| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
mGluR2
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
LY-354740 下调斑点 1014、1822(缺氧上调蛋白 1)、4513(蛋白二硫键异构酶 3 的亚型)、6204、6312、7306(26S 蛋白酶体非 ATP 酶调节亚基 7)以及蛋白斑点 1013 和6005(结蛋白),并上调小鼠皮质神经元中的点 6507(塌陷素反应介导蛋白 1)[2]。
LY379268和LY354740处理的培养皮层神经元的蛋白质组学分析[2] 将培养的小鼠皮质神经元暴露于LY379268或LY354740(均为1μM)24小时。对照培养物用等体积的生理盐水处理。2D电泳允许可重复地分离916个蛋白质点(图1),对其进行差异表达分析。在药物处理的培养物中,与对照培养物相比,共检测到17个斑点(11个通过质谱鉴定,如表1所示),其表达水平存在显著差异(被认为是±1.5倍的变化,p<0.05)。表2中报告了折叠变化差异,其中还显示了LY354740和LY379268处理细胞之间的显著差异。与对照培养物相比,在LY354740处理的培养物中检测到9个蛋白点的差异表达,在LY379268处理的培养液中检测到14个蛋白点。LY379268和LY354740均下调了点1014、1822(缺氧上调蛋白1)、4513(蛋白二硫键异构酶3的同工型)、6204、6312和7306(26S蛋白酶体非ATP酶调节亚基7),上调了点6507(胶原酶反应介导蛋白1)。 蛋白质斑点1013和6005(去丝蛋白)仅被LY354740下调。相比之下,蛋白质斑点3503(T-复合蛋白1亚基θ)、5106(异戊烯基二磷酸Δ异构酶1)、05310(Septin-2)、5321和7306(26S蛋白酶体非ATP酶调节亚基7)仅被LY379268下调。LY379268上调了斑点7518(T复合蛋白1亚基ζ)的表达。斑点4417(Rab GDIβ)和4418(未鉴定)被LY379268下调,并在LY354740的作用下呈上调趋势。 LY379268或LY354740处理的培养皮层和海马神经元中Rab GDIα和Rab GDIβ蛋白水平的测量[2] 我们可以使用用LY379268或LY354740处理的培养皮层神经元来验证蛋白质组学数据。使用特异性GDIα抗体的免疫印迹分析显示,在50kDa处有一条单链,对应于Rab GDIα的推断分子大小。Rab GDIβ可以用GDI2多克隆抗体检测。该抗体标记了46至50 kDa之间的两条带,较低的带(更微弱)对应于Rab GDIβ的推断分子大小(图2)。用LY379268(1μM)处理培养的皮质神经元24小时,降低了Rab GDIβ水平,但不影响Rab GDIα水平(图2A)。LY379268对Rab GDIβ水平的降低作用被优先的mGlu2/3拮抗剂LY341495(1μM)降低,LY354740(1μM)没有模仿(图2A)。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
LY-354740(15 或 30 mg/kg,ip)对 Gria1−/− 或 WT 小鼠的空间工作记忆表现没有影响,并且对 Gria1−/ 中短试验间隔的奖励交替测试没有影响- 和浓度为 30 mg/kg 的 WT 小鼠。 LY354740(15 或 30 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可降低野生型和 Gria1−/− 小鼠的自发运动活动[1]。 LY354740(15 mg/kg,腹膜内注射)可在首次接触的 GluA1-KO 和预处理的 GluA1-KO 雄性中引起新奇诱导的过度运动,但在雌性中则不然。 LY354740(15 mg/kg,腹腔注射)显着降低 GluA1-KO 雄性的 c-Fos 表达增加至 WT 雄性的水平,但不降低雌性的水平[3]。 LY354740(10 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可减弱固定应激诱导的大鼠 mPFC 中 BDNF mRNA 表达的增加[4]。
II组代谢型谷氨酸受体激动剂被认为是潜在的抗精神病药物,至少部分是基于激动剂LY354740似乎可以挽救非竞争性N-甲基-d-天冬氨酸受体(NMDAR)拮抗剂引起的认知缺陷,包括啮齿动物的空间工作记忆缺陷。在这里,我们测试了LY354740在缺乏AMPA谷氨酸受体GluA1亚基的小鼠中拯救空间工作记忆表现的能力,该亚基由Gria1编码,Gria1是最近通过全基因组关联研究与精神分裂症有关的基因。我们发现,LY354740在T迷宫的奖励交替表现中未能挽救Gria1-/-小鼠的空间工作记忆缺陷。相比之下,LY354740确实将这些动物的运动过度活跃程度降低到与对照组相似的水平。多巴胺受体拮抗剂氟哌啶醇也发现了类似的模式,尽管相同剂量的氟哌啶醇减少了Gria1-/-小鼠的运动过度活跃,但它们的空间工作记忆缺陷没有改善。LY354740的这些结果与使用非竞争性NMDAR拮抗剂在谷氨酸能减退模型中拯救空间工作记忆形成对比。未来的研究应确定II组mGluR激动剂是否可以通过其他NMDAR操作来挽救空间工作记忆缺陷,包括遗传模型和NMDAR功能的其他药理学操作。[1] LY379268和LY354740是mGlu2/3代谢型谷氨酸受体的两种激动剂,在精神分裂症小鼠模型中显示出不同的效力。这两种药物的这种差异效应仍然无法解释。我们在用LY379268或LY354740攻击的培养皮层神经元中进行了蛋白质组学分析。在受这两种药物不同影响的少数蛋白质中,Rab-GDP解离抑制剂β(Rab-GDIβ)被LY379268下调,并在LY354740的作用下呈上调趋势。在培养的海马神经元中,LY379268选择性下调Rab GDI的α亚型。Rab GDI抑制突触小泡相关蛋白Rab3A的活性,并在精神分裂症患者的大脑中降低。我们检测了暴露于产前应激的小鼠(“PRS小鼠”)中Rab GDI的表达,这些小鼠被描述为精神分裂症的推定模型。在出生后第1天和第21天(PND),PRS小鼠海马中的Rab GDIα蛋白水平升高,但在PND60时没有。在PND21时,PRS小鼠还表现出海马突触体中去极化诱发的[(3)H]d-天冬氨酸释放减少。用LY379268(1或10mg/kg,i.p.)治疗7天,PRS小鼠海马中Rab GDIα水平的增加被逆转,但用等剂量的LY354740治疗则没有逆转。这些数据加强了PRS小鼠作为精神分裂症模型的有效性,并首次显示了LY379268和LY354740之间的药效学差异,这可能被用来解释这两种药物在小鼠模型中的差异效应[2]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
