| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
丙卡巴肼处理(5 和 20 nM;1 小时)显示出不同程度的细胞活力 [1]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
丙卡巴肼(腹腔注射;每天一次;五天;50 和 150 mg/kg)会导致造血细胞中产生微核,但不会增加骨髓 (MF) 中 lacZ 突变的频率 [2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定 [1]
细胞类型: L1210 细胞 测试浓度: 5 和 20 nM 孵育时间: 1 小时 实验结果: 5 mM 和 20 mM 时细胞活力分别为 99.3% 和 99.9%。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male muta mice (7-8 weeks old) [2]
Doses: 50 and 150 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; 50 and 150 mg/kg; one time/day; 5-day Experimental Results: at 50 mg/kg , MN frequency was Dramatically increased, and peripheral blood micronucleus induction was observed. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Procarbazine is rapidly and completely absorbed. Procarbazine hydrochloride is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed from the GI tract following oral administration. Following oral administration of a single 30 mg dose of radiolabeled procarbazine hydrochloride, peak plasma radioactive concentrations of the drug were attained within 1 hour. Oral administration generally results in plasma concentrations similar to those achieved following IV administration of the drug. /Procarbazine hydrochloride/ Approximately 45% to 70% of a dose is excreted in the urine during the first 24 hr as metabolites. From 25 to 70% of an oral or parenteral dose given to man is recovered from the urine during the first 24 hours after administration; less than 5% is excreted as the unchanged compound, and the rest is mostly in the form of a metabolite, N-isopropylterephthalanic acid. Distribution studies in animals and humans using radiolabeled procarbazine hydrochloride administered IV have shown concentrations of radioactivity to be present in the liver, kidneys, intestinal wall and skin. The drug crosses the blood-brain barrier and distributes into CSF. Equilibration of procarbazine between plasma and CSF occurs rapidly following oral administration. It is not known whether procarbazine is distributed into milk. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PROCARBAZINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Procarbazine is metabolized primarily in the liver and kidneys. The drug appears to be auto-oxidized to the azo derivative with the release of hydrogen peroxide. The azo derivative isomerizes to the hydrazone, and following hydrolysis splits into a benzylaldehyde derivative and methylhydrazine. The methylhydrazine is further degraded to CO2 and CH4 and possibly hydrazine, whereas the aldehyde is oxidized to N-isopropylterephthalamic acid, which is excreted in the urine. It is rapidly metabolized in man ... . Oxidation of procarbazine produces the corresponding azo compound and hydrogen peroxide. Further metabolism, presumably in the liver, yields azoxy derivatives that circulate in the bloodstream and have potent cytotoxic activity. Procarbazine yields demethylprocarbazine probably in rats; yields n-isopropyl-alpha-methylazo-p-toluamide and terephthalic isopropylamide in rats. /from table/ Rats biotransformed ip dose of (14)C-monomethylhydrazine to (14)C-methane within 3 min of injection. ... Rats produced 25% (14)C-CH4 and 3% (14)C-CO2 in 90 min. ...(14)C-procarbazine ... was less readily biotransformed to CH4. After 90 min, 4% of dose...excreted as (14)C-CH4. /hydrochloride/ The NADPH-dependent microsomal metabolism of [14C]procarbazine labeled on the terminal N-methyl group resulted in the covalent binding of the drug to exogenously added DNA; this reaction was inhibited by metyrapone. Procarbazine metabolism was also shown to result in covalent binding of the methyl group of the drug to microsomal protein upon metabolism but the extent of protein binding was at least an order of magnitude smaller than that see with its primary oxidative metabolite. N-isopropyl-alpha-(2-methylazo)-p-toluamide. The characteristics of the reactions leading to the covalent binding of the N-methyl group of the azo derivative to microsomal protein and its metabolism to form methane, possessed a number of similarities in the apparent kinetic parameters (Km and Vmax), induction and inhibition patterns indicating a common pathway of metabolism to form a reactive intermediate and the involvement of cytochrome p450. Reduced glutathione stimulated methane formation and inhibited covalent binding