| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在孤立的杆状双极细胞中,DL-AP4 (500 μM) 通过在 -33 mV 的保持电位下阻断离子通道来减少强直内向电流 [1]。 DL-AP4(0.1 M;1h)通过离子电渗疗法作用于蝗虫肌膜上的受体来抑制谷氨酸的兴奋作用[2]。化合物 2 DL-AP4 的表观 Kd 为 2.5 μM,拮抗大鼠海马切片横向穿透通路中的兴奋性突触 [3]。 DL-AP4(50 µM;0–2 秒)可阻挡以下强度的一系列 10 ms 405 nm 闪光的光响应:3、10、30、100、300、990、3000 和 9900 个光子 µm- 2[4]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
进行了四个实验,以评估谷氨酸类似物2-氨基-4-膦酰基丁酸酯(APB)阻断ON通道对猴子亮度和对比度感知的影响。在实验1中,我们证明了比背景更亮的刺激(增量刺激)在ON通道阻断后显得不那么亮。这种亮度的降低不足以解释之前观察到的APB给药后检测增量刺激的阈值增加(Schiller等人,1986;Dolan&Schiller,1989)。实验2考察了ON和OFF通道在局部对比度和表观亮度之间相互作用中的作用。在正常条件下和APB给药后检查了同时对比的现象。我们发现,即使在ON通道阻断后,刺激的亮度也主要取决于它与直接背景的对比度。这表明,即使一个通道受到损害,同时对比中涉及的横向过程也可以运行。在实验3中,我们研究了ON通道在检测因背景与前景亮度变化而出现的刺激中的作用。我们发现,ON通道选择性地传达的信息不仅与将刺激定义为增量的时间性质有关,还与将其定义为递增的空间特征有关。在实验4中,我们检验了这样一个假设,即ON和OFF通道对增量和减量时间亮度斜坡的差异处理程度高于阶跃亮度变化。我们发现,检测增量斜坡的影响并不比检测APB给药后的增量步骤大。 [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8011580/]
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 880 mg/kg BEHAVIORAL: CHANGES IN MOTOR ACTIVITY (SPECIFIC ASSAY) Polish Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacy., 37(575), 1985
|
| 参考文献 |
[1]. 2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid as a glutamate antagonist on locust muscle. Nature. 1976 Jul 29;262(5567):408-9.
[2]. Responses of rod bipolar cells isolated from the rat retina to the glutamate agonist 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (APB). J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2372-82. [3]. Cyclic analogues of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid (APB) and their inhibition of hippocampal excitatory transmission and displacement of [3H]APB binding. J Med Chem. 1986 Oct;29(10):1988-95. [4]. Separate ON and OFF pathways in vertebrate vision first arose during the Cambrian. Curr Biol. 2020 Jun 8;30(11):R633-R634. |
| 其他信息 |
Isolated rod bipolar cells were obtained by enzymatic (papain) and mechanical dissociation of the adult rat retina. Virtually all intact bipolar cells in the dissociates expressed protein kinase C (PKC) immunoreactivity, a selective marker for rod bipolar cells in the in vivo retina. Whole-cell recordings were performed using nystatin in the patch pipette to minimize washout of those cytoplasmic components necessary for the maintenance of ionic currents. At holding potentials of -33 mV, a tonic inward current was observed. The glutamate agonist 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (APB) reduced this current by closing ion channels. Under normal conditions, Na+ appeared to be the main charge carrier. Both the internal and the external Ca2+ concentrations were found to exert a powerful influence on the APB-sensitive current. We conclude that the rod bipolar cell in situ is depolarized at light onset.[2]
Conformationally restricted analogues of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid (APB,2) were prepared where the structure of APB was incorporated into cyclopentane (3) or cyclohexane (4) rings. Hydrophosphinylation of the appropriate cycloalkenones followed by Strecker amino acid syntheses provided the desired analogues. Assignments of the relative configurations for 3a (trans), 3b (cis), 4a (cis), and 4b (trans) were determined through 13C NMR studies. Compounds 3b, 4a, and 4b possessed low activity as inhibitors of excitatory synaptic field potentials in the rat hippocampal perforant path. Analogues 4a and 4b also showed little activity in displacing [3H]APB from synaptic plasma membranes. The cyclopentyl APB analogue 36, on the other hand, was extremely potent in inhibiting the binding of [3H]APB, possessing an IC50 = 4.7 microM, thus giving further credence to the idea that the APB binding site in the rat brain synaptosomal membrane preparation is not the same as the receptor mediating APB-induced inhibition of the lateral perforant path. Of the four cyclic APB analogues, 3a most resembled APB in its spectrum of biological activity. It showed significant potency (IC50 = 130 microM) in inhibiting lateral entorhinal projections to hippocampal granule cells. Analogous to APB, 3a also showed selectivity for the lateral perforant path over the medial perforant path. Its activity in the radioligand binding assay paralleled its activity in inhibiting the lateral perforant path. It thus appears that 3a comes closest to mimicking the active conformation of APB and suggests that a folded conformation wherein the amino and phosphonate moieties are in a cis relationship to one another may approximate the active conformation of APB.[3] Ellis et al. show that retinal ON and OFF bipolar cells, and the novel metabotropic glutamate receptors of ON bipolar-cell dendrites, are both present in lamprey. They conclude that the fundamental organizing principle of separate ON and OFF pathways first appeared in the vertebrate visual system over 500 million years ago in the late Cambrian.[4] |
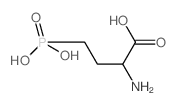
| 分子式 |
C4H10NO5P
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
183.099662303925
|
| 精确质量 |
183.03
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 26.24; H, 5.51; N, 7.65; O, 43.69; P, 16.92
|
| CAS号 |
6323-99-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1263093-79-3
|
| PubChem CID |
2207
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
-5.5
|
| tPSA |
130.66
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
11
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
187
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C(CP(=O)(O)O)C(C(=O)O)N
|
| InChi Key |
DDOQBQRIEWHWBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C4H10NO5P/c5-3(4(6)7)1-2-11(8,9)10/h3H,1-2,5H2,(H,6,7)(H2,8,9,10)
|
| 化学名 |
2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
6323-99-5; 2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid; 2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid; DL-AP4; 20263-07-4; DL-2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid; Butanoic acid, 2-amino-4-phosphono-; (+/-)-2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4615 mL | 27.3075 mL | 54.6150 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0923 mL | 5.4615 mL | 10.9230 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5461 mL | 2.7307 mL | 5.4615 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。