| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
LPA receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
1-油酰溶血磷脂酸 (0.1-10 μM) 钠可引起诱导和兔破骨细胞中 [Ca2+]i 的电位升高[2]。 1-油酰溶血磷脂酸 (5 μM) 钠诱导破细胞骨片状足的收缩[2]。
溶血磷脂酸(LPA)是一种具有生长因子样活性的天然磷脂[van Corven,Groenink,Jalink,Eichholtz&Moolenaar(1989)Cell 45,45-54]。我们研究了LPA的各种结构类似物刺激静止成纤维细胞DNA合成的能力。当酰基链长变化时,促有丝分裂效力的顺序为:1-油酰基LPA与1-棕榈酰基LPA一致,大于1-肉豆蔻酰基LPA,大于1-月桂酰基LPA大于1-癸酰基LPA;最后一种化合物在测试的浓度范围(1-100微M)内几乎没有活性。与浓度低于25微M的酯连接类似物相比,醚连接的LPA(1-O-十六烷基甘油3-磷酸)的促有丝分裂活性大大降低,在较高浓度下具有细胞毒性。缺乏甘油骨架的磷酸十六酯的活性可以忽略不计。以摩尔计,二酰基磷脂酸(PA)的效力与相应的LPA类似物大致相同,显示出类似的酰基链长度依赖性;这些数据反驳了PA的促有丝分裂作用是由于LPA污染痕迹的可能性。尽管LPA和PA的短链类似物不能拮抗长链(L)PA的作用,但聚阴离子药物苏拉明以可逆和剂量依赖的方式抑制LPA和BA诱导的DNA合成,其浓度[IC50(浓度为50%抑制)约为70微摩尔]不影响表皮生长因子诱导的DNA合成。苏拉明似乎在细胞周期的早期G0/G1期发挥作用,阻断对LPA的即时反应,如磷酸肌醇水解。我们得出结论,LPA和PA都可以作为促进生长的磷脂,脂肪酸链长是有丝分裂潜能的主要决定因素。[1] 溶血磷脂酸(LPA)是一种生物活性磷脂,其功能由多种G蛋白偶联受体介导。我们已经证明,成骨细胞产生LPA,这增加了它介导成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间细胞间信号传导的可能性。在这里,我们研究了破骨细胞中LPA受体的表达、信号传导和功能。局部应用LPA可引起细胞质钙浓度([Ca(2+)](i))的短暂增加,50%的破骨细胞在约400nm LPA处有反应。百日咳毒素或LPA(1/3)受体拮抗剂VPC-32183阻断了LPA诱导的[Ca(2+)](i)升高。LPA导致破骨细胞持续收缩,并破坏外周肌动蛋白带。回撤对VPC-32183或百日咳毒素不敏感,表明涉及不同的信号通路。在这方面,抑制Rho相关激酶刺激了LPA诱导收缩后的呼吸。实时逆转录PCR揭示了编码LPA(1)的转录本,并在较小程度上编码了LPA(2)、LPA(4)和LPA(5)受体亚型。LPA诱导NFATc1的核转位并增强破骨细胞存活,这些作用被VPC-32183或NFAT激活的特定肽抑制剂阻断。LPA在体外略微降低了破骨细胞的再吸收活性。因此,LPA与破骨细胞上的至少两种受体亚型结合:LPA(1)通过G(i/o)偶联以升高[Ca(2+)](i),激活NFATc1并促进存活,第二种受体可能通过G(12/13)和Rho偶联,通过肌动蛋白细胞骨架的重组来引发和维持回缩。这些发现揭示了骨中的一个信号轴,成骨细胞产生的LPA通过该轴作用于多种受体亚型,以诱导破骨细胞活性和功能的多效性效应[2]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
溶血磷脂酸(LPA)在控制情绪行为中的作用还有待确定。我们分析了1-油酰基-LPA(LPA18∶1)在大鼠进食、焦虑和抑郁行为测试中的中心给药效果。为此,进行了高架+迷宫、开阔场地、Y迷宫、强迫游泳和食物摄入测试。此外,还测定了c-Fos在中脑导水管背侧周围灰质(DPAG)中的表达。结果显示,LPA18∶1给药缩短了在高架+迷宫开放臂中的时间,并诱导开放域中的低运动,表明其具有焦虑样表型。有趣的是,在新奇条件下输注LPA18∶1后,这些效果是存在的,但在习惯条件下没有。在强迫游泳试验中,LPA18∶1的给药剂量依赖性地增加了抑郁样行为,根据静止时间进行评估。LPA处理对饲养没有影响。免疫组化分析显示,LPA18∶1可增加DPAG中c-Fos的表达。用免疫细胞化学方法检测了LPA18∶1的主要靶点之一LPA1受体在参与情绪行为控制的脑区的大量表达。这些发现表明,LPA是一种相关的递质,可能参与正常和病理性的情绪反应,包括焦虑和抑郁[3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
实时RT-PCR分析使用TRIZOL试剂和RNeasy Mini试剂盒(Qiagen)从纯化的骨髓来源的破骨细胞中分离总RNA。小鼠LPA1(Edg2,Mm00439145_m1)、LPA2(Edg4,Mm004 69562_m1),LPA3(Edg7,Mm04 69694_m1),LPA4(GPR23,Mm01228533_m1)和LPA5(GPR92,Mm02621109_s1),降钙素受体(Calcr,Mm0403227_1),甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(Gapdh,产品编号4308313)和18S核糖体RNA(产品编号4308329)的引物和探针来自Applied Biosystems(基因表达测定)。根据制造商的建议,使用TaqMan一步RT-PCR Master Mix试剂盒(Applied Biosystems)和ABI Prism 7900HT序列检测器(AppliedBiosystems。样品放大三份。使用从小鼠骨髓来源的破骨细胞、小肠、卵巢和MC3T3-E1细胞获得的总RNA的稀释液来验证引物/探针组的相对扩增效率。将mRNA的量标准化为相同样品中18S核糖体RNA的水平[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
骨髓来源的破骨细胞[2]
如前所述,使用6-10周龄雄性C57Bl/6小鼠股骨和胫骨的骨髓细胞制备破骨细胞。分离后,将细胞悬浮在补充有FBS(10%)和抗生素(1%)的α-最低必需培养基中,并用重组人巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(25 ng/ml)在T75组织培养瓶(每瓶15×106个细胞)中培养。24小时后,取出非粘附细胞并将其重悬于含有FBS(10%)、抗生素(1%)、巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(50ng/ml)和重组人RANKL(huRANKL-LZ,100ng/ml)的α-最低必需培养基中,并以10×104个细胞/cm2在悬浮培养皿 中铺板。将得到的细胞再培养3天。然后在4°C下,通过在不含Ca2+/Mg2+的PBS中孵育10分钟将细胞悬浮,并通过FBS的单位重力速度沉淀富集破骨细胞(2次)。 RAW-264.7衍生的破骨细胞样细胞[2] 小鼠白血病单核巨噬细胞系RAW 264.7从美国典型培养物保藏中心获得,并保存在含有FBS(10%)和抗生素溶液(1%)的Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基中。将RAW 264.7细胞以1.3×104个细胞/cm2的密度培养,并用huRANKL LZ(100ng/ml)处理4天以产生多核破骨细胞样细胞。 |
| 动物实验 |
Given the abundant distribution of the LPA receptors throughout the organism, the i.c.v. administration protocol was used to study the specific role of LPA in the brain, thereby avoiding confounding results derived from potential peripheral effects.[3]
For i.c.v. injections and administration, we used a previously described protocol. Stainless steel guide cannulae aimed at the left or right lateral ventricle were implanted in the rats. The animals were anesthetized with equithesin and placed in a stereotaxic apparatus with the incisor bar set at 5 mm above the interaural line. A guide cannula (7 mm and 23-gauge) was secured to the skull using two stainless steel screws and dental cement, and the opening was closed using 30-gauge obturators. The implantation coordinates were 0.6 mm posterior to bregma, ±2.0 mm lateral, and 3.2 mm below the surface of the skull, according to the rat brain stereotaxic coordinates of Paxinos and Watson. These coordinates placed the cannula 1 mm above the ventricle. After a 7-day postsurgical recovery period, the cannula patency was confirmed through the gravity flow of isotonic saline through an 8-mm long and 30-gauge injector inserted within the guide to 1 mm beyond the tip. This procedure was used to familiarize the animals with the injection technique (sham injection). The obturator was removed from the guide cannula, and an 8 mm injector (30 gauge stainless steel tubing), connected to 70 cm of calibrated polyethylene-10 tubing, was lowered into the ventricle. The tubing was subsequently raised until the flow was initiated, and 5 µL of drug or vehicle solution was infused over a 30–60 s period. The injector remained in the guide cannula for an additional 30 s to facilitate the diffusion of the solution and subsequently was removed. The xstylet was immediately replaced. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a naturally occurring phospholipid with growth-factor-like activities [van Corven, Groenink, Jalink, Eichholtz & Moolenaar (1989) Cell 45, 45-54]. We have examined various structural analogues of LPA for their ability to stimulate DNA synthesis in quiescent fibroblasts. When the acyl-chain length is varied, the rank order of mitogenic potency is: 1-oleoyl LPA congruent to 1-palmitoyl LPA greater than 1-myristoyl LPA greater than 1-lauroyl LPA greater than 1-decanoyl LPA; the last compound shows almost no activity over the concentration range tested (1-100 microM). An ether-linked LPA (1-O-hexadecylglycerol 3-phosphate) has much decreased mitogenic activity as compared with the ester-linked analogue at concentrations less than 25 microM, and becomes cytotoxic at higher concentrations. Hexadecylphosphate, which lacks a glycerol backbone, has negligible activity. On a molar basis, diacyl phosphatidic acid (PA) is about equally potent as the corresponding LPA analogue, showing similar acyl-chain-length dependence; the data argue against the possibility that the mitogenic action of PA is due to contaminating traces of LPA. Although the short-chain analogues of LPA and PA fail to antagonize the action of long-chain (L)PAs, the polyanionic drug suramin inhibits LPA- and PA-induced, DNA synthesis in a reversible and dose-dependent manner, at concentrations [IC50 (concn. giving 50% inhibition) approximately 70 microM] that do not affect epidermal-growth-factor-induced DNA synthesis. Suramin appears to act in the early G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle, blocking immediate responses to LPA such as phosphoinositide hydrolysis. We conclude that both LPA and PA can function as growth-promoting phospholipids, with the fatty acid chain length being a major determinant of mitogenic potency. [3]
