| 规格 | 价格 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg | |||
| 1g | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Microbial Metabolite; Endogenous Metabolite; Flavoring Agents; Alters several flavor and/or taste characteristics; Food additives; Fragrance Ingredients; Cosmetics -> Buffering; Environmental transformation -> Pesticide transformation products (metabolite, successor)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
农业碳水化合物的发酵产生琥珀酸氨丁三醇[2]。
琥珀酸被认为是一种重要的平台化学品。采用响应面法(RSM)通过中心复合设计(CCD)优化了产琥珀酸放线杆菌BE-1菌株的琥珀酸发酵。预测了琥珀酸的优化生产,并研究了葡萄糖、酵母提取物和碳酸镁之间的相互作用。因此,开发了一个预测琥珀酸生产浓度的模型。方差分析(ANOVA)证实了模型的准确性,验证实验进一步证明了模型的有效性,实验表明实际值和预测值之间的百分比误差在3.02%到6.38%之间。此外,观察到酵母提取物和碳酸镁之间的相互作用具有统计学意义。综上所述,RSM是优化培养基成分和研究相互作用效应的有效和有用的方法,可以为使用产琥珀酸A.菌株BE-1进行琥珀酸放大发酵提供有价值的信息[1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
琥珀酸氨丁三醇(3、6 mg/kg;口服)可增加雄性小鼠进入张开臂的百分比以及在张开臂中花费的时间 [3]。琥珀酸氨丁三醇(3、6、12 mg/kg;腹腔注射)在分娩 5 分钟后显着增加食物摄入量,并在给药后 40 分钟记录直肠温度,剂量为 1.5 mg/kg 琥珀酸,可预防应激引起的体温过高[3]。
|
| 动物实验 |
The putative anxiolytic activity of succinic acid was examined in male mice by using a number of experimental paradigms of anxiety and compared with that of the known anxiolytic compound diazepam. Use of the elevated plus-maze test revealed that diazepam (1.0, 2.0 and 4.0 mg/kg, PO) or succinic acid (3.0 or 6.0 mg/kg, PO) increased the percentage of entries into open arms and of time spent on open arms. In novel food consumption test, succinic acid (3.0, 6.0, and 12.0 mg/kg, IP) caused significant increases in food intake during 5 min when compared with the vehicle. In the stress-induced hyperthermia test, 40 min after drug administration rectal temperature was measured, succinic acid at dose of 1.5 mg/kg, inhibited stress-induced hyperthermia. Thus, these findings indicated that, in contrast with diazepam, succinic acid exhibits anxiolytic-like effect.[3]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Succinic acid occurs normally in human urine (1.9-8.8 mg/L). Metabolism / Metabolites Succinic acid is a normal intermediary metabolite and a constituent of the citric acid cycle. It is readily metabolized when administered to animals, but may be partly excreted unchanged in the urine if large doses are fed. Succinic acid can be converted into fumaric acid by oxidation via succinate dehydrogenase. Agrochemical Transformations Butanedioic acid is a known environmental transformation product of Sulcotrione. Succinic acid is a known environmental transformation product of Linuron. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Succinate can inhibit the activities of α-KG–dependent oxygenases (KDMs) and the TET family of 5-methlycytosine (5mC) hydroxylases. Succinate also mediates allosteric inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs). Inhibition of HIF PHDs leads to activation of HIF-mediated pseudohypoxic response, whereas inhibition of KDMs and TET family of 5mC hydroxylases causes epigenetic alterations that ultimately cause cancer. Succination of KEAP1 in FH deficiency results in the constitutive activation of the antioxidant defense pathway mediated by NRF2, conferring a reductive milieu that promotes cell proliferation. Succination of the Krebs cycle enzyme Aco2 impairs aconitase activity in Fh1-deficient MEFs. Succination also causes irreversible inactivation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Health Effects At acute doses or exposures succinic acid is a skin irritant. Chronically high doses of succinate can lead to succinylation or succination of a variety of enzymes. Partial succinate dehydrogenase deficiency (15% to 50% of normal reference enzyme activity) in skeletal muscle leads to elevated succinate levels and causes mitochondrial myopathy with various symptoms, for example, brain involvement, cardiomyopathy, and/or exercise intolerance. Exposure Routes Eye contact, Inhalation, Ingestion. Symptoms Acute Exposure: the clinical signs of acute toxicity are weakness and diarrhea. Adverse Effects Neurotoxin - Other CNS neurotoxin View More
