| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
ER; selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
无论激活 ERα 突变的表达水平如何,与野生型 (WT) ERα 相比,拉昔芬(1 nM-1 μM;48 小时)在 ER+ 乳腺癌细胞中表现出拮抗剂活性 [2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
拉索昔芬(4 毫克/小鼠;皮下注射;5 天/周;持续 43 天)通过降低软骨寡聚基质蛋白 (COMP)(软骨破坏的血清标志物)和降低血清 IL-6(一种炎症细胞因子)水平,减少小鼠关节炎的严重程度[1]。 Lasoxifene(4 mg/小鼠;皮下注射;5 天/周;持续 43 d)通过增加小鼠小梁骨矿物质密度 (BMD) 和皮质厚度来预防 CIA 的系统性骨质流失 [1]。拉索昔芬(5 和 10 毫克/千克;皮下注射;每周 5 天;持续 70 天)可抑制小鼠原发性肿瘤生长并减少肺和肝转移 [3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
Lasofoxifene是一种最初为治疗/预防骨质疏松症而开发的SERM,与ERWT相比,在表达ERY537S或ERD538G的细胞中进行评估时,它是唯一一种被发现具有拮抗作用的化合物(图2I)。后一项观察结果与我们小组最近的一项研究结果一致,该研究表明,在妇科癌症的细胞模型中,拉索菲芬作为ERmuts的抑制剂与ERWT一样有效。这些发现具有重要的临床意义,可以为治疗晚期ERmuts患者的ER拮抗剂的最佳选择提供信息[2]
考虑到SKBR3细胞中观察到的药理学,我们选择了氟维司群(两种突变体都观察到效力变化)、AZD9496(作为ERY537S抑制剂的效力丧失)和拉索菲芬(效力和效力不受突变状态的影响)在这些模型系统中进行分析。使用转染的ERE荧光素酶报告基因评估受体组合的转录活性和药理学[2]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: OVX (ovariectomized) DBA/1 mouse postmenopausal RA model (female DBA/1 mice, 8-10 weeks old, CIA treated) [1]
Doses: 4 mg/mouse/day Route of Administration: subcutaneous injection; 5 days per week from first signs of arthritis (Day 18); 43 days Experimental Results: Reduction in arthritis severity, including reduction in synovial inflammation and joint destruction. At 42 days post-immunization, the average incidence of arthritis was 47% compared with 81% in the vehicle group. Animal/Disease Models: NSG Mouse xenograft tumor model (MIND, mammary intraductal): WT, Y537S and D538G ERα renders tumors [3] Doses: 1, 5 or 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: SC; 5 days per week ; 70-day Experimental Results: Excellent inhibitory effect at 10 mg/kg, resulting in potential tumor shrinkage of Y537S and D538G tumors. At doses of 5 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg, tumor weight was diminished to 60% and 50% for Y537S and D538G, respectively. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) were reached in about 6.0 to 7.3 hours. Displays higher oral bioavailability compared to other SERMs with increased resistance to intestinal glucuronidation due to nonpolar tetrahydronaphthalene structure. In a comparative study in the rat, lasofoxifene showed bioavailability of 62%. Primarily fecal excretion and secondarily renal elimination as mainly metabolites, with less than 2% excreted in urine as unchanged parent drug. The apparent volume of distribution in postmenopausal women is 1350L. The apparent oral clearance (CL/F) of lasofoxifene in postmenopausal women is approximately 6.6 l/hr. Metabolism / Metabolites Phase I oxidation via hepatic CYP3A4/CYP3A5 and CYP2D6 accounts for nearly half of total metabolism of lasofoxifene. Phase II conjugation reactions include glucuronidation and sulfation. Its glucuronidation is catalyzed by UGTs that are expressed in both the liver (UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A6, and UGT1A9) and the intestine (UGT1A8 and UGT1A10). Further metabolites of lasofoxifene detected in plasma are the glucuronide of a hydroxylated metabolite, and the methylated catechols. Lasofoxifene has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(5R,6S)-6-phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl]oxy]oxane-2-carboxylic acid. Biological Half-Life Elimination half-life is approximately 6 days. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Lasofoxifene is highly bound to plasma proteins (>99%) where it predominantly binds to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
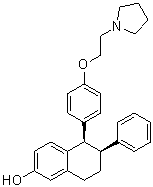
Lasofoxifene is a member of the class of tetralins that is 5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol in which the hydrogens at positions 5 and 6 are replaced by 4-[2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl and phenyl groups, respectively (the 5R,6S-stereoisomer). It is a selective estrogen receptor modulator indicated for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent, a cardioprotective agent, an estrogen receptor agonist, an estrogen receptor antagonist and a bone density conservation agent. It is a member of tetralins, an aromatic ether, a member of naphthols and a N-alkylpyrrolidine.
