| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Cephalosporin antibiotic; bacterial cell wall synthesis; penicillin binding proteins (PBPs)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
头孢氨苄赖氨酸 (10 μg/mL) 会灭活一种称为青霉素结合蛋白 (PBP) 的酶,该酶会干扰聚合物肽聚糖 (PG) 的合成 [1]。头孢氨苄赖氨酸抑制许多革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性细菌。炭疽杆菌、霍乱弧菌、爱德华氏菌属、多杀性巴斯德氏菌、迟缓爱德华氏菌和产碱菌的 MIC 值为 2。雷氏变形杆菌和雷氏变形杆菌分别为 2、2、2、4、4.4 和 5.7 μg/mL,见于[2]。 ]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
头孢氨苄赖氨酸(0-50 mg/kg;口服;3.5 小时)对感染微生物的雄性 Swiss-Webster 小鼠具有抗菌作用 [2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
青霉素和相关的β -内酰胺构成了我们最古老和最广泛使用的抗生素疗法之一。人们早就知道,这些药物的靶点是一种叫做青霉素结合蛋白(PBPs)的酶,这种酶负责构建细菌细胞壁。研究了靶抑制的下游后果,以及它们如何导致这些重要药物的致命作用,我们证明了β -内酰胺不仅仅是像通常认为的那样抑制PBPs。相反,它们诱导目标生物合成机制发生毒性故障,涉及细胞壁合成和降解的无效循环,从而耗尽细胞资源并增强其杀伤活性。这种作用模式的表征还揭示了细胞壁基质中裂解键的酶的质量控制功能。因此,这些结果提供了对细胞壁组装机制的深入了解,并建议如何最好地干预未来抗生素开发的过程。[1]
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Bacterially infected male Swiss-Webster mice [2]
Doses: 0-50 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (po (oral gavage)) 3.5 hrs (hrs (hours)) Experimental Results: Against Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus and several Antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria in mice. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
Well absorbed from the upper gastrointestinal tract with nearly 100% oral bioavailability. Cephalexin is not absorbed in the stomach but is absorbed in the upper intestine. Patients taking 250mg of cephalexin reach a maximum plasma concentration of 7.7mcg/mL and patients taking 500mg reach 12.3mcg/mL. Route of Elimination Cephalexin is over 90% excreted in the urine after 6 hours by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion with a mean urinary recovery of 99.3%. Cephalexin is unchanged in the urine. Volume of Distribution 5.2-5.8L. Clearance Clearance from one subject was 376mL/min. LESS THAN 10 TO 15%...IS BOUND TO PLASMA PROTEIN, & PLASMA DRUG CONCN FALL RAPIDLY... MORE THAN 90%...IS EXCRETED UNALTERED IN URINE WITHIN 6 HR, PRIMARILY BY RENAL TUBULAR SECRETION. ...THERAPEUTICALLY EFFECTIVE CONCN ARE STILL ACHIEVED IN URINE OF PT WITH DECR RENAL FUNCTION. CEPHALEXIN...IS WELL ABSORBED FROM GI TRACT. PEAK PLASMA CONCN, REACHED @ ABOUT 1 HR AFTER INGESTION OF DRUG, ARE APPROX 9 & 18 UG/ML AFTER ORAL DOSES OF 250 & 500 MG, RESPECTIVELY. INGESTION OF FOOD MAY DELAY ABSORPTION. BOTH ABSORPTION & EXCRETION OF CEPHALEXIN ARE IMPAIRED IN NEW-BORN INFANTS, WHERE 24-HR URINARY RECOVERY OF ANTIBIOTIC ACCOUNTED FOR 5-66% OF DAILY ORAL DOSE. Metabolism / Metabolites Cephalexin is not metabolized in the body. Biological Half-Life The half life of cephalexin is 49.5 minutes in a fasted state and 76.5 minutes with food though these times were not significantly different in the study. The serum half-life of cephalexin is 0.5-1.2 hr in adults with normal renal function. The serum half-life of the drug is reported to be about 5 hr in neonates and 2.5 hr in children 3-12 mo of age. In one study, the serum half-life was 7.7 hr in adults with creatinine clearances of 9.2 ml/min and 13.9 hr in adults with creatinine clearances of 4 ml/min. Protein Binding Cephalexin is 10-15% bound to serum proteins including serum albumin. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that maternal cephalexin produces low levels in milk that are usually not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Cephalexin is an alternative for the treatment of mastitis. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. A rare case of a severe allergic reaction occurred in an infant previously exposed to intravenous cefazolin whose mother began taking cephalexin while breastfeeding. Cephalexin is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants In a prospective follow-up study, 7 nursing mothers reported taking cephalexin (dosage not specified). Two mothers reported diarrhea in their infants. No rashes or candidiasis were reported among the exposed infants. A prospective, controlled study asked mothers who called an information service about adverse reactions experience by their breastfed infants. One of 11 cephalexin-exposed infants reportedly developed diarrhea during maternal cephalexin therapy. A woman received intravenous cephalothin 1 g every 6 hours for 3 days. Her breastfed infant had a green liquid stool, severe diarrhea, discomfort and crying. The mother's drug regimen was then changed to oral cephalexin 500 mg plus oral probenecid 500 mg 4 times daily for another 16 days. The infant continued to have diarrhea during this time. The authors rated the diarrhea as probably related to cephalexin in milk. A 4-month-old infant was treated with intravenous cefazolin for a urinary tract infection. Nine days after being discharged and cefazolin discontinuation, the infant developed a blistering rash over most of the body that was diagnosed as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). The infant was being breastfed (extent unspecified) by his mother who had begun cephalexin 2 days prior to the onset of symptoms. A lymphocyte transformation test performed 4 weeks after treatment for TEN was completed found sensitization to both cefazolin and cephalexin. The infant's reaction was probably caused by cephalexin in breastmilk after initial sensitization and subsequent cross-reaction to cefazolin. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. View More
◈ What is cephalexin?
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
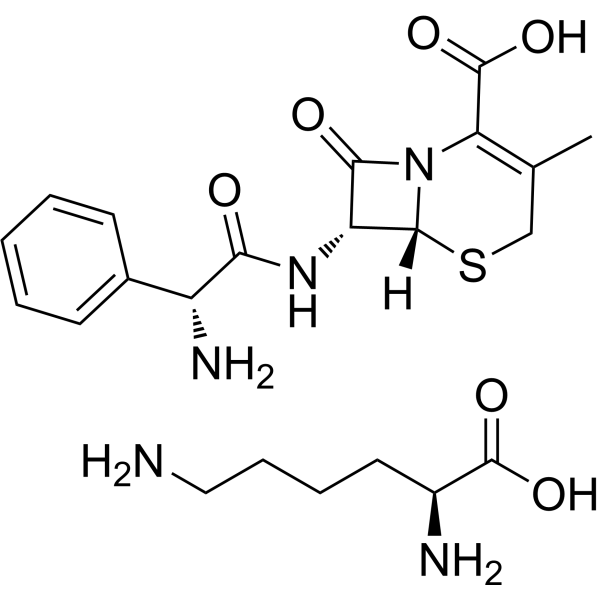
Cephalexin is a semisynthetic first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic having methyl and beta-(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido groups at the 3- and 7- of the cephem skeleton, respectively. It is effective against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive organisms, and is used for treatment of infections of the skin, respiratory tract and urinary tract. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is a cephalosporin, a semisynthetic derivative and a beta-lactam antibiotic allergen. It is a conjugate acid of a cephalexin(1-).