to protein. For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for PROCARBAZINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Procarbazine is metabolized primarily in the liver and kidneys. The drug appears to be auto-oxidized to the azo derivative with the release of hydrogen peroxide. The azo derivative isomerizes to the hydrazone, and following hydrolysis splits into a benzylaldehyde derivative and methylhydrazine. The methylhydrazine is further degraded to CO2 and CH4 and possibly hydrazine, whereas the aldehyde is oxidized to N-isopropylterephthalamic acid, which is excreted in the urine. Half Life: 10 minutes Biological Half-Life 10 minutes The biological half-life of procarbazine hydrochloride in both plasma and CSF is approximately 1 hour. /Procarbazine hydrochloride/ ... Half-life in blood after iv injection is approx 7 min. The plasma half-life of parent drug is approximately 10 minutes. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
The precise mode of cytotoxic action of procarbazine has not been clearly defined. There is evidence that the drug may act by inhibition of protein, RNA and DNA synthesis. Studies have suggested that procarbazine may inhibit transmethylation of methyl groups of methionine into t-RNA. The absence of functional t-RNA could cause the cessation of protein synthesis and consequently DNA and RNA synthesis. In addition, procarbazine may directly damage DNA. Hydrogen peroxide, formed during the auto-oxidation of the drug, may attack protein sulfhydryl groups contained in residual protein which is tightly bound to DNA. Hepatotoxicity Mild and transient elevations in serum aminotransferase levels are not uncommon during courses of systemic combination chemotherapy and the role of procarbazine in these abnormalities is often not clear. Aminotransferase elevations arise in more than half of patients and rise above 5 times ULN in 10 to 20% of patients. However, dose modification for serum enzyme elevations is rarely necessary. Clinically apparent liver disease with fever and marked elevations in serum aminotransferase levels without jaundice has been reported but is very rare. A single case report described self-limited, hepatocellular injury without jaundice during a second course of combination therapy and recurrence upon rechallenge with procarbazine, but not with the other antineoplastic agents being used. Likelihood score: D (possible rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Toxicity Data LD50=785 mg/kg (orally in rats) Interactions Concurrent use /of alcohol/ with procarbazine may result in a disulfiram like reaction and additive central nervous system depression and postural hypotension; also, possible tyramine content in alcoholic beverages, especially beer, wine, or ale, may induce hypertensive reactions. Concurrent use /of local anesthetics with epinephrine or levonordefrin, or cocaine/ with procarbazine may cause severe hypertension due to sympathomimetic effects. Cocaine should not be administered during or within 14 days following administration of an MAO inhibitor. Hypotensive effects may be potentiated when spinal anesthetics are used concurrently with procarbazine; discontinuation of procarbazine at least 10 days before elective surgery if spinal anesthesia is planned may be advisable. Concurrent use /of anticholinergics or other medications with anticholinergic activity, antidyskinetic agents, or antihistamines/ with procarbazine may intensify anticholinergic effects because of the secondary anticholinergic activities of MAO inhibitors; also MAO inhibitors may block detoxification of anticholinergics, thus potentiating their action; patients should be advised to report occurrence of gastrointestinal problems promptly since paralytic ileus may occur with concurrent therapy. Concurrent use with MAO inhibitors may also prolong and intensify CNS depressant and anticholinergic effects of antihistamines; concurrent use is not recommended. For more Interactions (Complete) data for PROCARBAZINE (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat IV 600 mg/kg body weight (at day 59) |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Antineoplastic Agents; Carcinogens MEDICATION (VET): Antineoplastic... /it is used/ exptl, against wide variety of transplanted animal tumors. /hydrochloride/ Procarbazine is indicated, in combination with other agents, for