Lasofoxifene is a non-steroidal 3rd generation selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) that selectively binds to both ERα and ERβ with high affinity. It is a naphthalene derivative marketed for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and for the treatment of vaginal atrophy. It was initially developed as Oporia by Pfizer as a treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis and vaginal atrophy, in which were both rejected for approval by FDA. Later Fablyn was developed as a result of a research collaboration between Pfizer and Ligand Pharmaceuticals with a newly submitted New Drug Application in 2008. It gained approval by European Commission in March 2009. Ligand Pharmaceuticals signed a license agreement with Sermonix Pharmaceuticals for the development and commercialization of oral lasofoxifene in the USA. Lasofoxifene is a non-steroidal, naphthalene-derived, third-generation selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with potential antineoplastic and anti-osteoporotic activities. Upon oral administration, lasofoxifene selectively binds to both estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha; ESR1) and estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta; ESR2) with high affinity and mimics the effects of endogenous estradiol with varying agonist and antagonist effects in ER-expressing tissues. Blockade of ERalpha by lasofoxifene may potentially inhibit estrogen-dependent cancer cell proliferation in ER-expressing cancers. Lasofoxifene may also bind to the certain mutant forms of ERalpha, including the Y537S ESR1 mutant, making it potentially useful in the treatment of tumors that have acquired resistance to other ER-targeting agents. See also: Lasofoxifene Tartrate (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Investigated for use/treatment in postmenopausal osteoporosis to reduce the risk of both vertebral and novertebral fractures, as well as address other postmenopausal conditions, including reduction in risk of breast cancer and treatment of vulvar and vaginal atrophy (VVA) Fablyn is indicated for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at increased risk of fracture. A significant reduction in the incidence of vertebral and non-vertebral fractures but not hip fractures has been demonstrated (see section 5. 1). When determining the choice of Fablyn or other therapies, including oestrogens, for a postmenopausal woman, consideration should be given to menopausal symptoms, effects on uterine and breast tissues, and cardiovascular risks and benefits (see section 5. 1). Mechanism of Action Lasofoxifene mediates an agonist effect on estrogen receptors expressed on bone to mimic the positive effects of estrogen to reduce the production and lifespan of osteoclasts via altering the NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin system, stimulation of osteoblast (the bone forming cells) activity and additional effects on calcium homeostasis. It acts as an antagonist at uterus and mammary glands by suppressing the estrogen signaling in oncogenic pathways and inhibits the downstream gene transcription. A study also suggests that lasofoxifene may also act as an inverse agonist at CB2 cannabinoid receptor which is expressed in bone to inhibit osteoclast formation and resorptive activity. Pharmacodynamics Lasofoxifene exhibits both significant estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity both in vitro and in vivo, targeting any tissues that possess ERs, such as bone, uterus, breast, blood vessels, and liver. Binding assays demonstrated high affinity of the compound for both ERα and ERβ in a tissue-dependent manner. It mimics the effects of estradiol with varying agonist and antagonist effects. |
| 分子量 |
413.55
|
|---|---|
| 精确质量 |
413.235
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 81.32; H, 7.56; N, 3.39; O, 7.74
|
| CAS号 |
180916-16-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lasofoxifene tartrate;190791-29-8
|
| PubChem CID |
216416
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.15g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
572.4ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
300ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
1.05E-13mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.613
|
| LogP |
5.666
|
| tPSA |
32.7
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
533
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)[C@H]2CCC3=CC(=CC=C3[C@H]2C4=CC=C(C=C4)OCCN5CCCC5)O
|
| InChi Key |
GXESHMAMLJKROZ-IAPPQJPRSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C28H31NO2/c30-24-11-15-27-23(20-24)10-14-26(21-6-2-1-3-7-21)28(27)22-8-12-25(13-9-22)31-19-18-29-16-4-5-17-29/h1-3,6-9,11-13,15,20,26,28,30H,4-5,10,14,16-19H2/t26-,28+/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(5R,6S)-6-phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol
|
| 别名 |
CP 336156; CP 336,156; Lasofoxifene; CP336,156; CP336156; CP-336156; CP-33,6156; rac-Lasofoxifene; Oporia; 180915-78-0; CP 336156; (5R,6S)-6-phenyl-5-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol; trade name Fably; Oporia;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4181 mL | 12.0904 mL | 24.1809 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4836 mL | 2.4181 mL | 4.8362 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2418 mL | 1.2090 mL | 2.4181 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。