| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
CBFβ SMMHC-RUNX1
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
AI-10-47(10 μM) 会弱抑制 CBFβ-RUNX 的结合 [2]。 AI-10-47显着抑制 ME-1、TUR、M0-91、THP-1 和 U937 细胞生长 [2]。
肝微粒体稳定性的测量表明,AI-10-47降低了代谢不稳定性,因此证明了二价衍生物AI-10-49的合成是合理的(表1)。AI-10-49是强效的(FRET IC50=260nM)(表1)[等温滴定量热法(ITC)测量得出解离常数(KD)=168 nM](图S6),改善了体内药代动力学特性(t½=380min)(图S5),与母体质子化二价化合物AI-4-83(IC50约为3μM)相比,对ME-1细胞生长的抑制活性增强(IC50=0.6 mM)(图1F)(图1E)。请注意,AI-10-49在正常人骨髓细胞中显示出可忽略的活性(IC50>25μM)(图1G),这表明了一个强大的潜在治疗窗口。在11种人类白血病细胞系中,ME-1细胞是唯一对AI-10-49高度敏感的细胞系(图S7)。 为了测试AI-10-49在人类inv(16)白血病治疗中的潜在效用,我们评估了用单价AI-10-47和二价AI-10-49剂量范围治疗48小时的四种原发inv(6)AML细胞样本的存活率。如图3B所示,用浓度为5和10μM的AI-10-49处理后,inv(16)患者细胞的存活率降低(个体剂量反应实验如图S12所示)。请注意,二价AI-10-49比单价化合物AI-10-47更有效,因此概括了在人类inv(16)细胞系ME-1中观察到的效果。相比之下,正常核型AML样本的存活率不受AI-10-49治疗的影响(图3C)。对另外五组AML样本的分析表明,AI-10-49治疗特异性降低了inv(16)白血病细胞的存活率,但对其分化没有明显影响(图S13)。当我们通过评估化合物暴露后的集落形成单位(CFU)来评估AML细胞形成集落的能力时,AI-10-49的特异性也很明显。与正常核型和t(8;21)AML患者样本相比,AI-10-49选择性降低了inv(16)AML细胞形成CFU的能力(图3D)。这种抑制作用是剂量依赖性的(在5和10μM时分别为40%和60%)(图3E),而用AI-10-47处理的AML细胞、具有正常核型的AML细胞(图3F)或CD34+脐带血细胞(图3G)的CFU没有变化。这些研究表明,AI-10-49选择性抑制inv(16)AML母细胞的存活率和CFU能力,而它对具有正常核型的AML母细胞或重要的是对正常人类造血祖细胞的影响可以忽略不计[1]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
FRET检测。[1]
如前所述,Cerulean Runt结构域被表达和纯化。Venus CBFβ-SMMHC是通过将6xHis标签和Venus插入NdeI和NcoI位点之间的pET22b载体中,并在NcoI和BamHI位点之间插入CBFβ-SSMHC(CBFβ/SMMHC构建体包含369个氨基酸,CBFβ为1-166,MYH11为166-369(氨基酸1526-1730))构建的。融合蛋白通过标准镍亲和层析纯化,柱上苯并酶处理以去除残留的DNA污染物。使用前,将蛋白质透析到FRET缓冲液(25mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.5,150mM KCl,2mM MgCl2)中。蛋白质浓度分别通过天蓝色和金星在433和513 nm处的紫外吸光度测定。Cerulean Runt结构域和Venus CBFβ-SMMHC以1:1混合,在96孔黑色COSTAR板中达到10nM的最终浓度。将化合物的DMSO溶液加入至DMSO的最终浓度为5%(v/v),然后在室温下在黑暗中孵育平板一小时。使用PHERAstar微孔板读数器测量荧光(激发波长为433 nm,发射波长为474和525 nm)。对于IC50测定,绘制525nm和474nm处的荧光强度比与化合物浓度的对数,并使用Origin7.0将所得曲线拟合为S形曲线。进行了三次独立的测量,并使用它们的平均值和偏差进行IC50数据拟合。 蛋白质核磁共振波谱[1] 所有核磁共振实验均在30°C下在配备低温探头的布鲁克800 MHz仪器上进行。所有NMR样品均在50 mM磷酸钾、0.1 mM EDTA、0.1 mM NaN3、1 mM DTT和5%(v/v)D2O中制备,最终pH值为7.5。15N1 H HSQC实验使用500µM样品,13C1 H HSQC试验在1 mM样品上进行。所有核磁共振数据均使用NMRPipe和Sparky进行处理。加权化学位移变化(百万分之几)通过以下方程式计算:�HN |+(|∆�N|/4.69) |
| 细胞实验 |
蛋白质印迹分析[2]
