| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Bcr-Abl
- BCR-ABL fusion protein: Dasatinib carbaldehyde induces proteasomal degradation of BCR-ABL with a DC₅₀ (concentration causing 50% degradation) of 0.8 μM in K562 cells; it inhibits ABL kinase activity with an IC₅₀ of 1.5 μM [1] - Cellular Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins (cIAP1/cIAP2): Dasatinib carbaldehyde binds to cIAP1 with a Ki of 0.5 μM and cIAP2 with a Ki of 0.7 μM (TR-FRET assay) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
一些癌症细胞发生染色体易位,导致慢性粒细胞白血病(CML)中包括BCR-ABL在内的异常致癌融合蛋白的表达。ABL酪氨酸激酶抑制剂,如伊马替尼和达沙替尼,显示出显著的治疗效果,尽管在长期治疗期间出现耐药性阻碍了治疗。治疗慢性粒细胞白血病的另一种方法是下调BCR-ABL蛋白。我们设计了一种名为凋亡蛋白特异性和非遗传抑制剂[IAP]依赖性蛋白清除器(SNIPR)的杂交分子的蛋白质敲除系统,旨在诱导IAP介导的靶蛋白泛素化和蛋白酶体降解,最近开发了一对针对BCR-ABL蛋白的SNIPR(ABL)。在这项研究中,我们测试了ABL抑制剂和IAP配体的各种组合,并针对SNIPER(ABL)的蛋白质敲除活性对接头进行了优化。由此产生的SNIPR(ABL)-39,其中达沙替尼通过聚乙二醇(PEG)×3接头与IAP配体LCL161衍生物偶联,显示出降解BCR-ABL蛋白的强大活性。机制分析表明,细胞凋亡抑制蛋白1(cIAP1)和X连锁凋亡抑制蛋白(XIAP)都在BCR-ABL蛋白的降解中发挥作用。与BCR-ABL蛋白的降解一致,SNIPER(ABL)-39抑制了信号转导子和转录激活子5(STAT5)和Crk样原癌基因(CrkL)的磷酸化,并抑制了BCR-ABL阳性CML细胞的生长。这些结果表明,SNIPER(ABL)-39可能是一种针对BCR-ABL阳性CML的基于降解的新型抗癌药物的候选者[1]。
1. BCR-ABL降解活性:达沙替尼甲醛 以剂量依赖方式降解K562(BCR-ABL阳性慢性髓系白血病细胞)和KU812细胞中的BCR-ABL蛋白,DC₅₀值分别为0.8 μM和1.1 μM。在K562细胞中,5 μM浓度时达到最大降解率(>90%),该效应可被蛋白酶体抑制剂MG132(10 μM)逆转 [1] 2. 抗增殖活性:该化合物抑制BCR-ABL阳性白血病细胞增殖,IC₅₀值如下:K562(1.2 μM)、KU812(1.6 μM)、Ba/F3-BCR-ABL(1.4 μM)。对BCR-ABL阴性细胞(RPMI8226)无显著抗增殖作用(IC₅₀ > 30 μM)[1] 3. 凋亡诱导:达沙替尼甲醛(2 μM,24小时)诱导K562细胞凋亡,Annexin V/PI染色显示凋亡率从溶剂组的4.5%升至41.2%。Western blot显示切割型caspase-3(3.8倍)和切割型PARP(3.2倍)上调 [1] 4. ABL激酶抑制:达沙替尼甲醛 体外抑制重组BCR-ABL激酶活性,IC₅₀=1.5 μM。2 μM浓度时,可使K562细胞中BCR-ABL磷酸化(p-BCR-ABL)及其下游底物Crkl磷酸化(p-Crkl)分别降低75%和80% [1] 5. IAP结合活性:该化合物通过其IAP配体部分结合cIAP1(Ki=0.5 μM)和cIAP2(Ki=0.7 μM),TR-FRET结合实验证实了这一相互作用 [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
1. K562异种移植模型抗肿瘤疗效:裸鼠右侧皮下接种K562细胞(5×10⁶个/只),肿瘤体积达100–150 mm³时,给予达沙替尼甲醛腹腔注射(10、20 mg/kg,每日1次)治疗14天。20 mg/kg组肿瘤生长抑制率(TGIR)为88%,10 mg/kg组为65%(相较于溶剂对照组)。肿瘤重量分别减少85%(20 mg/kg)和62%(10 mg/kg)[1]
2. 肿瘤中BCR-ABL降解:Western blot分析显示,达沙替尼甲醛(20 mg/kg)处理的K562肿瘤组织中,BCR-ABL蛋白水平降低82%,p-Crkl水平降低78%(相较于溶剂组)[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
与ATP结合位点结合的ABL1抑制剂的抑制剂活性测定[1]
在加入检测板之前,将三倍浓度的His-ABL1蛋白、Tb-SA和生物素化抗His抗体混合在检测缓冲液中,并在室温下孵育1小时以上。将溶解在测定缓冲液中的几种浓度的试验抑制剂分配到测定板中。随后,将ABL/抗体/Tb-SA预混物分配到每个孔中,并在室温下孵育120分钟。通过加入含有13.5 nM BODIPY-达沙替尼的测定缓冲液引发反应。将平板在室温下孵育30分钟,使用EnVision Multilabel平板阅读器测量TR‐FRET信号。Tb-SA、生物素化抗His、ABL1蛋白和BODIPY-dasatinib的最终浓度分别为0.2、0.4、0.38和4.5 nM。0和100%对照的值分别是在3μM达沙替尼存在和不存在的情况下获得的信号。 IAP/肽相互作用抑制活性的测定[1] His-IAP蛋白(XIAP、cIAP1或cIAP2)、FITC-Smac、Tb-SA和生物素化抗His抗体在检测缓冲液中混合,在室温下孵育1小时以上,然后加入检测板。在分析板中分配了几种浓度的测试抑制剂,并将蛋白质探针预混物分配到每个孔中。所有测定均使用0.6 nM的IAP蛋白进行。