MALDI-ToF质谱法鉴定蛋白质[2]
从凝胶中手动切下感兴趣的蛋白质斑点,用高纯水和50%乙腈/水洗涤,并用100%乙腈脱水。凝胶切片在室温下在含有25 ng/μL胰蛋白酶(胰蛋白酶金,质谱级)的20μL 40 mM NH4HCO3/10%乙腈中膨胀。1小时后,加入50μL 40 mM·NH4HCO3/10%乙腈,在37°C下消化过夜。用50%乙腈/5%三氟乙酸提取产生的肽(TFA,2步,每次在室温下20分钟),通过真空离心干燥,悬浮在0.1%TFA中,通过微型ZipTip C18移液管尖端,直接用光谱仪基质溶液(10 mg/mlα-氰基-4-羟基肉桂酸在50%乙腈/1%TFA中)洗脱。使用Voyager DE MALDI ToF质谱仪获得胰蛋白酶肽的质谱。使用MASCOT搜索引擎进行肽质量指纹数据库搜索(http://www.matrixscience.com)在NCBInr/Swis-Prot数据库中。参数设置为允许每个肽有一个缺失的切割,质量耐受性为0.5Da,并将半胱氨酸的脲甲基化视为固定修饰,将蛋氨酸的氧化视为可变修饰。用于接受鉴定的标准包括序列覆盖范围、匹配肽的数量和概率得分,详见表1。 |
| 细胞实验 |
小鼠皮质神经元原代培养[2]
如前所述(Di Menna等人,2013),在胚胎第15天从CD1小鼠中获得皮质神经元的原代培养物(三种制剂)。简而言之,在无Ca2+/Mg2+的缓冲液中解剖每个制备的14-16个胚胎的皮质,并机械分离。将皮质细胞以2×106/皿的密度铺在35 mm的培养皿上,培养皿上预先涂有0.1 mg/ml聚-d-赖氨酸(分子量70000-150000,0.1 mg/ml)和0.002 mg/ml层粘连蛋白,在Neurobasel-a B27培养基中补充以下成分:牛血清白蛋白(10 mg/ml)、胰岛素(10μg/ml)、转铁蛋白(100μg/ml),腐胺(100μM)、孕酮(20 nM)、硒(30 nM),谷氨酰胺(2 mm),葡萄糖(6 mg/ml),青霉素/链霉素(100 U/ml至100μg/ml。在接种后18小时向培养物中加入胞嘧啶-d-阿拉伯呋喃糖苷(10μM),以避免非神经元元件的增殖,并在更换培养基前保持3天。这种方法产生了99%以上的纯神经元培养物(Di Menna等人,2013)。将含有成熟神经元的体外培养物(DIV)暴露于LY379268或与LY341495联合或不联合的LY354740中24小时(均为1μM)。对照培养物用等体积的生理盐水处理。 富含海马神经元的原代培养物[2] 在出生后第1天和第2天,从12-13只CD1小鼠的海马中获得培养物(两种制剂)。在无Ca2+/Mg2+缓冲液中解剖海马,机械分离,然后用火焰抛光的巴斯德吸管研磨,将组织分离成单细胞。离心(1500×g,6分钟)后,将细胞沉淀重新悬浮在补充了500 mM l-谷氨酰胺的Neurobase-B27培养基中,并以4×105-7×105个细胞/ml的密度铺在预涂有0.1 mg/ml聚-d-赖氨酸的24孔多板中。为了避免非神经元元件的增殖,在接种后24小时将胞嘧啶-d-阿拉比诺呋喃糖苷(10μM)加入海马培养物中,并在更换培养基前保持3天。这种方法产生的海马神经元培养物含有>85%的神经元和约10-12%的神经胶质细胞。海马培养物在37°C、含5%二氧化碳的加湿气氛中生长。在12 DIV时,将培养物暴露于LY379268或LY354740中24小时,无论是否与LY341495结合(均为1μM),而对照培养物则用等体积的生理盐水处理。 凝胶图像的差异分析和统计[2] 每种情况下,从三个不同的培养皿中获得皮质神经元的蛋白质样本(用生理盐水、LY354740或LY379268处理)。然后对每个蛋白质样品进行三次技术重复分析,每种条件下获得9个凝胶。使用Bio-Rad PDQuest软件7.1.0版进行图像分析。将斑点数量归一化为有效斑点的总密度,有效斑点定义为每个技术复制组内变异系数≤5%的斑点。然后将归一化的现货数量导入NCSS软件进行统计分析。使用单因素方差分析检验(p≤0.05)来检验三组(生理盐水、LY354740和LY379268)之间蛋白质表达的差异,然后使用Tukey-Kramer多重比较检验对各组进行事后比较。统计学意义设定为p<0.05。表达增加或减少至少1.5倍且p<0.05的蛋白质被定义为差异表达。 |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Experiment 1A involves 30 drug-free testing trials (five trials per day for six days) for wild-type (female: N = 6; male: N = 5) and Gria1−/− (female: N = 7; male: N = 8) mice. Each animal is then tested on rewarded alternation following an injection of either Eglumegad (LY354740) (15 mg/kg) or vehicle. Animals are given injections, and then they are kept in their home cage for 30 minutes before behavioral testing starts. In the T-maze, ten trials of rewarded alternation are given to each animal. Mice are allowed a maximum of 120 seconds to finish a trial. The animals are retested without receiving any medication at least 24 hours after the initial round of drug testing to make sure the drug has no long-term effects and the mice continue to perform at a high level during alternation. After retesting for twenty-four hours, mice are given ten more trials of rewarded alternation testing, but this time they are administered a drug that they have not previously received. Considering the quantity of mice, every effort is made to counterbalance the order of drug exposure within genotype and sex. All trials in which the animal alternated are counted, along with the amount of time it took to run (sample latency) from the start arm to the food well and the amount of time it took to make a decision (choice latency) during the choice run. Utilizing a stopwatch, the researcher determines latencies. For the duration of the experiment, the researcher is blind to the animals' genotype and drug allocations. A higher dose of Eglumegad (LY354740) (30 mg/kg) or a vehicle is given to distinct groups of male wild-type (N = 7) and Gria1−/− mice (N = 7) after they undergo the same procedure as in Experiment 1A. The process used in Experiment 1B is then repeated in Experiment 1C to examine the possible effects of increased proactive interference. The drug dose (30 mg/kg) and the mice are used, but a modified testing protocol is used this time, reducing the interval between trials to 20 s.
Rats: Two experiments are conducted. In the first experiment, rats kept in their home cages or rats exposed to two hours of immobilization stress in plastic cones are compared for the effects of LY354740 (10 mg/kg, i.p., neutralized to a pH ~ 7.4) or vehicle (0.9% saline neutralized to pH ~ 7.4) (n = 7, cage control/vehicle; n = 7, cage control/LY354740; n = 6, stress/vehicle; n = 6, stress/Eglumegad (LY354740)). In the second experiment, rats given a 2-hour immobilization stress are compared to rats given vehicle in their home cages, or two lower doses of LY354740 (1 and 3 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle (n = 4 for all groups). Fifteen minutes before they are placed in plastic cones with the open end tightly closed, all animals receive an injection of either Eglumegad (LY354740) or a vehicle. Every immobilized rat is taken to a quiet room away from the animal colony, put in a plexiglass chamber with bedding on the bottom, and then put right into a plastic cone. The rats are beheaded and placed in the plastic containers; this is done two hours later. After removal, the brains are preserved at -80°C by freezing them on dry ice.
|
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Eglumetad is a L-alpha-amino acid.
Eglumetad is a L-alpha-amino acid. Both a 5-hydroxytryptamine2A (5-HT2A) agonist and immobilization stress previously have been shown to differentially alter brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA expression in the neocortex and hippocampus. Both 5-HT2A receptor activation and immobilization stress also increase glutamate release in the rat prefrontal cortex. Given that the metabotropic glutamate2/3 receptor (mGluR2/3) agonist (1S,2S,5R,6S)-2-aminobicyclo[3.1.0] hexane-2,6-dicarboxylate monohydrate (LY354740) suppressed electrophysiological, behavioral and biochemical effects of 5-HT2A receptor activation in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), we assessed the efficacy of the mGluR2/3 agonist in suppressing the stress-induced increase in BDNF mRNA expression. LY35740 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) attenuated the immobilization stress-induced increase in BDNF mRNA expression in the rat mPFC. This result is consistent with the hypothesis that mGlu2/3 agonists may be an efficacious treatment for stress-induced neuropsychiatric syndromes.[4] Dysfunctional glutamatergic neurotransmission has been implicated in schizophrenia and mood disorders. As a putative model for these disorders, a mouse line lacking the GluA1 subunit (GluA1-KO) of the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) glutamate receptor displays a robust novelty-induced hyperlocomotion associated with excessive neuronal activation in the hippocampus. Agonists of metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptors (mGluR2/3) inhibit glutamate release in various brain regions and they have been shown to inhibit neuronal activation in the hippocampus. Here, we tested a hypothesis that novelty-induced hyperlocomotion in the GluA1-KO mice is mediated via excessive hippocampal neuronal activation by analyzing whether an mGluR2/3 agonist inhibits this phenotypic feature. GluA1-KO mice and littermate wildtype (WT) controls were administered with (1S,2S,5R,6S)-2-aminobicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2,6-dicarboxylic acid (LY354740) (15 mg/kg, i.p.) 30 min before a 2-h exposure to novel arenas after which c-Fos immunopositive cells were analyzed in the hippocampus. LY354740 (15 mg/kg) decreased hyperactivity in male GluA1-KO mice, with only a minimal effect in WT controls. This was observed in two cohorts of animals, one naïve to handling and injections, another pre-handled and accustomed to injections. LY354740 (15 mg/kg) also reduced the excessive c-Fos expression in the dorsal hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell layer in maleGluA1-KO mice, while not affecting c-Fos levels in WT mice. In female mice, no significant effect for LY354740 (15 mg/kg) on hyperactive behavior or hippocampal c-Fos was observed in either genotype or treatment cohort. A higher dose of LY354740 (30 mg/kg) alleviated hyperlocomotion of GluA1-KO males, but not that of GluA1-KO females. In conclusion, the excessive behavioral hyperactivity of GluA1-KO mice can be partly prevented by reducing neuronal excitability in the hippocampus with the mGluR2/3 agonist suggesting that the hippocampal reactivity is strongly involved in the behavioral phenotype of GluA1-KO mice.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C8H11NO4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
185.18
|
| 精确质量 |
185.068
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 51.89; H, 5.99; N, 7.56; O, 34.56
|
| CAS号 |
176027-90-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Eglumegad;176199-48-7;Eglumegad hydrochloride
|
| PubChem CID |
213056
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
376.4±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
181.4±25.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.619
|
| LogP |
-1.22
|
| tPSA |
101
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
13
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
290
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
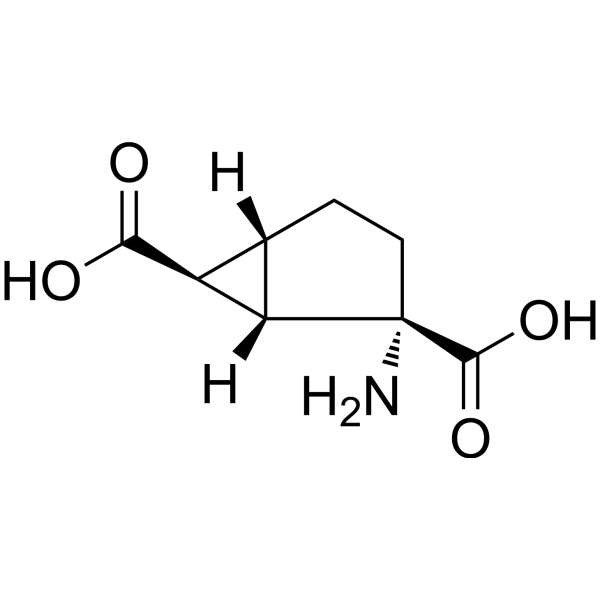
C1C[C@]([C@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]2C(=O)O)(C(=O)O)N
|
| InChi Key |
VTAARTQTOOYTES-RGDLXGNYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H11NO4/c9-8(7(12)13)2-1-3-4(5(3)8)6(10)11/h3-5H,1-2,9H2,(H,10,11)(H,12,13)/t3-,4-,5-,8-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(1S,2S,5R,6S)-2-aminobicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2,6-dicarboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
2-aminobicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2,6-dicarboxylic acid; 177317-28-1; 2-Aminobicyclo(3.1.0)hexane-2,6-dicarboxylic acid; 176027-90-0; LY366563;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4002 mL | 27.0008 mL | 54.0015 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0800 mL | 5.4002 mL | 10.8003 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5400 mL | 2.7001 mL | 5.4002 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。