| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Contrast agent
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
钆特酸在细胞性肝癌(特别是富血管病变)的 DCE-MRI 中提供早期改善的吸收性、更强的漱口水以及更好、更明显的可修复性 [1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
使用肝细胞特异性造影剂(HSCA)作为研究局灶性肝损伤的护理标准,对肝脏进行动态对比增强MRI(DCE-MRI)的常规使用并不被广泛接受,反对者提出了细胞外造影剂(ECA)近100%特异性丧失的风险,以及需要进行前瞻性的头对头比较研究来评估两种造影剂的诊断性能。这项前瞻性个体内研究的目的是在肝硬化和HCC患者中使用HSCA和ECA对DCE-MRI进行定量和定性的头对头比较。23名肝硬化和已证实的HCC患者接受了两次3次T-MR检查,一次是ECA(钆酸)检查,另一次是HSCA(钆草酸)检查。评估了LI-RADS v2018的信噪比(SNR)、对比度(CNR)、冲洗、冲洗、图像质量、伪影、病变显著性和主要成像特征。与HSCA相比,ECA的洗入和洗出明显更强(分别P<0.001和0.006)。在动脉晚期(LAP),ECA的CNR显著降低(P=0.005),而SNR没有显著差异(P=0.39)。在定性分析中,与HSCA相比,ECA在门静脉期(PVP)和延迟期(DP)产生了更好的整体图像质量(P=0.041和0.008),在LAP和PVP中显示出更少的伪影(P=0.003和0.034),在LAP和PVP中显示出更高的病变显著性(P=0.004和0.037)。LAP期间的总体图像质量(P=1)、DP期间的伪影和病变显著性(P=0.078和0.073)或三个主要LI-RADS v2018成像特征的频率没有显著差异。总之,ECA为HCC提供了更好的对比,尤其是DCE-MR中的高血管HCC病变,因为它具有更好的早期增强感知能力和更强的清除能力。[1]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Within the studied dose range (0.1 to 0.3 mmol/kg), the kinetics of total gadolinium appear to be linear. Following the administration of 0.1 mmol/kg of gadoterate meglumine in healthy volunteers, the Cmax, Tmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞ were measured to be 799.03 (192.63) µmol/L, 5.00 (0.10-10.00) min, 953.51 (76.22) µmol*h/L, and 970.72 (73.34) µmol*h/L for female and 836.85 (451.02) µmol/L, 5.00 (0.11-10.00) min, 1038.74 (240.46) µmol*h/L, and 1061.16 (239.24) µmol*h/L for male subjects respectively. Following a 0.1 mmol/kg dose of gadoterate, total gadolinium is excreted primarily in the urine with 72.9 ± 17.0% and 85.4 ± 9.7% (mean ± SD) eliminated within 48 hours, in female and male subjects, respectively. Similar values were achieved after a cumulative dose of 0.3 mmol/kg (0.1 + 0.2 mmol/kg, 20 minutes later), with 85.5 ± 13.2% and 92.0 ± 12.0% recovered in urine within 48 hrs in female and male subjects respectively. The volume of distribution at steady state of total gadolinium in healthy subjects is 179 ± 26 and 211 ± 35 mL/kg in female and male subjects respectively, roughly equivalent to that of extracellular water. The extent of blood cell partitioning of gadoterate is not known. In healthy subjects, the renal and total clearance rates of total gadolinium are comparable (1.27 ± 0.32 and 1.74 ± 0.12 mL/min/kg in females; and 1.40 ± 0.31 and 1.64 ± 0.35 mL/min/kg in males, respectively) indicating that the drug is primarily cleared through the kidneys. Metabolism / Metabolites Gadoterate is not known to be metabolized. Biological Half-Life Following an intravenously administered 0.1 mmol/kg, gadoterate demonstrates a mean elimination half-life of about 1.4 ± 0.2 hr and 2.0 ± 0.7 hr in female and male subjects, respectively.L49911] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Gadoterate is one of the most stable gadolinium agents, theoretically making it one of the safer drugs to use during breastfeeding. Guidelines developed by several professional organizations state that breastfeeding need not be disrupted after a nursing mother receives a gadolinium-containing contrast medium. However, because there is no published experience with gadoterate during breastfeeding, other agents may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Gadoterate does not undergo protein binding in vitro. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
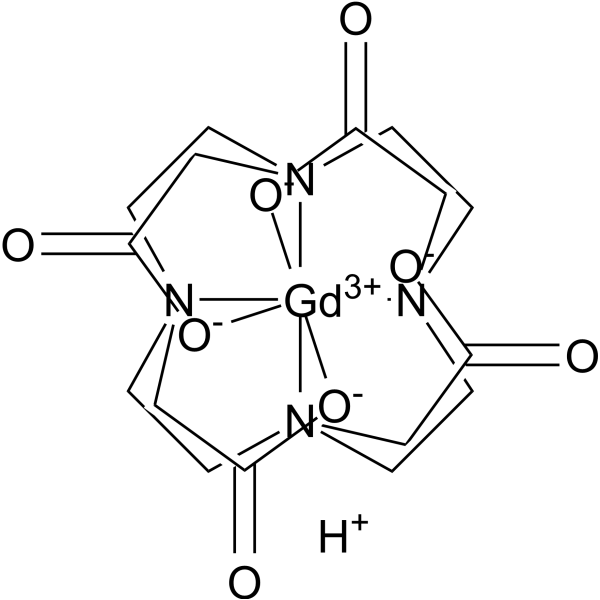