FITC-Smac的浓度描述如下:XIAP为27 nM,cIAP1为12 nM,而cIAP2为19 nM。Tb-SA和生物素化抗His抗体的最终浓度分别为0.2和0.4 nM。在室温下孵育1小时后,使用EnVision多标签平板阅读器测量TR‐FRET信号。0和100%对照的值分别是在IAP蛋白存在和不存在的情况下获得的信号。 1. ABL激酶活性抑制实验流程:将重组BCR-ABL激酶结构域与系列浓度的达沙替尼甲醛(0.01–30 μM)及ATP(10 μM)在反应缓冲液中孵育。通过均相时间分辨荧光(HTRF)实验检测特异性肽底物的磷酸化水平,根据激酶活性抑制的剂量-反应曲线计算IC₅₀值 [1] 2. IAP结合实验流程(TR-FRET法):将重组cIAP1/cIAP2蛋白与系列浓度的达沙替尼甲醛(0.001–10 μM)及荧光标记的IAP配体共孵育,检测时间分辨荧光共振能量转移(TR-FRET)信号评估结合亲和力,从竞争结合曲线推导Ki值 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
根据制造商的说明,使用水溶性四唑WST-8(4-[3-(2-甲氧基-4-硝基苯基)-2-(4-硝基苯基)-2H-5-四唑基]-1,3-苯二磺酸盐)进行分光光度测定,以确定细胞存活率。细胞以每孔5×103个细胞的浓度接种在96孔培养板上。24小时后,用指定化合物处理细胞48小时。加入WST-8试剂,在37°C、5%CO2的加湿气氛中孵育细胞0.5小时[1]。 1. 抗增殖实验流程:将BCR-ABL阳性白血病细胞(K562、KU812、Ba/F3-BCR-ABL)和BCR-ABL阴性细胞(RPMI8226)接种于96孔板,用达沙替尼甲醛(0.1–100 μM)处理72小时。采用细胞增殖检测试剂盒测定细胞活力,计算IC₅₀值 [1] 2. BCR-ABL降解实验流程:K562细胞用达沙替尼甲醛(0.1–10 μM)处理6小时;蛋白酶体依赖性验证实验中,细胞先用MG132(10 μM)预孵育1小时再加入药物。裂解细胞后,Western blot检测BCR-ABL、p-BCR-ABL及p-Crkl蛋白水平,根据BCR-ABL蛋白减少的剂量-反应曲线计算DC₅₀ [1] 3. 凋亡实验流程:达沙替尼甲醛(2 μM)处理K562细胞24小时后,用Annexin V-FITC和PI染色,流式细胞术定量凋亡细胞;Western blot检测切割型caspase-3和切割型PARP [1] |
| 动物实验 |
1. K562 xenograft model: Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old) were subcutaneously inoculated with K562 cells (5×10⁶ cells/mouse) in the right flank. When tumors reached 100–150 mm³, mice were randomly divided into vehicle (10% DMSO/40% PEG400/50% saline) and Dasatinib carbaldehyde groups (10, 20 mg/kg). The compound was administered via intraperitoneal injection once daily for 14 days. Tumor volume and body weight were measured every 2 days. At the end of treatment, mice were sacrificed, and tumors were collected for Western blot analysis of BCR-ABL and p-Crkl [1]
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. In vitro cytotoxicity: Dasatinib carbaldehyde showed no significant cytotoxicity in normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) at concentrations up to 30 μM (cell viability ≥85% vs. control) [1]
2. In vivo toxicity: Mice treated with Dasatinib carbaldehyde (20 mg/kg ip QD for 14 days) showed no significant changes in body weight (change ≤5% vs. control) or behavioral abnormalities. Histopathological analysis of liver, kidney, and spleen revealed no obvious tissue damage [1] 3. Plasma protein binding: Dasatinib carbaldehyde had a plasma protein binding rate of 93 ± 2% (human plasma) and 91 ± 3% (mouse plasma) [1] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