细胞类型: 4 × 106 SEM 细胞。 测试浓度:10μM。 孵化持续时间:6 小时。 实验结果:细胞中CBFβ与RUNX1的结合微弱减弱(可能是由于其溶解性差)。 共免疫沉淀试验[2] 4×106 SEM细胞用DMSO或10μM的AI-4-88、AI-10-47、AI-10-10-104、AI-12-126和AI-14-91处理6小时。细胞在改良的RIPA缓冲液(50 mM Tris pH 7.5、150 mM NaCl、1%NP40、0.25%脱氧胆酸钠和1 mM EDTA)中裂解。使用抗RUNX1抗体和蛋白-A琼脂糖珠从细胞裂解物中免疫沉淀RUNX1,如下所示:将细胞裂解物与蛋白A琼脂糖珠和2μg RUNX1抗体在IP缓冲液I(50 mM Tris pH 7.5,150 mM NaCl,0.5%NP40,0.25%脱氧胆酸钠)中混合,并以10 rpm的速度旋转5小时。用IP缓冲液Ⅰ洗涤琼脂糖珠两次,然后用IP缓冲溶液II(50 mM Tris pH 7.5,0.1%NP40,0.05%脱氧胆酸钠。)洗涤。所有裂解、免疫沉淀和洗涤步骤都包括DMSO/相应的抑制剂(10μM)。在蛋白质印迹加载缓冲液(100 mM Tris-HCL pH 6.8,200 mM DTT,4%SDS,0.2%溴酚蓝,20%甘油)中,将珠粒在95°C下加热12分钟。洗脱的蛋白质在12%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶中溶解。使用抗CBFβ抗体检测CBFβ。用抗RUNX1抗体重新探测膜,并使用Clean Blot IP检测试剂进行检测。 |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Analysis of the pharmacokinetic properties of AI-4-57 (analog of AI-10-49) showed that the compound has a short half-life (t½ = 37 min) in mouse plasma (fig. S5) and that loss of the methyl group from the methoxy functionality is the primary metabolite. Trifluoromethoxy (CF3O) substitutions have been shown to be less reactive (18, 19), so we synthesized AI-10-47 with this substitution. FRET measurements show that this substitution actually enhances the activity of the monovalent compound (Table 1). Measurements of stability in liver microsomes showed that AI-10-47 reduced the metabolic liability and so justified the synthesis of the bivalent derivative AI-10-49 (Table 1).AI-10-49 is potent (FRET IC50=260nM) (Table 1) [isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) measurements yielded a dissociation constant (KD) = 168 nM] (fig. S6), has improved in vivo pharmacokinetic properties (t½ = 380min) (fig. S5), and has enhanced inhibitory activity on ME-1 cell growth (IC50 = 0.6 mM) (Fig. 1F) compared with the parent protonated bivalent compound AI-4-83 (IC50 of ~3 μM) (Fig. 1E). Note that AI-10-49 showed negligible activity (IC50 > 25 μM) in normal human bone marrow cells (Fig. 1G), which indicated a robust potential therapeutic window. In a panel of 11 human leukemia cell lines, ME-1 cells were the only cell line highly sensitive to AI-10-49 (fig. S7). [1]
|
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Chemical biology. A small-molecule inhibitor of the aberrant transcription factor CBFβ-SMMHC delays leukemia in mice. Science. 2015 Feb 13;347(6223):779-84.