Gadoteric acid, commonly used in the salt form gadoterate meglumine, is a macrocyclic, ionic gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA). It is composed of the organic acid DOTA (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid) used for its chelating properties, and gadolinium (Gd3+). Gadoterate meglumine has one of the highest thermodynamic stability, apparent stability, and kinetic stability, partly due to its macrocyclic structure, and thus has a more favorable safety profile due to a decreased tendency of gadolinium dechelation. Gadoterate is approved by the FDA under the brand name DOTAREM on 20th March 2013 for intravenous uses with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the brain (intracranial), spine, and associated tissues in adult and pediatric patients (2 years of age and older) to detect and visualize areas with disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and/or abnormal vascularity.
Drug Indication Gadoteric acid is indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the brain (intracranial), spine, and associated tissues in adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates) to detect and visualize areas with disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and/or abnormal vascularity. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Gadoterate is a paramagnetic molecule that develops a magnetic moment when placed in a magnetic field. The magnetic moment enhances the relaxation rates of water protons in its vicinity, leading to an increase in signal intensity (brightness) of tissues. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), visualization of normal and pathological tissue depends in part on variations in the radiofrequency signal intensity that occur with differences in proton density, spin-lattice or longitudinal relaxation times (T1), and differences in the spin-spin or transverse relaxation time (T2). When placed in a magnetic field, gadoterate shortens the T1 and T2 relaxation times in target tissues. At recommended doses, the effect is observed with greatest sensitivity in the T1-weighted sequences. |
| 分子式 |
C16H25GDN4O8
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
558.65
|
| 精确质量 |
559.091
|
| CAS号 |
72573-82-1
|
| PubChem CID |
158536
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid
|
| 沸点 |
701.6ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
378.1ºC
|
| tPSA |
160.93
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
510
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1CN(CCN(CCN(CCN1CC(=O)O)CC(=O)[O-])CC(=O)[O-])CC(=O)[O-].[Gd+3]
|
| InChi Key |
GFSTXYOTEVLASN-UHFFFAOYSA-K
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H28N4O8.Gd/c21-13(22)9-17-1-2-18(10-14(23)24)5-6-20(12-16(27)28)8-7-19(4-3-17)11-15(25)26;/h1-12H2,(H,21,22)(H,23,24)(H,25,26)(H,27,28);/q;+3/p-3
|
| 化学名 |
2-[4,7-bis(carboxylatomethyl)-10-(carboxymethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetrazacyclododec-1-yl]acetate;gadolinium(3+)
|
| 别名 |
Gadoteric acid; 72573-82-1; DOTA-Gd; Artirem; Artirem (TN);
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~179.01 mM; with ultrasonication (<60°C))
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7900 mL | 8.9501 mL | 17.9003 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3580 mL | 1.7900 mL | 3.5801 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1790 mL | 0.8950 mL | 1.7900 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。