In this study, we tested various combinations of ABL inhibitors and IAP ligands to develop SNIPER(ABL) that induces the degradation of oncogenic kinase BCR‐ABL, and the linker length was optimized for the activity. We found that SNIPER(ABL)‐39, in which dasatinib is conjugated to an LCL161 derivative with PEG × 3 linker, shows the most potent activity to degrade the BCR‐ABL protein. SNIPER(ABL)‐39 showed an effective protein knockdown activity at 10 nM and the maximum activity was observed at 100 nM. Notably, the protein knockdown activity was rather attenuated at higher concentrations of SNIPER(ABL)‐39 (Fig. 2c). This is known as a high‐dose hook effect, where a certain pharmaceutical activity is interfered with higher concentration of drugs. We speculate that formation of ternary complex consisting of BCR‐ABL/SNIPER(ABL)‐39/IAP required for the protein knockdown activity would be suppressed by higher concentrations of SNIPER(ABL)‐39, and, therefore, the protein knockdown activity is attenuated.[1]
With respect to the small compounds that induce the degradation of BCR‐ABL protein, PROTAC against BCR‐ABL were reported by conjugation of dasatinib to a von Hippel‐Lindau (VHL) E3 ligase ligand or a thalidomide derivative, pomalidomide, that is a ligand for Cereblon (CRBN) E3 ligase.32 Interestingly, CRBN‐based PROTAC can reduce BCR‐ABL protein at 25 nM, whereas VHL‐based PROTAC cannot. Because IAP‐based SNIPER(ABL) can induce the degradation of BCR‐ABL protein, it is suggested that IAP and CRBN are appropriate E3 ligases to degrade BCR‐ABL protein when dasatinib is incorporated as a ligand for BCR‐ABL protein. Probably, SNIPER(ABL)‐39 and CRBN‐based PROTAC can recruit E3 ligases to an appropriate position so that the lysine residues on the surface of BCR‐ABL can be ubiquitylated. Thus, the combination of an E3 ligase ligand and a target ligand is critically important to develop the degradation inducers such as SNIPER and PROTAC.[1] Consistent with the degradation of BCR‐ABL protein, SNIPER(ABL)‐39 inhibited the BCR‐ABL‐related signaling pathway and proliferation of BCR‐ABL positive CML, such as K562, KCL‐22 and KU812 cell, expressing native BCR‐ABL protein. However, in SK‐9 cells expressing T315I mutant BCR‐ABL protein, SNIPER(ABL)‐39 did not reduce the BCR‐ABL protein nor inhibit cell proliferation. This may be attributed that SNIPER(ABL)‐39 could not bind to the T315I mutant BCR‐ABL protein, because the T315I is a gatekeeper mutation that prevents the binding of dasatinib.39, 42 However, BCR‐ABL protein has multiple domains, such as pleckstrin homology, Src homology (SH) 2 and SH3 domains, to which novel ligands could be developed. Incorporation of such ligands into SNIPER would allow us to develop a novel SNIPER(ABL) that can induce the degradation of BCR‐ABL proteins resistant to kinase inhibitors, which could be a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance against kinase inhibitors.