[2]. Small Molecule Inhibitor of CBFβ-RUNX Binding for RUNX Transcription Factor Driven Cancers. EBioMedicine. 2016 Jun;8:117-131. |
| 其他信息 |
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common form of adult leukemia. The transcription factor fusion CBFβ-SMMHC (core binding factor β and the smooth-muscle myosin heavy chain), expressed in AML with the chromosome inversion inv(16)(p13q22), outcompetes wild-type CBFβ for binding to the transcription factor RUNX1, deregulates RUNX1 activity in hematopoiesis, and induces AML. Current inv(16) AML treatment with nonselective cytotoxic chemotherapy results in a good initial response but limited long-term survival. Here, we report the development of a protein-protein interaction inhibitor, AI-10-49, that selectively binds to CBFβ-SMMHC and disrupts its binding to RUNX1. AI-10-49 restores RUNX1 transcriptional activity, displays favorable pharmacokinetics, and delays leukemia progression in mice. Treatment of primary inv(16) AML patient blasts with AI-10-49 triggers selective cell death. These data suggest that direct inhibition of the oncogenic CBFβ-SMMHC fusion protein may be an effective therapeutic approach for inv(16) AML, and they provide support for transcription factor targeted therapy in other cancers. [1]
Transcription factors have traditionally been viewed with skepticism as viable drug targets, but they offer the potential for completely novel mechanisms of action that could more effectively address the stem cell like properties, such as self-renewal and chemo-resistance, that lead to the failure of traditional chemotherapy approaches. Core binding factor is a heterodimeric transcription factor comprised of one of 3 RUNX proteins (RUNX1-3) and a CBFβ binding partner. CBFβ enhances DNA binding of RUNX subunits by relieving auto-inhibition. Both RUNX1 and CBFβ are frequently mutated in human leukemia. More recently, RUNX proteins have been shown to be key players in epithelial cancers, suggesting the targeting of this pathway could have broad utility. In order to test this, we developed small molecules which bind to CBFβ and inhibit its