| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Class A KPC-2 (IC50 = 4 nM), Class C AmpC (IC50 = 14 nM), D OXA-24 (IC50 = 190 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
杜洛巴坦是一种比其他DBOs阿维巴坦和雷巴坦更有效的BlaC抑制剂;杜洛巴坦是结核分枝杆菌几种肽聚糖转肽酶的有效抑制剂;杜洛巴坦恢复结核分枝杆菌分离株对β-内酰胺的易感性[3]
ETX2514是一种具有内在抗菌活性的抗氧化剂,可以增强其恢复碳青霉烯对CRE菌株的活性的能力。耐多药细菌感染是对公众健康的严重威胁。最令人担忧的耐药性趋势之一是β-内酰胺酶的数量和多样性的迅速增加,β-内胺酶是一类使β-内酰胺失活的酶,几十年来一直是治疗的支柱。尽管一些新的β-内酰胺酶抑制剂已经被批准或正在进行临床试验,但它们的活性谱并不能解决多药耐药病原体,如鲍曼不动杆菌。本报告描述了扩谱丝氨酸β-内酰胺酶抑制剂的合理设计和特性,该抑制剂能有效抑制临床相关的A、C和D类β-内酶以及青霉素结合蛋白,从而对肠杆菌科产生内在抗菌活性,并在广泛的耐多药革兰阴性病原体中恢复β-内内酰胺活性。舒巴坦-ETX2514是最有前景的组合之一,其强大的抗菌活性、对耐多药鲍曼菌感染的体内疗效和有希望的临床前安全性证明了其解决这一重大未满足医疗需求的潜力[1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
舒巴坦–ETX2514在耐多药鲍曼氏杆菌感染小鼠模型中显示出体内疗效[1]
单用舒巴坦的体内中性粒细胞减少性肺和大腿感染模型研究[4] 在单用舒巴坦与鲍曼不动杆菌ARC2058进行的大腿研究中,与1-log10 CFU/g减少、2-log10 CFU/g减少和EC80相关的%fT>MIC幅度分别为20.5、31.5和47.0(表3)。在肺模型中,与1-log10 CFU/g减少、2-log10 CFU/g减少和EC80相关的平均%fT>MIC幅度分别为37.8、50.1和68.5 舒巴坦联合硬洛巴坦与CRAB菌株的体内中性粒细胞减少性大腿和肺部感染模型研究[4] 表3总结了舒巴坦用于大腿和肺部感染模型的单个菌株%fT>MIC估计值,以实现1-log10 CFU/g减少、2-log10 CFU/g减少的PK/PD终点,以及EC80与CRAB菌株的比较。多个CRAB菌株和舒巴坦易感菌株ARC2058的%fT>MIC舒巴坦暴露反应数据(与杜洛巴坦联合给药时)的联合建模如图所示。1用于大腿和肺模型。表3总结了与1-log10 CFU/g减少、2-log10 CFU/g减少和联合建模数据的EC80相关的舒巴坦%fT>MIC幅度。1-log10需要%fT>MIC的幅度,与通过数据联合建模确定的PK/PD终点相比,在所有菌株中确定的单个PK/PD端点的平均值之间,2-log10 CFU的减少几乎相同 硬洛巴坦是一种β-内酰胺/β-内酶抑制剂组合,目前正在开发中,用于治疗不动杆菌引起的感染,包括耐多药(MDR)分离株。尽管舒巴坦是Ambler a类酶亚群的β-内酰胺酶抑制剂,但它也对包括不动杆菌在内的有限数量的细菌表现出固有的抗菌活性,并已有效用于治疗易感不动杆菌相关感染。然而,越来越多的β-内酰胺酶介导的耐药性已经削弱了舒巴坦治疗这种病原体的有效性。杜拉巴坦是一种设计合理的二氮杂双环辛烷类β-内酰胺酶抑制剂。该化合物表现出对丝氨酸β-内酰胺酶活性的广谱抑制作用,对D类酶具有特别强的活性,这是它与其他DBO抑制剂的区别。当与舒巴坦联合使用时,杜洛巴坦通过抑制β-内酰胺酶有效地恢复耐药菌株的易感性。本综述描述了在多药耐药鲍曼不动杆菌分离株的非临床感染模型中建立的与舒巴坦和硬洛巴坦活性相关的药代动力学/药效学(PK/PD)关系。这些信息有助于确定PK/PD的疗效靶点,可用于预测联合用药在人类中的有效剂量方案。5. |
| 细胞实验 |
体外药敏试验[3]
ATCC结核分枝杆菌H37Ra、H37Rv和9个当代临床结核分枝杆菌分离株通过肉汤微量稀释进行抗菌药物敏感性测试。抗生素化合物是从商业来源购买的,但由Entasis Therapeutics慷慨提供的杜洛巴坦除外。Middlebrook 7H9肉汤补充有10%(v/v)油酸白蛋白-葡萄糖-过氧化氢酶(OADC)、0.05%(v/vTween 80和0.5%(v/v甘油)作为培养基。使用96孔微孔板对药物进行连续2倍稀释。对于组合,添加固定浓度为2.5μg/mL的棒酸盐;所有其他组合(β-内酰胺/杜洛巴坦或双β-内胺)以1:1质量/体积比组合。用约5×105菌落形成单位(CFU)/mL接种微孔板孔。在37°C下培养14-18天后,阻止可见生长的最低抗生素浓度记录为MIC。用基于雷沙祖林的试剂alamarBlue HS确认可见生长。 |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Durlobactam demonstrated dose-proportional pharmacokinetics across the dose range studied (0.25 times the recommended single dose to 2 times the recommended single dose infused over 3 hours every 6 hours), with the Cmax, AUC0-24, and AUC0-6/ELF plasma ratio calculated to be 29.2 ± 13.2 µg/mL, 471 ± 240 h.µg/mL, and 0.37 respectively. The major route of elimination of durlobactam is through the kidney, with 78% of durlobactam excreted unchanged in the urine. The volume of distribution of durlobactam as stead state (ss) was estimated to be 30.3 ± 12.9 L. The clearance of durlobactam was calculated to be 9.96 ± 3.11 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Durlobactam is minimally metabolized. Biological Half-Life The elimination half-life of durlobactam was calculated to be 2.52 ± 0.77 h. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Sulbactam produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. It is likely that durlobactam produces similar levels in milk. Occasionally, disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush, have been reported with penicillins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Sulbactam-durlobactam is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding The binding of durlobactam to human serum proteins was 10%. |
| 参考文献 |
[1]ETX2514 is a broad-spectrum \u03b2-lactamase inhibitor for the treatment of drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria includingAcinetobacter baumannii. Nat Microbiol. 2017 Jun 30;2:17104.