Toxicity Data
Treatment EYES: irrigate opened eyes for several minutes under running water. INGESTION: do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water (never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person). Seek immediate medical advice. SKIN: should be treated immediately by rinsing the affected parts in cold running water for at least 15 minutes, followed by thorough washing with soap and water. If necessary, the person should shower and change contaminated clothing and shoes, and then must seek medical attention. INHALATION: supply fresh air. If required provide artificial respiration. Human Toxicity Excerpts /OTHER TOXICITY INFORMATION/ Primary irritant effects are present with a number of ... /aliphatic dicarboxylic/ acids, particularly in concentrated solution or as dusts- sensitization is rare. /Aliphatic dicarboxylic acids/ International Labour Office. Encyclopedia of Occupational Health and Safety. Volumes I and II. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1971., p. 30 Non-Human Toxicity Excerpts /LABORATORY ANIMALS: Acute Exposure/ Succinic acid is slight skin irritant and a strong eye irritant in rats. Application of 750 ug of succinic acid as a 15% solution produced severe damage in rabbit eyes. The clinical signs of acute toxicity in rats are weakness and diarrhea. /LABORATORY ANIMALS: Acute Exposure/ Large iv doses of sodium succinate produced vomiting and diarrhea in cats... . /LABORATORY ANIMALS: Subchronic or Prechronic Exposure/ Rats/Fischer (F344) males and females,10 per group /were exposed for/ 13 weeks ad libitum /to/ 0, 0.3, 0.6, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10% monosodium succinate, purity 100.2%. ...Severe suppression of body weight gain occurred in rats in the 10% group, and all of the rats in this group died during the first 4 weeks of the experiment. However, in the other dose groups all of the rats survived to the end of the experiment. Suppression of body weight gain was observed at >/=2.5%. The volume of drinking water consumed was very small in the highest dose groups, although it was larger in the 5% group than in the other groups. No specific dose-related changes were observed in any parameters in the hematological and biochemical investigations. Rats that died during the experiment were severely emaciated. However, no toxic lesions caused by the test substance were found in any organs of these rats histopathologically, although atrophy of the organs was observed. No specific lesions were observed histologically in any of the other test groups. On the basis of body weight depression, the maximum tolerated dose of monosodium succinate was determined to be approximately 2-2.5% when given in the drinking water. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 2260 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Succinic acid appears as white crystals or shiny white odorless crystalline powder. pH of 0.1 molar solution: 2.7. Very acid taste. (NTP, 1992)
National Toxicology Program, Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NTP). 1992. National Toxicology Program Chemical Repository Database. Research Triangle Park, North Carolina.
