| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
- Histamine H₁ receptor (antagonist activity, no IC₅₀/Ki provided)[1,3,12]
- Human Ether-à-go-go-Related Gene (hERG) K⁺ channel (IC₅₀ = 12 nM for blocking IHERG current)[7] - P2X₇ receptor (allosteric sensitizer, enhances ATP-induced cation entry)[8] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
- 抗组胺活性:氯马斯汀竞争性阻断效应细胞(如血管内皮细胞、气道平滑肌)上的H₁受体,减少组胺介导的血管扩张和支气管收缩。该效应在豚鼠离体气管条和大鼠肠系膜动脉实验中得到验证[3,12]
- hERG通道抑制:在表达hERG通道的HEK293细胞中,氯马斯汀(12 nM)显著降低峰值IHERG电流约50%,其作用依赖于通道门控状态,并与S6螺旋的Y652A/F656A突变相关[7] - P2X₇受体调节:在稳定表达P2X₇受体的HEK293细胞中,氯马斯汀(1-10 μM)增强ATP诱导的Ca²⁺内流,加速孔道扩张(Yo-Pro-1摄取),并增加对NMDG⁺的通透性。在人单核细胞来源的巨噬细胞和小鼠骨髓来源的巨噬细胞中观察到类似效应[8] - 自噬促进:在LPS刺激的H9c2心肌细胞中,氯马斯汀(10-50 μM)增加LC3-II/LC3-I比值、Beclin-1表达和自噬体形成,该效应可被自噬抑制剂3-甲基腺嘌呤阻断[11] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
- 过敏性鼻炎模型:20名过敏受试者口服氯马斯汀(1 mg)4-6小时后,过敏原激发导致的喷嚏频率(p < 0.01)和鼻漏严重程度显著降低。效应呈剂量依赖性,持续时间≥12小时[6]
- 脓毒症心肌损伤模型:在CLP诱导的脓毒症大鼠中,腹腔注射氯马斯汀(30-50 mg/kg)将7天存活率从30%提升至60%,降低血清cTnI水平,保护左心室射血分数,并减轻线粒体碎片化。在LPS刺激的H9c2细胞中观察到类似保护作用[11] - 视神经炎模型:16名急性视神经炎患者口服氯马斯汀(1 mg每日两次,持续90天)后,颞侧/颞上象限视网膜神经纤维层(RNFL)厚度得以保留,视觉诱发电位P100波幅恢复优于安慰剂组[10] |
| 酶活实验 |
- hERG通道电生理实验:在表达hERG通道的HEK293细胞上进行全细胞膜片钳记录。细胞在37°C Tyrode液中灌流氯马斯汀(1-100 nM),记录去极化至+20 mV后-40 mV的IHERG尾电流。IC₅₀通过非线性回归计算[7]
- P2X₇受体钙流实验:HEK293-P2X₇细胞负载Fluo-4 AM,经氯马斯汀(1-10 μM)预处理后加入ATP(100 μM),荧光显微镜记录钙瞬变。流式细胞术检测Yo-Pro-1摄取以评估孔道形成[8] |
| 细胞实验 |
- H₁受体拮抗实验:豚鼠气管环段与氯马斯汀(0.1-10 μM)孵育后,用组胺(1 μM)刺激,记录等长张力变化以测定拮抗效力[3,12]
- 自噬检测实验:H9c2心肌细胞经氯马斯汀(10-50 μM)和LPS(1 μg/mL)处理后,Western blot分析LC3-II/LC3-I比值和Beclin-1表达。透射电镜观察自噬体[11] |
| 动物实验 |
- Sepsis model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250-300 g) underwent cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Clemastine (10-50 mg/kg) was dissolved in 0.9% saline and administered intraperitoneally 30 minutes post-CLP. Survival was monitored for 7 days, and cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography on day 3[11]
- Allergic rhinitis model: Human subjects received oral clemastine (1 mg) or placebo in a double-blind crossover design. Nasal allergen challenges were performed 1, 4, and 6 hours post-dose. Sneeze counts and nasal secretion weights were recorded[6] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Urinary excretion is the major mode of elimination. Metabolism / Metabolites Antihistamines appear to be metabolized in the liver chiefly via mono- and didemethylation and glucuronide conjugation. - Absorption: Rapid oral absorption with ~40% bioavailability. Peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 1-2 ng/mL occurs within 2-4 hours[12] - Distribution: Extensive tissue distribution (volume of distribution ~800 L), crosses blood-brain barrier. Plasma protein binding ~95%[12] - Metabolism: Extensively metabolized in liver via O-dealkylation, oxidation, and glucuronidation. Major metabolites include desmethylclemastine and hydroxylated derivatives[12] - Excretion: ~42% excreted in urine (primarily as metabolites), 27% in feces. Terminal half-life ~21 hours[12] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Despite widespread use, the first generation antihistamines such as clemastine have rarely been linked to liver test abnormalities or to clinically apparent liver injury. The reason for their safety may relate to low daily dose and limited duration of use. Likelihood score: E (unlikely to be a cause of clinically apparent liver injury). References on the safety and potential hepatotoxicity of antihistamines