| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
HCV NS5B
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:VX-222 与 HCV RNA 依赖性 RNA 聚合酶的拇指 II 变构袋结合。 VX-222 对基因型 1a 和 1b 的 HCV NS5B 表现出非竞争性和选择性抑制,IC50 分别为 0.94 和 1.2 μM。 VX-222 选择性抑制亚基因组 HCV 基因型 1a 和 1b 的复制,EC50 分别为 22.3 和 11.2 nM。同样,最近的一项研究表明,VX-222 抑制 1b/Con1 HCV 亚基因组复制子,EC50 为 5 nM。 VX-222 优先抑制引物依赖性 RNA 合成,对从头启动的 RNA 合成仅显示出适度的影响或没有影响。激酶测定:VX-222 对 HCV NS5B 活性的抑制作用是通过使用均聚物 RNA 模板/引物(即聚 rA)评估新合成的 RNA 中酶的 C 末端 Δ21 截短形式掺入的放射性标记 UTP 的量来测量的。 / 寡聚 dT。使用液体闪烁计数器对掺入的放射性进行定量检测。 VX-222 抑制基因型 1b 菌株 BK 的 HCV NS5B 的体外动力学是使用 NS5B 的 C 末端 Δ21 截短版本确定的。 VX-222(1 至 1.5 μM)在 10 至 75 μM 非放射性 UTP 与 0.89 至 6.70 μCi 的 [α-33P] 标记 UTP 混合的情况下进行测试。 RNA 依赖性 RNA 聚合酶反应可在 22 °C 下进行 18 分钟。细胞测定:将含有 HCV RNA 复制子的 Huh7.5 细胞用胰蛋白酶处理,并以 4 × 104 个细胞/孔的浓度接种到 48 孔板中。第二天更换培养基,并将 VX-222 添加到 200 μL 完全培养基中。 48 小时后,提取总 RNA,并通过实时逆转录 PCR (RT-PCR) 定量病毒 RNA。通过对数曲线拟合的非线性回归分析计算使 HCV RNA 复制子水平降低 50% 的有效药物浓度 (EC50)。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在大鼠和狗中,VCH-222 显示出良好的药代动力学特征,包括较低的全身清除率和出色的口服生物利用度(大于 30%)以及良好的 ADME 特性。 VCH-222 可通过多种酶(CYP1A1、2A6、2B6、2C8、CYP 3A4、UGT1A3)进行生物转化,预计会在肝脏中主动转运,并在胆汁中或以葡萄糖醛酸加合物的形式主要完整地排泄。
|
| 酶活实验 |
VX-222 对 HCV NS5B 活性的抑制作用是通过使用称为聚 rA / 寡聚 dT 的均聚物 RNA 模板/引物测量新鲜合成的 RNA 中酶的 C 末端 Δ21 截短形式掺入的放射性标记 UTP 的量来量化的。液体闪烁计数器用于定量检测掺入的放射性。通过使用 NS5B 的 C 末端 Δ21 截短形式,确定了 VX-222 诱导的对基因型 1b 菌株 BK 的 HCV NS5B 抑制的体外动力学。当VX-222(1至1.5μM)与0.89至6.70μCi的[α-33P]标记UTP和10至75μM非放射性UTP组合时,进行测试。 RNA 依赖性 RNA 聚合酶反应在 22 °C 下进行 18 分钟。
|
| 细胞实验 |
将含有 HCV RNA 复制子的胰蛋白酶处理的 Huh7.5 细胞以每孔 4 × 104 细胞的密度接种到 48 孔板中。第二天,将 200 μL 完整培养基与 VX-222 一起添加到新培养基中。 48 小时后,提取总 RNA,并使用实时逆转录 PCR (RT-PCR) 定量病毒 RNA。通过使用非线性回归分析和对数曲线拟合,确定了使 HCV RNA 复制子水平降低 50% 的有效药物浓度 (EC50)。
|
| 动物实验 |
Rat IV formulations were prepared as solutions in 10% DMI/15% EtOH/35% PPG/40% dextrose/5% in water. IV formulations for dogs and monkeys were prepared as solutions in saline. PO formulations for rats were prepared as suspensions in 0.5% MC/0.1% SLS/99.4% water. For the PO studies, male Sprague-Dawley rats were instrumented with either a carotid artery cannula to facilitate blood collection and/or a single bile duct cannula to facilitate bile collection. For IV studies, male Sprague-Dawley rats were additionally fitted with a jugular vein catheter for dose administration. Blood samples were collected at intervals to 72 hours post dose. EDTA was used as anticoagulant and plasma was prepared by centrifugation. Bile duct cannulated rats received a 15mg/kg PO dose; bile, urine, and feces were collected at intervals to 72 hours. In the tissue distribution study, male Sprague-Dawley rats received a 10 mg/kg PO dose and specified tissues were collected following euthanasia at 1, 2, 4, 7 and 24 hours post dose.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017;8(2):251-255.