Succinic acid is an alpha,omega-dicarboxylic acid resulting from the formal oxidation of each of the terminal methyl groups of butane to the corresponding carboxy group. It is an intermediate metabolite in the citric acid cycle. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a radiation protective agent, an anti-ulcer drug, a micronutrient and a fundamental metabolite. It is an alpha,omega-dicarboxylic acid and a C4-dicarboxylic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a succinate(1-). A water-soluble, colorless crystal with an acid taste that is used as a chemical intermediate, in medicine, the manufacture of lacquers, and to make perfume esters. It is also used in foods as a sequestrant, buffer, and a neutralizing agent. (Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary, 12th ed, p1099; McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific and Technical Terms, 4th ed, p1851) Succinic acid is a metabolite found in or produced by Escherichia coli (strain K12, MG1655). Succinic Acid has been reported in Camellia sinensis, Phomopsis velata, and other organisms with data available. Succinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid. The anion, succinate, is a component of the citric acid cycle capable of donating electrons to the electron transfer chain. Succinic acid is created as a byproduct of the fermentation of sugar. It lends to fermented beverages such as wine and beer a common taste that is a combination of saltiness, bitterness and acidity. Succinate is commonly used as a chemical intermediate, in medicine, the manufacture of lacquers, and to make perfume esters. It is also used in foods as a sequestrant, buffer, and a neutralizing agent. Succinate plays a role in the citric acid cycle, an energy-yielding process and is metabolized by succinate dehydrogenase to fumarate. Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) plays an important role in the mitochondria, being both part of the respiratory chain and the Krebs cycle. SDH with a covalently attached FAD prosthetic group, binds enzyme substrates (succinate and fumarate) and physiological regulators (oxaloacetate and ATP). Oxidizing succinate links SDH to the fast-cycling Krebs cycle portion where it participates in the breakdown of acetyl-CoA throughout the whole Krebs cycle. Succinate can readily be imported into the mitochondrial matrix by the n-butylmalonate- (or phenylsuccinate-) sensitive dicarboxylate carrier in exchange with inorganic phosphate or another organic acid, e.g. malate. (A3509) Mutations in the four genes encoding the subunits of succinate dehydrogenase are associated with a wide spectrum of clinical presentations (i.e.: Huntington's disease. (A3510). Succinate also acts as an oncometabolite. Succinate inhibits 2-oxoglutarate-dependent histone and DNA demethylase enzymes, resulting in epigenetic silencing that affects neuroendocrine differentiation. A water-soluble, colorless crystal with an acid taste that is used as a chemical intermediate, in medicine, the manufacture of lacquers, and to make perfume esters. It is also used in foods as a sequestrant, buffer, and a neutralizing agent. View More
Drug Indication
Therapeutic Uses /EXPTL THER/ Succinic acid (100 mM) significantly inhibited systemic anaphylaxis induced by compound 48/80 /a potent mast cell degranulator/ in mice and dose-dependently inhibited local anaphylaxis activated by anti-dinitrophenyl IgE. Further 10 and 100 mM significantly inhibited histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells activated by compound 48/80 or anti-dinitrophenyl IgE. In addition succinic acid (0.1 and 1 mM) had a significant inhibitory effect on anti-dinitrophenyl IgE-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion from rat peritoneal mast cells. The level of cyclic AMP in rat peritoneal mast cells, when succinic acid (100 mM) was added, transiently and significantly increased about 4 times compared with that of basal cells. These results suggest a possible use of succinic acid in managing mast cell-dependent anaphylaxis. Mechanism of Action Succinate is an essential component of the Krebs or citric acid cycle and serves an electron donor in the production of fumaric acid and FADH2. It also has been shown to be a good "natural" antibiotic