treatment of Hodgkin's disease (Stage III and IV) ... . /Included in US product labeling/ /Procarbazine is indicated, in combination with other agents, for treatment of/ some non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. /NOT included in US product labeling/ For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PROCARBAZINE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Procarbazine is a highly toxic drug and should be used only under constant supervision by a clinician experienced in cancer chemotherapy. When appropriate, procarbazine therapy should be initiated with the patient hospitalized; the patient's clinical and histologic diagnosis and hematologic, renal, and hepatic status should be carefully considered. Although appropriate studies with procarbazine have not been performed in the geriatric population, the potential for increased vascular accidents (especially in the event of sudden hypertensive episodes), increased sensitivity to hypotensive effects, and reduced metabolic capacity discourages the first-time use of MAO inhibitors in patients over 60 years of age. When an MAo inhibitor is prescribed for an elderly patient, the patient's history of depression, ability to comply with prescribing instructions, and any potential drug interactions must also be considered. In addition, elderly patients are more likely to have age-related renal function impairment, which may require a lower dosage or, in severe cases, avoidance of use of procarbazine. Patients should be warned not to drink alcoholic beverages and to avoid food with high tyramine content, such as yogurt, cheese, and bananas, while receiving procarbazine. Patients should also be instructed to avoid use of over-the-counter preparations containing antihistamine or sympathomimetic drugs and to discuss any prescription medications they are taking with the clinician who is supervising procarbazine therapy. Pregnancy risk category: D /POSITIVE EVIDENCE OF RISK. Studies in humans, or investigational or post-marketing data, have demonstrated fetal risk. Nevertheless, potential benefits from the use of the drug may outweigh the potential risk. For example, the drug may be acceptable if needed in a life-threatening situation or serious disease for which safer drugs cannot be used or are ineffective./ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PROCARBAZINE (24 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Procarbazine is an antineoplastic in the class of alkylating agents and is used to treat various forms of cancer. Alkylating agents are so named because of their ability to add alkyl groups to many electronegative groups under conditions present in cells. They stop tumor growth by cross-linking guanine bases in DNA double-helix strands - directly attacking DNA. This makes the strands unable to uncoil and separate. As this is necessary in DNA replication, the cells can no longer divide. In addition, these drugs add methyl or other alkyl groups onto molecules where they do not belong which in turn inhibits their correct utilization by base pairing and causes a miscoding of DNA. Procarbazine is cell-phase specific for the S phase of cell division. |
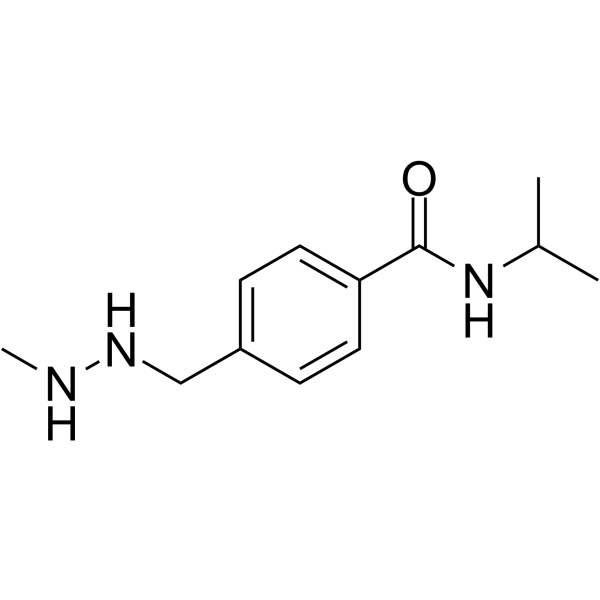
| 分子式 |
C12H19N3O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
221.29876
|
| 精确质量 |
221.152
|
| CAS号 |
671-16-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Procarbazine Hydrochloride;366-70-1
|
| PubChem CID |
4915
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.0±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
384.6±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
148.9±26.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.529
|
| LogP |
0.77
|
| tPSA |
53.16
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
210
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(NC(C)C)C1=CC=C(CNNC)C=C1
|
| InChi Key |
CPTBDICYNRMXFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H19N3O/c1-9(2)15-12(16)11-6-4-10(5-7-11)8-14-13-3/h4-7,9,13-14H,8H2,1-3H3,(H,15,16)
|
| 化学名 |
4-[(2-methylhydrazinyl)methyl]-N-propan-2-ylbenzamide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.5188 mL | 22.5938 mL | 45.1875 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.9038 mL | 4.5188 mL | 9.0375 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4519 mL | 2.2594 mL | 4.5188 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。