are given together after the Overview section on Antihistamines. Drug Class: Antihistamines Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Small occasional doses of clemastine are acceptable during breastfeeding. Larger doses or more prolonged use may cause drowsiness and other effects in the infant or decrease the milk supply, particularly in combination with a sympathomimetic such as pseudoephedrine or before lactation is well established. Single bedtime doses after the last feeding of the day may be adequate for many women and will minimize any effects of the drug. The nonsedating antihistamines are preferred alternatives. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A 10-week-old breastfed infant whose mother was taking clemastine, phenytoin and carbamazepine was drowsy, refused to feed, was irritable, and had high-pitched crying. These side effects were possibly caused by clemastine in breastmilk, but the other drugs could also have contributed. In one telephone follow-up study, mothers reported irritability and colicky symptoms 10% of infants exposed to various antihistamines and drowsiness was reported in 1.6% of infants. None of the reactions required medical attention. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Antihistamines in relatively high doses given by injection can decrease basal serum prolactin in nonlactating women and in early postpartum women. However, suckling-induced prolactin secretion is not affected by antihistamine pretreatment of postpartum mothers. Whether lower oral doses of antihistamines have the same effect on serum prolactin or whether the effects on prolactin have any consequences on breastfeeding success have not been studied. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. - Acute toxicity: LD₅₀ in mice >100 mg/kg (oral). Common adverse effects include sedation, dry mouth, blurred vision, and urinary retention due to anticholinergic activity[12] - Cardiotoxicity: At supra-therapeutic concentrations (≥1 μM), clemastine prolongs QT interval in isolated feline hearts, but no clinical QT prolongation reported at therapeutic doses (1-6 mg/day)[7,12] - Drug interactions: Potentiates CNS depression with alcohol, opioids, or benzodiazepines. Contraindicated with MAO inhibitors due to risk of hypertensive crisis[12] |
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;42(2):227-34. [2]. Cell Immunol. 1983 Oct 1;81(1):45-60. [3]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Jan;280(1):114-21. [4].J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006 Jan;40(1):107-18. [5]. J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 1;286(13):11067-81. [6]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Jan;280(1):114-21. [7]. Preprint from Research Square, 29 Jun 2020 |
| 其他信息 |
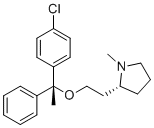
Clemastine is 2-[(2R)-1-Methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]ethanol in which the hydrogen of the hydroxy group is substituted by a 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenylethyl group (R configuration). An antihistamine with antimuscarinic and moderate sedative properties, it is used as its fumarate salt for the symptomatic relief of allergic conditions such as rhinitis, urticaria, conjunctivitis and in pruritic (severe itching) skin conditions. It has a role as a H1-receptor antagonist, an anti-allergic agent, a muscarinic antagonist and an antipruritic drug. It is a N-alkylpyrrolidine and a member of monochlorobenzenes.
