| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Somatostatin type 2 (SST2) receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
肢端肥大症是一种与生长激素分泌过多及随后胰岛素样生长因子I生成增加相关的激素紊乱疾病。与天然生长抑素类似,帕妥索汀能够抑制GH和IGF-I的分泌。该药物通过选择性激动生长抑素2型受体发挥药理活性(选择性超过4000倍),对其他生长抑素受体亚型几乎没有亲和力。帕妥索汀通过激活人源SSTR2抑制环磷酸腺苷积累,其半数有效浓度(EC50)为0.25 nM。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
帕妥索汀作为一种生长抑素受体激动剂,在20至60毫克治疗剂量范围内,能以剂量依赖的方式降低肢端肥大症患者的胰岛素样生长因子-1水平。该药物可能抑制胆囊收缩功能并减少胆汁分泌,进而增加胆囊结石或胆汁淤积的风险。帕妥索汀还可能引起葡萄糖代谢异常,可能导致高血糖,少数情况下也可能引发低血糖。包括帕妥索汀在内的生长抑素类似物可能抑制促甲状腺激素分泌,从而引起甲状腺功能减退。此外,这类药物还会抑制胰腺酶和胆汁酸分泌,可能导致膳食脂肪吸收不良和脂肪泻。维生素B12水平下降的现象也有报道。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption
Paltusotine exhibited dose-proportional increases in exposures for doses ranging from 20 mg (lowest approved recommended dosage) to 120 mg (2 times the highest approved recommended dosage) in healthy participants. Apparent dose proportional increase was observed for mean steady-state trough concentrations up to 60 mg once daily in participants with acromegaly. Following once daily administration, paltusotine reaches steady-state exposure within one week. When administered as an oral solution, 20 mg of paltusotine had geometric mean absolute bioavailability of 69%, with low interindividual variability. Following oral administration of paltusotine, the median time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is one to four hours regardless of post-dose fasting duration. Food was shown to reduce drug AUC and Cmax. Route of Elimination Following oral administration of radiolabeled paltusotine, fecal excretion was the predominant route of elimination with observed mean recovery of total administered radioactivity being 90% in feces and 3.9% in urine. Unchanged paltusotine was a major component in excreta. Volume of Distribution The volume of distribution (Vz) of paltusotine is 220 L. Clearance After a single oral dose of 20 mg paltusotine, the geometric mean (geometric %CV) apparent oral clearance (CL/F) was 8.4 (27.1) L/h. Protein Binding Paltusotine is highly plasma protein bound (99%). Metabolism / Metabolites Paltusotine is mainly metabolized in the liver. The primary metabolic pathway is glucuronidation, which is mainly facilitated by the enzymes UGT1A1 and UGT1A9. A secondary pathway is oxidation, which is primarily catalyzed by CYP3A4/5 and, to a lesser extent, CYP2D6. Four metabolites have been identified (M632/1, M472/1, M648/1 and M676/1), with the main pathways being glucuronidation, mono-oxidation, and N-carbamoyl glucuronidation. Biological Half-Life After maximal concentrations were attained, paltusotine concentration declined with apparent terminal half-life of 28 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Safety Information
Palsonify increases the risk of cholelithiasis (gallstones); hyperglycemia (high blood sugar); hypoglycemia (low blood sugar); bradycardia (low heart rate); thyroid function abnormalities; steatorrhea (excessive fat in the stool) and malabsorption of dietary fats; and changes in vitamin B12 levels. The most common side effects are diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, decreased appetite, bradycardia, hyperglycemia, and gastroenteritis (stomach inflammation). Dosing and Administration The recommended initial dosage is 40 mg taken orally once daily with water on an empty stomach, at least 6 hours after a meal (i.e., after overnight fasting) and at least 1 hour before the next meal. During the initiation period, Palsonify may be temporarily reduced to 20 mg once daily if needed, based on tolerability. Once adverse reactions have resolved, patients should resume Palsonify 40 mg once daily. After 2 to 4 weeks on Palsonify 40 mg once daily and based on their IGF-1 levels, patients may be advised to increase the dosage to 60 mg once daily. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
The approval is based on data from the PATHFNDR-1 and PATHFNDR-2 Phase 3 pivotal trials, which evaluated PALSONIFY’s safety and efficacy in previously treated and medically untreated adults with acromegaly. Across both trials, PALSONIFY consistently demonstrated rapid onset, reliable biochemical control, and sustained efficacy.
Participants also reported significant reductions in signs and symptoms associated with acromegaly as measured by the Acromegaly Symptom Diary (ASD) — an FDA-aligned patient-reported outcome tool developed to capture the symptoms that matter to people living with acromegaly. Symptoms include headaches, joint pain, sweating, fatigue, weakness, swelling, and/or numbness/tingling. PALSONIFY was generally well-tolerated, with no serious adverse events reported in the randomized controlled portion of the trial.
Long-term results from the open-label extension (OLE) phases of both trials were presented at this year’s Endocrine Society’s annual meeting, ENDO 2025, providing further evidence of PALSONIFY’s ability to deliver durable IGF-1 control, sustained improvements in patient symptom burden, and a consistent safety profile. Ninety-one percent of patients from PATHFNDR-1 and 97 percent of completers from PATHFNDR-2 enrolled in the OLE.
“The PATHFNDR clinical development program set a new standard for acromegaly treatment by demonstrating the ability of Palsonify to drive both biochemical and symptom control, regardless of the degree of underlying disease severity,” said Dr. Shlomo Melmed, Executive Vice President of Medicine and Health Sciences and Dean of the Medical Faculty at Cedars-Sinai, “The approval of Palsonify is a significant advancement for our patients, as there is an unmet need for an easy-to-administer and safe therapeutic option with a rapid action and durable response that can consistently manage acromegaly.”
“For people living with acromegaly, treatment once meant burdensome injections, breakthrough symptoms, and lifestyle sacrifices just to stay on track,” said Jill Sisco, President of Acromegaly Community. “What matters most to our community – maintaining consistent control so the disease doesn’t control us – led us to partner with the FDA on Externally Led Patient-Focused Drug Development meetings. This new treatment reflects that our voices have been heard in shaping the next generation of acromegaly care.”
|
| 分子式 |
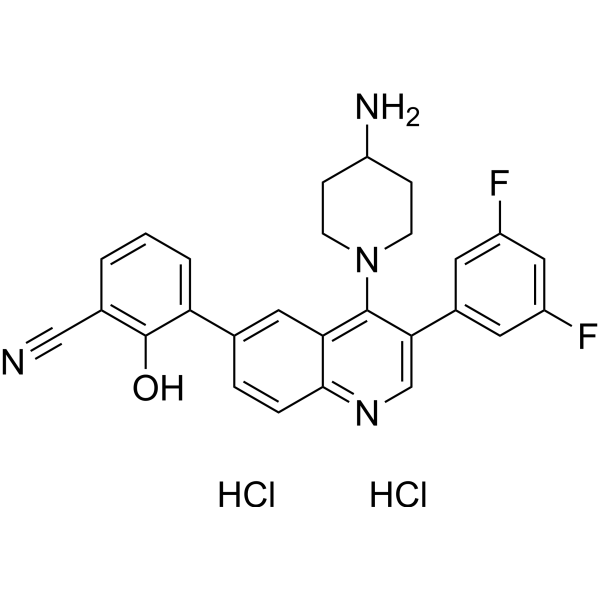
C27H24CL2F2N4O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
529.41
|
| 精确质量 |
528.12952
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 61.26; H, 4.57; Cl, 13.39; F, 7.18; N, 10.58; O, 3.02
|
| CAS号 |
2172875-40-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
2172870-89-0; 2361216-83-1 (HCl); 2172875-40-8 (2HCl)
|
| PubChem CID |
139299823
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solids at room temperature
|
| tPSA |
86.2 Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
36
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
727
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
FC1C=C(C=C(C=1)C1=CN=C2C=CC(C3C=CC=C(C#N)C=3O)=CC2=C1N1CCC(CC1)N)F
|
| InChi Key |
GVTGYFQUBMBIAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H22F2N4O.2ClH/c28-19-10-18(11-20(29)13-19)24-15-32-25-5-4-16(22-3-1-2-17(14-30)27(22)34)12-23(25)26(24)33-8-6-21(31)7-9-33;;/h1-5,10-13,15,21,34H,6-9,31H2;2*1H
|
| 化学名 |
3-[4-(4-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-3-(3,5-difluorophenyl)quinolin-6-yl]-2-hydroxybenzonitrile;dihydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
CRN00808 dihydrochloride; Paltusotine di-hydrochloride; FZT5Z83JNS; UNII-FZT5Z83JNS; 2361216-83-1; Benzonitrile, 3-(4-(4-amino-1-piperidinyl)-3-(3,5-difluorophenyl)-6-quinolinyl)-2-hydroxy-, hydrochloride (1:1); 2172875-40-8; Paltusotine dihydrochloride; 3-(4-(4-Aminopiperidin-1-yl)-3-(3,5-difluorophenyl)quinolin-6-yl)-2-hydroxybenzonitrile dihydrochloride; Paltusotine (hydrochloride);
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8889 mL | 9.4445 mL | 18.8890 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3778 mL | 1.8889 mL | 3.7778 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1889 mL | 0.9444 mL | 1.8889 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。