[2] Plasma and Intrapulmonary Concentrations of ETX2514 and Sulbactam following Intravenous Administration of ETX2514SUL to Healthy Adult Subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Aug 20. pii: AAC.01089-18. [2]. In vitro antibacterial activity of sulbactam-durlobactam in combination with other antimicrobial agents against Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis . 2024 May 9;109(3):116344. [3]. Durlobactam, a Diazabicyclooctane β-Lactamase Inhibitor, Inhibits BlaC and Peptidoglycan Transpeptidases of Mycobacterium tubercul. ACS Infect Dis . 2024 May 10;10(5):1767-1779. [4]. In vivo dose response and efficacy of the β-lactamase inhibitor, durlobactam, in combination with sulbactam against the Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Jan; 68(1): e00800-23. [5]. he Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamic Relationship of Durlobactam in Combination With Sulbactam in In Vitro and In Vivo Infection Model Systems Versus Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus Complex. Clin Infect Dis . 2023 May 1;76(Suppl 2):S202-S209. |
| 其他信息 |
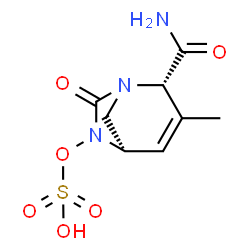
Durlobactam is a member of the class of azabicycloalkanes that is (1R,2S,5R)-3-methyl-7-oxo-1,6-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-ene-2-carboxamide in which the amino hydrogen at position 6 is replaced by a sulfooxy group. It has a role as an EC 3.5.2.6 (beta-lactamase) inhibitor and an antibacterial drug. It is a primary carboxamide, an azabicycloalkane, a hydroxylamine O-sulfonic acid and a monocarboxylic acid amide. It is a conjugate acid of a durlobactam(1-).
Durlobactam is a diazabicyclooctane non-beta-lactam, beta-lactamase inhibitor. It is typically given in combination with [sulbactam] to protect it from degradation by certain serine-beta-lactamases. The combination product of durlobactam and sulbactam was first approved by the FDA in May 2023. It is used to treat hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP), caused by susceptible isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. Durlobactam is a beta Lactamase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of durlobactam is as a beta Lactamase Inhibitor. See also: Durlobactam Sodium (active moiety of). Drug Indication In combination with [sulbactam], durlobactam is indicated in adults for the treatment of hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP), caused by susceptible isolates of _Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus_ complex. Mechanism of Action Durlobactam is a diazabicyclooctane non-beta-lactam, beta-lactamase inhibitor. When given in combination with [sulbactam], it protects sulbactam from degradation by certain serine-beta-lactamases. Durlobactam is carbamoylated by β-lactamase by the serine nucleophile in the enzyme active site: The covalent bond between durlobactam and β-lactamase is reversible due to recyclization by the sulfated amine group on durlobactam, demonstrating that durlobactam can be exchanged from one enzyme molecule to another, also known as acylation exchange. Pharmacodynamics Durlobactam has an extended spectrum of activity compared to other β-lactamase inhibitors with a displayed potent inhibition against class A, C, and D serine β-lactamases. Durlobactam is not active against class B metallo-β-lactamases, which is an enzyme class rarely observed in _Acinetobacter_ clinical isolates. Durlobactam alone does not have antibacterial activity against _Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus_ complex isolates. |
| 分子式 |
C8H11N3O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
277.25
|
| 精确质量 |
277.036
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 34.66; H, 4.00; N, 15.16; O, 34.62; S, 11.56
|
| CAS号 |
1467829-71-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1467829-71-5 (free acid);1467157-21-6 (sodium);
|
| PubChem CID |
89851852
|
| 外观&性状 |
Solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.8±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 折射率 |
1.691
|
| LogP |
-2.53
|
| tPSA |
139
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
18
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
536
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
C1(=C[C@@H]2C[N@@](C(N2OS(=O)(=O)O)=O)[C@@H]1C(N)=O)C
|
| InChi Key |
BISPBXFUKNXOQY-RITPCOANSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H11N3O6S/c1-4-2-5-3-10(6(4)7(9)12)8(13)11(5)17-18(14,15)16/h2,5-6H,3H2,1H3,(H2,9,12)(H,14,15,16)/t5-,6+/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(1R,2S,5R)-2-carbamoyl-3-methyl-7-oxo-1,6-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-en-6-yl hydrogen sulfate
|
| 别名 |
ETX 2514ETX-2514 ETX2514 Durlobactam Durlobactam.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: > 10 mM
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6069 mL | 18.0343 mL | 36.0685 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7214 mL | 3.6069 mL | 7.2137 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3607 mL | 1.8034 mL | 3.6069 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。