-life is thus sufficiently long that it is distributed to areas of low blood flow. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of carbachol ophthalmic drops during breastfeeding. Because of its short half-life, it is not likely to reach the bloodstream of the infant or cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information in nursing mothers was not found as of the revision date. In animals, cholinergic drugs increase oxytocin release, and have variable effects on serum prolactin. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Interactions Acetylcholine and methacholine are hydrolyzed by acetylcholinesterase and their effects are markedly enhanced by the prior administration of anticholinesterase agents. The latter drugs produce only additive effects with the stable analogs, carbachol and bethanechol. The muscarinic actions of all the drugs of this class are blocked selectively by atropine, through competitive occupation of cholinergic receptor sites on the autonomic effector cells and on the secondary muscarinic receptors of autonomic ganglion cells. When used in conjunction with topical epinephrine, topical timolol, and/or systemically admin carbonic anhydrase inhibitiors, the effect of miotics in lowering intraocular pressure may be additive. /Miotics/ Although the clinical importance has not been established, the miotic and/or ocular hypotensive effects of miotics reportedly may be antagonized by long-term topical or systemic corticosteroid therapy, systemic anticholinergics, antihistamines, meperidine, sympathomimetics, & tricyclic antidepressants ... . Ophthalmic carbachol may be ineffective when administred following ophthalmic flubiprofen; the pharmacologic basis for this interference is not known. Concurrent use of ... /ophthalmic belladona alkaloids or cyclopentolate/ may interfere with the antiglucoma action of carbachol; also concurrent use with carbachol counteracts the myrdiatic effects of these medications ... . Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Mouse oral 5 mg/kg LD50 Mouse iv 0.3 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Mechanism of chloride secretion induced by carbachol in a colonic epithelial cell line.. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):348–354.
[2]. Induction of rapid eye movement sleep by carbachol infusion into the pontine reticular formation in the rat. Neuroreport. 1995 Feb 15;6(3):532-6. |
| 其他信息 |
Prismatic crystals or powder. Odorless, but develops a faint odor of aliphatic amine upon standing in an open container. Cholinergic, parasympathomimetic, used chiefly in large animals, especially for colic in the horse. (EPA, 1998)
Carbachol is an ammonium salt and a carbamate ester. It has a role as a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, a muscarinic agonist, a non-narcotic analgesic, a cardiotonic drug and a miotic. Carbachol is a synthetic choline ester and a positively charged quaternary ammonium compound. Carbachol is a parasympathomimetic that mimics the effect of acetylcholine on both the muscarinic and nicotinic receptors. This drug is administered ocularly to induce miosis to reduce intraocular pressure in the treatment of glaucoma. Carbachol is also used to stimulate micturition by contraction of detrusor muscle. This drug may cause hypotension, bradycardia, nausea, vomiting, bronchospasm, and abdominal cramps. A slowly hydrolyzed CHOLINERGIC AGONIST that acts at both MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS and NICOTINIC RECEPTORS. See also: Carbamoylcholine (has active moiety). Mechanism of Action The pharmacologic effects of all miotics are similar; they differ primarily in ocular and systemic absorption, duration of action and degree of effects. Acetylcholine, an endogenous mediator of nerve impulses, stimulates cholinergic receptors, resulting in muscarinic and nicotinic effects. The action of acetylcholine is transient. ... Pilocarpine, carbachol, and methacholine also directly stimulate cholinergic receptors; however, these drugs have a more prolonged duration of action (several hours) than does acetylcholine. There is some evidence that carbachol also has a weak anticholinesterase effect ... . Miotics reduce intraocular pressure in normal and glaucomatous eyes. The mechanism of action of the drugs in lowering intraocular pressure has not been precisely determined. In patients with open-angle (chronic simple, noncongestive) glaucoma, the drugs facilitate aqueous humor outflow, apparently by causing contraction of the ciliary muscle and widening of the trabecular meshwork. ... Miotics decrease activity of extraocular muscles of convergence. ... Systemically absorbed miotics produce parasympathomimetic effects on various body systems. /Miotics/ /Carbachol acts/ ... with selectivity on the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract ... Carbachol /also/ retains substantial nicotinic activity, particularly on autonomic ganglia. It is likely that both its peripheral and its ganglionic actions are due, in part, to the release of endogenous acetylcholine from the terminals of cholinergic fibers. The choline esters /carbachol & bethanechol/ increase ureteral peristalsis, contract the detrusor muscle of the urinary bladder, increase the maximal voluntary voiding pressure, and decrease the capacity of the bladder. In addition, the trigone and external sphincter are relaxed. In animals with experimental lesions of the spinal cord or sacral roots, these drugs bring about satisfactory evacuation of the neurogenic bladder. For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for CARBACHOL CHLORIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Therapeutic Uses Analgesics, Non-Narcotic; Cardiotonic Agents; Cholinergic Agonists; Miotics; Muscarinic Agonists; Nicotinic Agonists; Parasympathomimetics Acetylcholine, 1%, or carbachol, 0.01%, is used in cataract extractions and certain other surgical procedures on the anterior segment when it is desired to produce miosis rapidly; the action of acetylcholine is brief. For the chronic therapy of noncongestive, wide-angle glaucoma, carbachol (0.75 to 3.0%) has been employed. Carbachol has been used in the treatment of postoperative intestinal atony and postoperative retention of urine, for which it has been given by subcutaneous injection ... or by mouth. It has also been used to stop supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia when all other measures have failed. Carbachol has a miotic action and eye-drops ... have been used to lower intraocular pressure in glaucoma ... Even in comparatively late cases of sun blindness the symptoms could in many instances be alleviated ... by retrobulbar injection of carbachol. Pilocarpine (or occasionally carbachol) is used to lower intraocular pressure in the emergency treatment of acute (congestive) angle-closure glaucoma prior to surgery. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for CARBACHOL CHLORIDE (11 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Topical carbachol shares the toxic potentials of the direct-acting miotics, and the usual precautions of miotic therapy should be observed. The manufacturer states that intraocular carbachol does not produce the adverse effects of topically applied carbachol; bullous keratopathy and postoperative iritis following cataract extraction have been reported in some patients. Corneal edema may occur if excessive amounts of carbachol are introduced into the anterior chamber or if the drug is used in patients with an already compromised endothelium, eg, Fuchs' dystrophy, corneal transplants, cataract surgery that requires more manipulation than usual. It is recommended that carbachol should not be used as eye-drops in patients with a corneal abrasion as there may be excessive absorption. The sensitivity of asthmatic patients to carbachol bronchoconstriction was increased when inhalation of carbachol was preceded by maximum respiratory maneurvers. Drugs of this class should be admin only by the oral or subcutaneous route for systemic effects; they are also used locally in the eye. If they are given intravenously or intramuscularly, their relative selectivity of action no longer holds, and the incidence and severity of toxic side effects are greatly increased. /Choline esters/ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for CARBACHOL CHLORIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
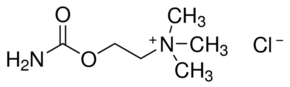
| 分子式 |
C6H15CLN2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
182.65
|
| 精确质量 |
182.082
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 39.46; H, 8.28; Cl, 19.41; N, 15.34; O, 17.52
|
| CAS号 |
51-83-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
51-83-2
|
| PubChem CID |
5831
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 熔点 |
200-204 ºC
|
| 闪点 |
90°C(lit.)
|
| tPSA |
52.32
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
11
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
117
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)N.[Cl-]
|
| InChi Key |
AIXAANGOTKPUOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C6H14N2O2.ClH/c1-8(2,3)4-5-10-6(7)9/h4-5H2,1-3H3,(H-,7,9)1H
|
| 化学名 |
2-carbamoyloxyethyl(trimethyl)azaniumchloride
|
| 别名 |
Carbastat; Carboptic; carbachol; 51-83-2; Carbamoylcholine chloride; Carbamylcholine chloride; Miostat; CARBACHOL CHLORIDE; Jestryl; Isopto Carbachol, Miostat, Carbamylcholine
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ≥ 50 mg/mL (~273.75 mM)
DMSO : ~6.4 mg/mL (~35.04 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4750 mL | 27.3748 mL | 54.7495 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0950 mL | 5.4750 mL | 10.9499 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5475 mL | 2.7375 mL | 5.4750 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。