[1] 1. Dasatinib carbaldehyde is a Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) composed of a Dasatinib-derived ABL kinase-binding moiety and an IAP ligand moiety [1] 2. Its mechanism of action involves dual binding to BCR-ABL and IAP proteins, recruiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (via IAP) to BCR-ABL, inducing ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of BCR-ABL [1] 3. The compound exhibits potent activity against BCR-ABL⁺ leukemia cells and xenograft tumors, overcoming potential resistance to conventional ABL kinase inhibitors by degrading the oncogenic protein rather than just inhibiting its activity [1] 4. It shows high selectivity for BCR-ABL⁺ cells with low toxicity to normal cells, supporting its potential for treating chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) [1] |
| 分子式 |
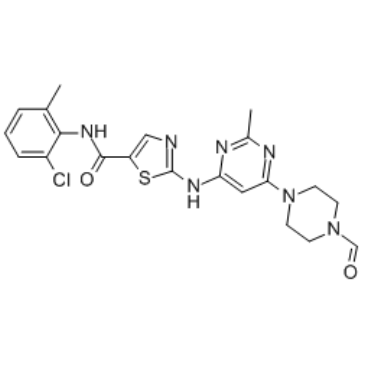
C21H22CLN7O2S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
471.96
|
| 精确质量 |
471.12
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.44; H, 4.70; Cl, 7.51; N, 20.77; O, 6.78; S, 6.79
|
| CAS号 |
2112837-79-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
863127-77-9 (hydrate);302962-49-8 (free);2112837-79-1 (cabaldehyde);910297-52-8 (N-oxide);
|
| PubChem CID |
138377562
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.7
|
| tPSA |
132Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
654
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1C(C)=C(C(=CC=1)Cl)NC(C1SC(NC2=CC(=NC(C)=N2)N2CCN(CC2)C=O)=NC=1)=O
|
| InChi Key |
BKDGDNUWAYNWBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H22ClN7O2S/c1-13-4-3-5-15(22)19(13)27-20(31)16-11-23-21(32-16)26-17-10-18(25-14(2)24-17)29-8-6-28(12-30)7-9-29/h3-5,10-12H,6-9H2,1-2H3,(H,27,31)(H,23,24,25,26)
|
| 化学名 |
N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-((6-(4-formylpiperazin-1-yl)-2-methylpyrimidin-4-yl)amino)thiazole-5-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
Dasatinib carbaldehyde; 2112837-79-1; 5-Thiazolecarboxamide, N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-(4-formyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]- (ACI); N-(2-Chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-(4-formyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino]-5-thiazolecarboxamide (ACI); SCHEMBL21340693;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~33.33 mg/mL (~70.62 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1188 mL | 10.5941 mL | 21.1882 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4238 mL | 2.1188 mL | 4.2376 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2119 mL | 1.0594 mL | 2.1188 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。