An ethanolamine-derivative, first generation histamine H1 antagonist used in hay fever, rhinitis, allergic skin conditions, and pruritus. It causes drowsiness. Clemastine is a first generation antihistamine that is used for symptoms of allergic rhinitis and the common cold. Clemastine has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Clemastine is a synthetic ethanolamine, with anticholinergic, sedative, and histamine H1 antagonistic activities. Upon administration, clemastine blocks the H1 histamine receptor and prevents the symptoms that are caused by histamine activity on capillaries, bronchial and gastrointestinal smooth muscles, including vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, bronchoconstriction, and spasmodic contraction of gastrointestinal smooth muscles. Clemastine also prevents histamine-induced pain and itching of mucous membranes. A histamine H1 antagonist used as the hydrogen fumarate in hay fever, rhinitis, allergic skin conditions, and pruritus. It causes drowsiness. See also: Clemastine Fumarate (has salt form). Drug Indication For the relief of symptoms associated with allergic rhinitis such as sneezing, rhinorrhea, pruritus and acrimation. Also for the management of mild, uncomplicated allergic skin manifestations of urticaria and angioedema. Used as self-medication for temporary relief of symptoms associated with the common cold. Mechanism of Action Clemastine is a selective histamine H1 antagonist and binds to the histamine H1 receptor. This blocks the action of endogenous histamine, which subsequently leads to temporary relief of the negative symptoms brought on by histamine. - Mechanism of action: Antihistamine effects via H₁ receptor blockade; cardiotoxicity linked to hERG channel inhibition; neuroprotective effects in optic neuritis may involve autophagy induction and anti-inflammatory pathways[6,7,10,11] - Therapeutic uses: Approved for allergic rhinitis, urticaria, and pruritus. Investigational use in sepsis-induced myocardial injury and optic neuritis[6,10,11] - FDA status: Available over-the-counter (1 mg tablets) and by prescription (2 mg tablets). Pregnancy category B[12] |
| 分子式 |
C21H26CLNO
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
343.895
|
| 精确质量 |
343.17
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 73.35; H, 7.62; Cl, 10.31; N, 4.07; O, 4.65
|
| CAS号 |
15686-51-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Clemastine fumarate;14976-57-9
|
| PubChem CID |
26987
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.097 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
425.2ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
211ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.553
|
| LogP |
5.042
|
| tPSA |
12.47
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
376
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C[C@@](C1=CC=CC=C1)(C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl)OCC[C@H]3CCCN3C
|
| InChi Key |
YNNUSGIPVFPVBX-NHCUHLMSSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H26ClNO/c1-21(17-7-4-3-5-8-17,18-10-12-19(22)13-11-18)24-16-14-20-9-6-15-23(20)2/h3-5,7-8,10-13,20H,6,9,14-16H2,1-2H3/t20-,21-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2R)-2-[2-[(1R)-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-phenylethoxy]ethyl]-1-methylpyrrolidine
|
| 别名 |
Clemastine; HS-592; clemastine; 15686-51-8; Meclastin; Mecloprodin; Clemastina; HS592; Clemastinum; HS 592
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9078 mL | 14.5391 mL | 29.0782 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5816 mL | 2.9078 mL | 5.8156 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2908 mL | 1.4539 mL | 2.9078 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT06039137 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Cetirizine | Solid Tumor | Erasmus Medical Center | June 1, 2022 | N/A |
| NCT03109288 | Recruiting | Drug: Pioglitazone Drug: clemastine fumarate Drug: Dantrolene Drug: Pirfenidone |
Multiple Sclerosis | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) |
August 11, 2017 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT02521311 | Recruiting | Drug: Clemastine Drug: Placebo |
Optic Neuritis | University of California, San Francisco |
February 28, 2017 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05359653 | Recruiting | Drug: Clemastine Fumarate Drug: Placebo |
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Multiple Sclerosis Relapse Multiple Sclerosis Benign |
University of California, San Francisco |
August 1, 2023 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT06065670 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Clemastine Fumarate Drug: Placebo |
Demyelinating Diseases Multiple Sclerosis Brain Lesion |
University of California, San Francisco |
November 1, 2023 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |