| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 μg |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
CXCR4/chemokine receptor C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
越来越多的文献报道了C-X-C基序趋化因子受体4(CXCR4)在各种癌症实体中的上调,使该受体成为分子成像和放射治疗的合适靶点。例如,CXCR4靶向正电子发射断层扫描(PET)剂[68 Ga]PentixaFor已被证明可用于全面评估实体瘤的现状,包括肾上腺皮质癌或小细胞肺癌癌症。此外,[68 Ga]PentixaFor还为血液系统恶性肿瘤提供了极好的读数,如多发性骨髓瘤、边缘区淋巴瘤或套细胞淋巴瘤。基于PET的体内CXCR4能力定量允许选择适合使用治疗等效物[177Lu]/[90Y]PentixaTher治疗的候选者。这种CXCR4导向的治疗概念已被用作造血干细胞移植前的调节方案,并实现足够的抗淋巴瘤/肿瘤活性,特别是对辐射高度敏感的恶性组织,如血液系统。为了增加安全裕度,常规进行治疗前剂量测定,以确定最佳活性,从而提高疗效并减少脱靶不良事件[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在受CXCR4影响的小鼠中( −) 或CXCR4( +) 白血病异种移植物中观察到[68Ga]PentixaFor信号增加[1]。
经静脉给药后[177Lu], PentixaTher与代谢稳定性较高的血浆蛋白结合,只有约4%的一小部分通过CXCR4结合到白细胞和血小板上。在肾、肝、脾和骨髓以及表达cxcr4的恶性组织中均可发现闪烁可检测的活性积累。图5显示了MM患者器官和组织中活动保留的测量时间函数。除非另有说明,该图与下面总结的结果一样,摘自最近发表的一项关于PentixaTher生物动力学和剂量学的研究[177Lu]。[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
生物动力学和治疗前剂量测定[1]
静脉注射后,[177Lu]PentixaTher以高代谢稳定性与血浆蛋白结合,只有约4%的一小部分通过CXCR4结合与白细胞和血小板结合。在肾脏、肝脏、脾脏和骨髓以及表达CXCR4的恶性组织中发现了闪烁检测到的活性积聚。图5显示了MM患者器官和组织中活动保留的测量时间函数示例。除非另有说明,否则该图与下文总结的结果一样,取自最近发表的关于[177Lu]PentixaTher生物动力学和剂量学的研究。 |
| 动物实验 |
Aiming to provide a roadmap among a broad spectrum of neoplasms, a recent bicentric study assessed [68Ga]PentixaFor uptake and image contrast among the largest cohort of subjects imaged with CXCR4-directed PET to date, thereby determining the most relevant clinical applications. Investigating 690 patients affected with various solid tumors and hematological neoplasms scheduled for 777 scans, 68.9% demonstrated uptake in sites of disease The highest tracer uptake was recorded in MM (maximum SUV > 12). The second highest uptake was then found in ACC, MCL, adrenocortical adenoma, and SCL. Osteosarcoma, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, and Ewing sarcoma, on the other hand, exhibited the lowest average SUV (< 6; Fig. 4A). Comparable findings were recorded for target-to-background ratio (TBR), thereby reflecting image contrast. Again, the highest TBR was found in advanced blood cancers, including MM, MCL, and acute lymphoblastoid leukemia (Fig. 4B). Moreover, lower specific activity is characterized by higher amounts of cold mass, thereby having a relevant impact on image interpretation. The authors did not record any relevant significant associations with semiquantitative parameters and specific activity, supporting the hypothesis that read-out capabilities are not hampered, regardless of the amount of specific activities[1].
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The total body 177Lu activity typically decays bi-exponentially. About half of the activity is eliminated with a median effective half-life of about 10 h mainly by renal excretion; the remainder decays with a mean effective half-life of about 4 days. Activity concentration in blood typically shows three components with about 10%, 2.5%, and 0.2% of the administered activity per liter of blood decaying with half-lives of 0.23 h, 7 h, and 40 h, respectively.