Cephalexin is the first of the first generation cephalosporins. This antibiotic contains a beta lactam and a dihydrothiazide. Cephalexin is used to treat a number of susceptible bacterial infections through inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Cephalexin was approved by the FDA on 4 January 1971. Cephalexin anhydrous is a Cephalosporin Antibacterial. Keflet has been reported in Streptomyces. Cephalexin is a beta-lactam, first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic with bactericidal activity. Cephalexin binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Inactivation of PBPs interferes with the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. This results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis. Compared to second and third generation cephalosporins, cephalexin is more active against gram-positive and less active against gram-negative organisms. Cephalexin Anhydrous is the anhydrous form of cephalexin, a semisynthetic first-generation cephalosporin with antibacterial activity. Cephalexin binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. PBPs are enzymes involved in the terminal stages of assembling the bacterial cell wall and in reshaping the cell wall during growth and division. Inactivation of PBPs interferes with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. This results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis. A semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic with antimicrobial activity similar to that of CEPHALORIDINE or CEPHALOTHIN, but somewhat less potent. It is effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. View More
Drug Indication
Pharmacodynamics Cephalexin (also called Cefalexin) is a first generation cephalosporin antibiotic. It is one of the most widely prescribed antibiotics, often used for the treatment of superficial infections that result as complications of minor wounds or lacerations. It is effective against most gram-positive bacteria through its inihibition of the cross linking reaction between N-acetyl muramicacid and N-acetylglucosamine in the cell wall, leading to cell lysis. Mechanism of Action Cephalexin is a first generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Cephalosporins contain a beta lactam and dihydrothiazide. Unlike penicillins, cephalosprins are more resistant to the action of beta lactamase. Cephalexin inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading breakdown and eventualy cell death. CEPHALOTHIN & ITS CONGENERS INHIBIT BACTERIAL CELL-WALL SYNTHESIS IN MANNER SIMILAR TO THAT OF PENICILLIN. /CEPHALOSPORINS/ The penicillins and their metabolites are potent immunogens because of their ability to combine with proteins and act as haptens for acute antibody-mediated reactions. The most frequent (about 95 percent) or "major" determinant of penicillin allergy is the penicilloyl determinant produced by opening the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin. This allows linkage of the penicillin to protein at the amide group. "Minor" determinants (less frequent) are the other metabolites formed, including native penicillin and penicilloic acids. /Penicillins/ Bactericidal; action depends on ability to reach and bind penicillin-binding proteins located in bacterial cytoplasmic membranes; cephalosporins inhibit bacterial septum and cell wall synthesis, probably by acylation of membrane-bound transpeptidase enzymes. This prevents cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains, which is necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. Also, cell division and growth are inhibited, and lysis and elongation of susceptible bacteria frequently occur. Rapidly dividing bacteria are those most susceptible to the action of cephalosporins. /Cephalosporins/ |
| 分子式 |
C16H17N3O4S.C6H14N2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
493.57644
|
| 精确质量 |
493.199
|
| CAS号 |
53950-14-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Cephalexin;15686-71-2;Cephalexin hydrochloride;59695-59-9;Cephalexin monohydrate;23325-78-2;Cephalexin hydrochloride monohydrate;105879-42-3
|
| PubChem CID |
92135907
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
227
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
34
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
706
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
CC1=C(N2[C@@H]([C@@H](C2=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](C3=CC=CC=C3)N)SC1)C(=O)O.C(CCN)C[C@@H](C(=O)O)N
|
| InChi Key |
CSXICSKZWGBACI-SSDGIDNNSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H17N3O4S.C6H14N2O2/c1-8-7-24-15-11(14(21)19(15)12(8)16(22)23)18-13(20)10(17)9-5-3-2-4-6-9;7-4-2-1-3-5(8)6(9)10/h2-6,10-11,15H,7,17H2,1H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23);5H,1-4,7-8H2,(H,9,10)/t10-,11-,15-;5-/m10/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid;(2S)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
53950-14-4; Cephalexin lysinate; (6R,7R)-7-[(2-amino-2-phenylacetyl)amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid;(2S)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid; L-lysine compound with (6R,7R)-7-(2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (1:1); L-lysine mono[[6R-[6alpha,7beta(R*)]]-7-[(aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate]; DTXSID30968760; CSXICSKZWGBACI-ZMZYGIGZSA-N; DB-230587;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0260 mL | 10.1301 mL | 20.2601 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4052 mL | 2.0260 mL | 4.0520 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2026 mL | 1.0130 mL | 2.0260 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。