LPA is as a potent mitogen and motility factor that has been implicated in the metastasis of breast and ovarian tumors to bone. Moreover, breast cancer cells overexpressing LPA1 promote the recruitment of osteoclasts to metastatic sites and stimulate bone resorption. Our previous findings demonstrate that osteoblasts can produce LPA. This LPA may attract and activate tumor cells, as well as regulate osteoclast motility and survival. Thus, LPA released from osteoblasts may be an important autocrine and paracrine mediator, physiologically regulating skeletal development and remodeling, and pathologically contributing to metastatic bone disease.[2] |
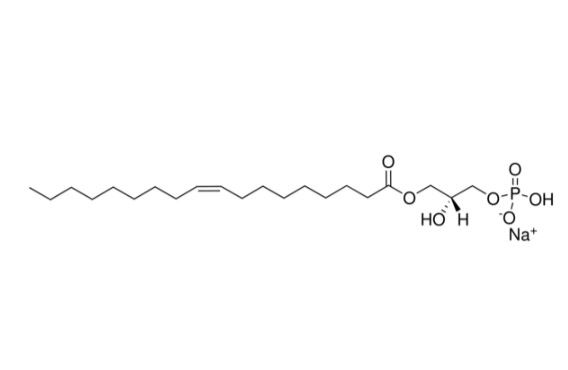
| 分子式 |
C21H40O7P.NA
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
458.50
|
| 精确质量 |
458.24
|
| CAS号 |
325465-93-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1-Oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid; 65528-98-5
|
| PubChem CID |
44159357
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid
|
| tPSA |
116
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
21
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
474
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
CCCCCCCC/C=C\CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP(=O)(O)[O-])O.[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
XGRLSUFHELJJAB-JGSYTFBMSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C21H41O7P.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-21(23)27-18-20(22)19-28-29(24,25)26;/h9-10,20,22H,2-8,11-19H2,1H3,(H2,24,25,26);/q;+1/p-1/b10-9-;/t20-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium;[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(Z)-octadec-9-enoyl]oxypropyl] hydrogen phosphate
|
| 别名 |
Lysophosphatidic acid; 325465-93-8; 1-Oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid sodium salt; Sodium (R,Z)-2-hydroxy-3-(oleoyloxy)propyl hydrogenphosphate; sodium;[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-[(Z)-octadec-9-enoyl]oxypropyl] hydrogen phosphate; MFCD00133427; 1-Oleoyl lysophosphatidic acid (sodium); 22556-62-3; 1-oleoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (sodium salt);
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~218.10 mM)
DMSO : ~1.85 mg/mL (~4.03 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1810 mL | 10.9051 mL | 21.8103 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4362 mL | 2.1810 mL | 4.3621 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2181 mL | 1.0905 mL | 2.1810 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01766817 | Completed | Drug: BMS-986020 Drug: Placebo matching with BMS-986020 |
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis | Bristol-Myers Squibb | January 31, 2013 | Phase 2 |
| NCT00986206 | Completed | Diagnostic Test: Biomarker LPA and HE4 |
brca1 Mutation Carrier brca2 Mutation Carrier Ovarian Cancer |
Women and Infants Hospital of Rhode Island |
June 2009 | N/A |