binding to RUNX. Treatment with these inhibitors reduces binding of RUNX1 to target genes, alters the expression of RUNX1 target genes, and impacts cell survival and differentiation. These inhibitors show efficacy against leukemia cells as well as basal-like (triple-negative) breast cancer cells. These inhibitors provide effective tools to probe the utility of targeting RUNX transcription factor function in other cancers. [2] |
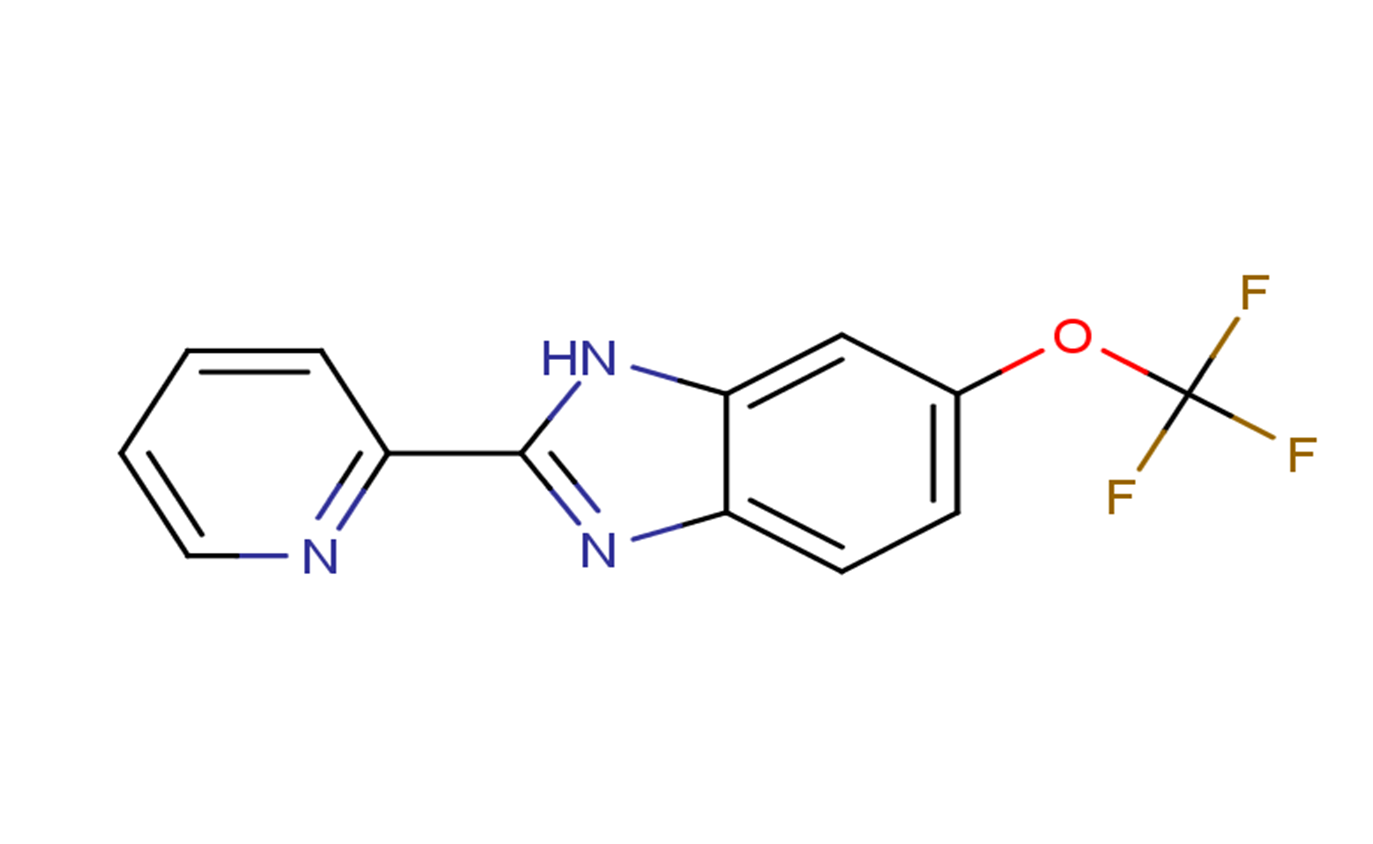
| 分子式 |
C13H8F3N3O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
279.2173
|
| 精确质量 |
279.061
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 55.92; H, 2.89; F, 20.41; N, 15.05; O, 5.73
|
| CAS号 |
1256094-31-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
63053-14-5
|
| PubChem CID |
49804932
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to gray solid powder
|
| LogP |
3.3
|
| tPSA |
50.8
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
339
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
FC(OC1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])N([H])C(C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=N1)=N2)(F)F
|
| InChi Key |
JSNWHSDKJSOXET-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H8F3N3O/c14-13(15,16)20-8-4-5-9-11(7-8)19-12(18-9)10-3-1-2-6-17-10/h1-7H,(H,18,19)
|
| 化学名 |
2-pyridin-2-yl-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1H-benzimidazole
|
| 别名 |
AI-10-47; AI-10 47; 1256094-31-1; 2-(Pyridin-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole; 1H-Benzimidazole, 2-(2-pyridinyl)-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-AI-10-47; 2-(pyridin-2-yl)-5-(trifluoromethoxy)-1H-1,3-benzodiazole; SCHEMBL179143; 2-pyridin-2-yl-6-(trifluoromethoxy)-1H-benzimidazole; CHEMBL3675778; AI10-47; AI 10-47
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~358.14 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5814 mL | 17.9070 mL | 35.8141 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7163 mL | 3.5814 mL | 7.1628 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3581 mL | 1.7907 mL | 3.5814 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。