because of its relative acidic or caustic nature (high concentrations can even cause burns). Succinate supplements have been shown to help reduce the effects of hangovers by activating the degradation of acetaldehyde - a toxic byproduct of alcohol metabolism - into CO2 and H2O through aerobic metabolism. Succinic acid has been shown to stimulate neural system recovery and bolster the immune system. Claims have also been made that it boosts awareness, concentration and reflexes. Sources/Uses Found in fossils, fungi, and lichens; [Merck Index] Present in nearly all plant and animal tissues; Used to make lacquers, dyes, esters for perfumes, alkyd resins, pharmaceuticals, plasticizers, lubricants, and pesticides; Also used in photography, as a sequestrant in foods, a buffering and neutralizing agent, for radiation dosimetry, and to promote plant growth and increased yields in food crops Uses of succinic acid range from scientific applications such as radiation dosimetry and standard buffer solutions to applications in agriculture, food, medicine, plastics, cosmetics, textiles, plating, and waste-gas scrubbing Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. 3rd ed., Volumes 1-26. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons, 1978-1984., p. V21 848 Succinic acid is used as starting material in the manufacture of alkyd resins, dyes, pharmaceuticals, and pesticides. Reaction with glycols gives polyesters; esters formed by reaction with monoalcohols are important plasticizers and lubricants. In the growing of food, it is a biogenic stimulant leading to faster plant growth and increased yields. Succinic acid is a precursor to some specialized polyesters. It is also a component of some alkyd resins. Succinic acid is used in the food and beverage industry, primarily as an acidity regulator. It is also sold as a food additive and dietary supplement, and is generally recognized as safe by the US FDA. Methods of Manufacturing Hydrogenation of maleic acid, maleic anhydride, or fumaric acid produces good yields of succinic acid. 1,4-Butanediol can be oxidized to succinic acid in several ways: (1) with O2 in an aqueous solution of an alkaline-earth hydroxide at 90-110 °C in the presence of Pd-C; (2) by ozonolysis in aqueous acetic acid; or (3) by reaction with N2O4 at low temperature. Succinic acid can ... be obtained by phase-transfer-catalyzed reaction of 2-haloacetates, electrolytic dimerization of bromoacetic acid or ester, oxidation of 3-cyanopropanal, and fermentation of n-alkanes. |
| 分子式 |
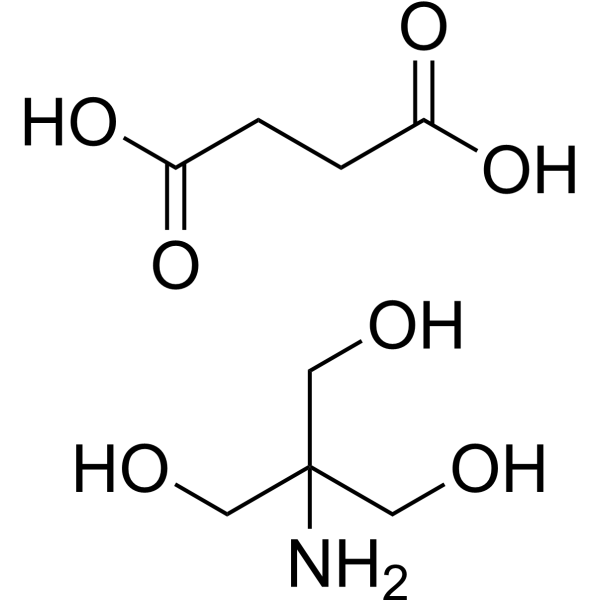
C4H6O4.2[C4H11NO3]
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
360.35812
|
| 精确质量 |
360.174
|
| CAS号 |
84540-64-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Succinic acid;110-15-6; 84540-64-7 (Succinic acid tromethamine); 150-90-3 (Disodium succinate); 26776-24-9;14047-56-4 (Succinic acid sodium)
|
| PubChem CID |
3086186
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 沸点 |
633.5ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
138-141ºC
|
| 闪点 |
336.9ºC
|
| tPSA |
248.02
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
10
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
24
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
147
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C(CC(=O)O)C(=O)O.C(C(CO)(CO)N)O.C(C(CO)(CO)N)O
|
| InChi Key |
CFJZQNZZGQDONE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/2C4H11NO3.C4H6O4/c2*5-4(1-6,2-7)3-8;5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h2*6-8H,1-3,5H2;1-2H2,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)
|
| 化学名 |
2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol;butanedioic acid
|
| 别名 |
Tris succinate; 85169-32-0; 84540-64-7; Di(tris[hydroxymethyl]aminomethane) succinate; Succinic acid, compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol (1:2); 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol;butanedioic acid; EINECS 285-975-2; EINECS 283-159-0;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7750 mL | 13.8750 mL | 27.7500 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5550 mL | 2.7750 mL | 5.5500 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2775 mL | 1.3875 mL | 2.7750 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。