[177Lu]PentixaTher accumulates in the bone marrow and remains there with a half-life of several days, making the bone marrow the critical organ where acute toxicity is foremost expected. The calculated specific bone marrow doses were heterogeneous, ranging from 0.14 to 2.3 (median value, 0.5) Gy/GBq 177Lu. Given high individual variability and the uncertainties of bone marrow dosimetry, therapeutic use of PentixaTher may be confined to myeloablative therapies. However, it must be considered in myeloablative treatment that the long residence time of the activity in the bone marrow requires a long decay time before a stem cell transplantation can be safely performed. Therefore, in order to reduce the duration of the phase of aplasia and the associated risk of threatening complications, therapy is usually performed with the nuclide 90Y instead of 177Lu[1]. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity profile[1]
Investigating the safety profile, 22 patients with advanced blood cancer treated with [177Lu] or [90Y]PentixaTher and subsequent chemotherapy followed by HSCT were investigated. As expected, all patients developed cytopenia (including hemoglobin, leukocytes, granulocytes, and platelets; Fig. 7A). One patient developed tumor lysis syndrome, followed by grade 3 acute kidney failure, while all other adverse effects were manageable and did not cause any delay for further treatment. In this regard, time interval between CXCR4 ERT and conditioning therapy was significantly longer with [177Lu]PentixaTher, which can be explained by the longer half-life of 6.7 days when compared to [90Y]PentixaTher (2.7 days; Fig. 7B). The ongoing COLPRIT trial is a prospective phase I/II study which will further elucidate the therapeutic efficacy and safety of this theranostic strategy in patients with advanced blood cancer (Eudra‐CT 2015‐001817‐28). |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
CXCR4 is upregulated on various cancer cells, rendering this receptor as a potential target for tumor read-out and treatment strategies. The CXCR4-targeted PET agent [68Ga]PentixaFor has been successfully applied to patients with solid and advanced blood cancers, demonstrating substantially increased radiotracer accumulation in ACC, SCLC, MM, MZL, MCL, or gastric MALT. In addition to assessment of widespread disease, such a functional imaging approach allows to assess the capacities of the target in-vivo. Thus, quantification of [68Ga]PentixaFor accumulation may then allow to estimate the efficacy of non-radioactive CXCR4 inhibitory treatments (e.g., with anti-human CXCR4 IgG monoclonal antibodies for MM patients) or to identify patients that would be eligible for treatment with hot CXCR4-directed theranostic radiotracers, such as [177Lu]/[90Y]PentixaTher. The latter concept has already been applied to hematological malignancies known to be sensitive to radiation, e.g., in advanced MM, ALL, or diffuse large B cell lymphoma. In this context, pretherapeutic dosimetry can determine the appropriate amount of activity to achieve anti-tumor effects and to minimize off-target effects. CXCR4 ERT also caused desired bone marrow ablation and has therefore been incorporated in the therapeutic algorithm of advanced blood cancer patients (allogenic/autologous HSCT following CXCR4 ERT along with successful engraftment). Therapeutic efficacy of those treatment regimens led to remarkable outcome benefits in those heavily pretreated patients. Given substantial high doses in the tumor, some patients experienced tumor lysis syndrome and thus, those individuals should be closely monitored[1].
|
| 分子式 |
C60H80N14O14
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
1221.36261367798
|
| 精确质量 |
1220.597
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.00; H, 6.60; N, 16.06; O, 18.34
|
| CAS号 |
1341207-62-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1341207-62-2;1342253-77-3 (Gallium);1345698-96-5 (Ga-68);
|
| PubChem CID |
54575322
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
-6.3
|
| tPSA |
404Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
12
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
19
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
23
|
| 重原子数目 |
88
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
2330
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
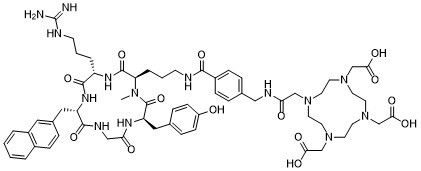
CN1[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](C1=O)CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)CC3=CC4=CC=CC=C4C=C3)CCCN=C(N)N)CCCNC(=O)C5=CC=C(C=C5)CNC(=O)CN6CCN(CCN(CCN(CC6)CC(=O)O)CC(=O)O)CC(=O)O
|
| InChi Key |
OSUJVKAXNLHVRB-HUMWUIFSSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
nChI=1S/C60H80N14O14/c1-70-49(9-5-20-63-55(84)43-16-10-40(11-17-43)33-65-51(77)35-71-22-24-72(36-52(78)79)26-28-74(38-54(82)83)29-27-73(25-23-71)37-53(80)81)58(87)68-46(8-4-21-64-60(61)62)57(86)69-47(32-41-12-15-42-6-2-3-7-44(42)30-41)56(85)66-34-50(76)67-48(59(70)88)31-39-13-18-45(75)19-14-39/h2-3,6-7,10-19,30,46-49,75H,4-5,8-9,20-29,31-38H2,1H3,(H,63,84)(H,65,77)(H,66,85)(H,67,76)(H,68,87)(H,69,86)(H,78,79)(H,80,81)(H,82,83)(H4,61,62,64)/t46-,47-,48+,49+/m0/s1
SMILES Code: OC1=CC=C(C[C@@H](NC(CNC([C@H](CC2=CC3=C(C=CC=C3)C=C2)NC4=O)=O)=O)C(N(C)[C@H](CCCNC(C5=CC=C(CNC(CN6CCN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC6)=O)C=C5)=O)C(N[C@H]4CCCNC(N)=N)=O)=O)C=C1
|
| 化学名 |
2,2',2''-(10-(2-((4-((3-((2R,5S,8S,14R)-5-(3-guanidinopropyl)-14-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-1-methyl-8-(naphthalen-2-ylmethyl)-3,6,9,12,15-pentaoxo-1,4,7,10,13-pentaazacyclopentadecan-2-yl)propyl)carbamoyl)benzyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triyl)triacetic acid
|
| 别名 |
CPCR 4-2; CPCR4-2; CPCR-4-2; CPCR42; CPCR4-2; TOZ93UY3AX; UNII-TOZ93UY3AX; 2-[4,7-bis(carboxymethyl)-10-[2-[[4-[3-[(2R,5S,8S,14R)-5-[3-(diaminomethylideneamino)propyl]-14-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-1-methyl-8-(naphthalen-2-ylmethyl)-3,6,9,12,15-pentaoxo-1,4,7,10,13-pentazacyclopentadec-2-yl]propylcarbamoyl]phenyl]methylamino]-2-oxoethyl]-1,4,7,10-tetrazacyclododec-1-yl]acetic acid; (68GA)PENTIXAFOR; BOCLATIXAFORTIDE; Ligand of gallium Ga 68-pentixafor; CPCR-42; CPCR 42; Pentixafor
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (81.9 mM)
Methanol: ≥ 125 mg/mL (102.3 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.8188 mL | 4.0938 mL | 8.1876 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1638 mL | 0.8188 mL | 1.6375 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0819 mL | 0.4094 mL | 0.8188 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。