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
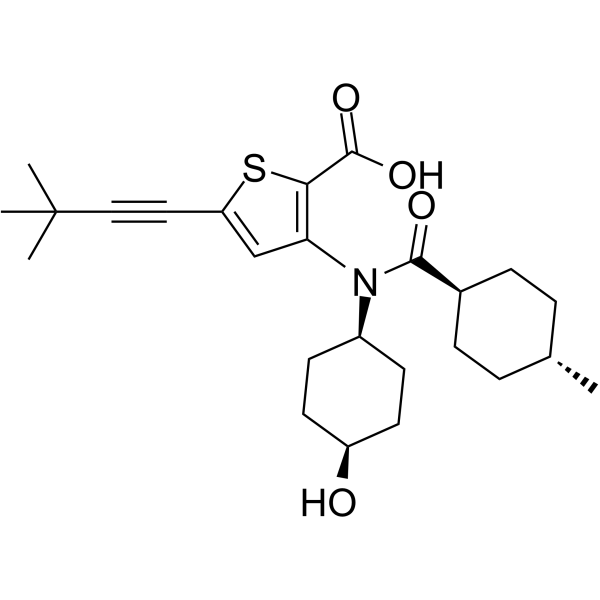
5-(3,3-dimethylbut-1-ynyl)-3-[(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)-[(4-methylcyclohexyl)-oxomethyl]amino]-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid is a thiophenecarboxylic acid.
Lomibuvir has been used in trials studying the treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C Virus and Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Filibuvir and VX-222 are nonnucleoside inhibitors (NNIs) that bind to the thumb II allosteric pocket of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Both compounds have shown significant promise in clinical trials and, therefore, it is relevant to better understand their mechanisms of inhibition. In our study, filibuvir and VX-222 inhibited the 1b/Con1 HCV subgenomic replicon, with 50% effective concentrations (EC(50)s) of 70 nM and 5 nM, respectively. Using several RNA templates in biochemical assays, we found that both compounds preferentially inhibited primer-dependent RNA synthesis but had either no or only modest effects on de novo-initiated RNA synthesis. Filibuvir and VX-222 bind to the HCV polymerase with dissociation constants of 29 and 17 nM, respectively. Three potential resistance mutations in the thumb II pocket were analyzed for effects on inhibition by the two compounds. The M423T substitution in the RNA polymerase was at least 100-fold more resistant to filibuvir in the subgenomic replicon and in the enzymatic assays. This resistance was the result of a 250-fold loss in the binding affinity (K(d)) of the mutated enzyme to filibuvir. In contrast, the inhibitory activity of VX-222 was only modestly affected by the M423T substitution but more significantly affected by an I482L substitution.[1] The current standard of chronic hepatitis C therapy is the combined use of pegylated IFN-alpha 2a (PegIFN-alpha) and rybavirin (RBV). The new form of interferon, IFN-alpha 2b, was also introduced with no better results. Overall, the effectiveness of therapy with the use of the above scheme is not satisfactory. Thus the search for new therapeutic agents for hepatitis C is ongoing. These studies have the goal to find new preparations inhibiting the replication cycle of HCV. The new analogue of RBV, eg. tarybavirin was introduced, with lesser side effects, but the same effectiveness. The activity of new agents relies upon the inhibition of the most important enzymes of the HCV replication cycle: RNA polymerase, protease and helicase. Polymerase NS5 inhibitors are divided into nucleoside (R-7128) and nonnucleoside (ANA-598, GS 9190, VCH-759, VX-222). The intensive studies on the R-7128 analogue are ongoing. The effects of action of particular compounds in the I and II studies were summarized. The promised prodrug is nonnucleoside polymerase inhibitor, ANA-598 which when administrated to patients, gave 75% SVR. The combined administration of the newly described agents is the basis of specifically targeted antiviral therapies for HCV (STAT-C). These therapies allow to achieve better effectiveness of treatment, its shortening, the diminishment and limitation of side effects.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C25H35NO4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
445.6147
|
| 精确质量 |
445.228
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 67.38; H, 7.92; N, 3.14; O, 14.36; S, 7.19
|
| CAS号 |
1026785-59-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lomibuvir;1026785-55-6
|
| PubChem CID |
24798764
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
640.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
341.2±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.589
|
| LogP |
5.15
|
| tPSA |
106.08
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
717
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1=C(N([C@@H]2CC[C@H](O)CC2)C([C@H]3CC[C@H](C)CC3)=O)C=C(C#CC(C)(C)C)S1)O
|
| InChi Key |
WPMJNLCLKAKMLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H35NO4S/c1-16-5-7-17(8-6-16)23(28)26(18-9-11-19(27)12-10-18)21-15-20(13-14-25(2,3)4)31-22(21)24(29)30/h15-19,27H,5-12H2,1-4H3,(H,29,30)
|
| 化学名 |
5-(3,3-dimethylbut-1-ynyl)-3-[(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)-(4-methylcyclohexanecarbonyl)amino]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
Lomibuvir; VX-222; 1026785-59-0; 1026785-55-6; VCH-222; VX-222 (VCH-222, Lomibuvir); cis-Lomibuvir; Lomibuvir (VX-222);
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2441 mL | 11.2206 mL | 22.4411 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4488 mL | 2.2441 mL | 4.4882 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2244 mL | 1.1221 mL | 2.2441 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。