| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
calcium channel (IC50 = 1 μM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
尼卡碱(0.1–10 μM;24-48 小时)都会降低血管平滑肌细胞 (VSMC) 的活力、增殖和迁移能力 [2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
尼卡地平(0.3-10 mg/kg)是一种具有抗高血压作用的口服药物[3]。尼卡地平对雄性和雌性Sprague-Dawley大鼠的致死剂量(LD50)分别为口服643mg/kg和557mg/kg; 18.1mg/kg静脉注射和25.0mg/kg静脉注射;皮下注射735mg/kg和皮下注射683mg/kg;腹膜内注射 171 mg/kg 和腹膜内注射 155 mg/kg [3]。尼卡地平对雄性 Wistar 大鼠的 LD50 口服给药时为 187 mg/kg,静脉注射给药时为 15.5 mg/kg [3]。尼卡地平对雄性和雌性小鼠的致死剂量(LD50)分别为634 mg/kg和650 mg/kg; 20.7 mg/kg 和 19.9 mg/kg,皮下注射; 540 mg/kg 和 710 mg/kg kg,皮下注射; 144 mg/kg 和 161 mg/kg,腹膜内注射 [3]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[2]
细胞类型:从新西兰兔主动脉制备物中分离出的 VSMC 测试浓度: 0.1 μM、1 μM、3 μM、10 μM 孵育持续时间:24-48 小时 实验结果: 治疗在存在以下物质的情况下显着降低细胞活力并抑制 VSMC 增殖10% FBS呈剂量依赖性,0.1 μM、1 μM、3 μM和10后,范围从205.4±17.5%到176.6±17%、160.6±5.7%、150.4±11.2%和61.22±7.83%。分别为μM。对待。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Conscious normotensive rat (NR)[3]
Doses: 0.3-10 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral Experimental Results: Induced dose-dependent hypotensive response (maximum decrease in mean blood pressure, supine position) without any body positioning hypotensive reaction. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
While nicardipine is completely absorbed, it is subject to saturable first pass metabolism and the systemic bioavailability is about 35% following a 30 mg oral dose at steady state. Nicardipine has been shown to be rapidly and extensively metabolized by the liver. 8.3 L/kg 0.4 L/hr∙kg [Following infusion] Metabolism / Metabolites Nicardipine HCl is metabolized extensively by the liver. Nicardipine has known human metabolites that include De-benzylated nicardipine and Dehydronicardipine. Biological Half-Life 8.6 hours |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Nicardipine has not been associated with significant increases in rates of elevations in serum aminotransferase or alkaline phosphatase levels, even with chronic long term therapy. Cases of idiosyncratic liver injury have not been published, although a single instance of marked serum enzyme elevations without jaundice has been reported with the use of intravenous nicardipine. Large trials of nicardipine have not mentioned liver injury, serum aminotransferase elevations or discontinuation of drug because of hepatic adverse events. Thus, clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice due to nicardipine must be rare, if it occurs at all. Likelihood Score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). The reason why some calcium channel blockers are known to cause idiosyncratic liver injury while others such as nicardipine do not, is unknown. Drug Class: Cardiovascular Agents, Calcium Channel Blockers Other Drugs in the Subclass, Calcium Channel Blockers: Amlodipine, Diltiazem, Felodipine, Isradipine, Nifedipine, Nimodipine, Nisoldipine, Verapamil Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because of the low levels of nicardipine in breastmilk, amounts ingested by the infant are small and would not be expected to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. No special precautions are required. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding >95% |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Nicardipine is a racemate comprising equimolar amounts of (R)- and (S)-nicardipine. It is a calcium channel blocker which is used to treat hypertension. It has a role as an antihypertensive agent, a calcium channel blocker, a vasodilator agent and an autophagy inhibitor. It contains a (S)-nicardipine and a (R)-nicardipine.
Nicardipine is a Dihydropyridine Calcium Channel Blocker. The mechanism of action of nicardipine is as a Calcium Channel Antagonist, and Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2D6 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2C8 Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 2C19 Inhibitor. Nicardipine is a second generation calcium channel blocker used in the treatment of hypertension and stable angina pectoris. Nicardipene therapy has been associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations, but has not been linked convincingly to instances of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice. Nicardipine is a synthetic derivative of nitrophenyl-pyridine and potent calcium channel blocker, Nicardipine (Nifedipine Family) blocks calcium ions from certain cell walls and inhibits contraction of coronary and peripheral arteries, resulting in lowered oxygen requirements for heart muscle and decreased arterial contraction and spasm. It is used clinically as a cerebral and coronary vasodilator. A potent calcium channel blockader with marked vasodilator action. It has antihypertensive properties and is effective in the treatment of angina and coronary spasms without showing cardiodepressant effects. It has also been used in the treatment of asthma and enhances the action of specific antineoplastic agents. See also: Nicardipine Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication Used for the management of patients with chronic stable angina and for the treatment of hypertension. FDA Label Mechanism of Action By deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, nicardipine inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload. Pharmacodynamics Nicardipine, a dihydropyridine calcium-channel blocker, is used alone or with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, to treat hypertension, chronic stable angina pectoris, and Prinzmetal's variant angina. Nicardipine is similar to other peripheral vasodilators. Nicardipine inhibits the influx of extra cellular calcium across the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes possibly by deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The decrease in intracellular calcium inhibits the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells, causing dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries, increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased total peripheral resistance, decreased systemic blood pressure, and decreased afterload. |
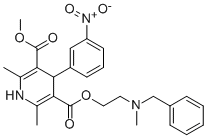
| 分子式 |
C26H29N3O6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
479.525
|
| 精确质量 |
479.206
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 65.12; H, 6.10; N, 8.76; O, 20.02
|
| CAS号 |
55985-32-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Nicardipine hydrochloride;54527-84-3;Nicardipine-d3 hydrochloride;1432061-50-1;(S)-Nicardipine;76093-36-2;(R)-Nicardipine;76093-35-1
|
| PubChem CID |
4474
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as light yellow to yellow solids at room temperature
|
| 密度 |
1.23 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
603.4ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
136-138ºC
|
| 闪点 |
318.7ºC
|
| LogP |
4.529
|
| tPSA |
113.69
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
856
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1=C(C)NC(C)=C(C(OCCN(C)CC2=CC=CC=C2)=O)C1C3=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C3)OC
|
| InChi Key |
ZBBHBTPTTSWHBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H29N3O6/c1-17-22(25(30)34-4)24(20-11-8-12-21(15-20)29(32)33)23(18(2)27-17)26(31)35-14-13-28(3)16-19-9-6-5-7-10-19/h5-12,15,24,27H,13-14,16H2,1-4H3
|
| 化学名 |
3-(2-(benzyl(methyl)amino)ethyl) 5-methyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
|
| 别名 |
DaganFlusemide; Nicardipine; Cardene; nicardipine; 55985-32-5; Nicardipinum; Nicardipino; Perpidine; Nicardipinum [INN-Latin]; Nicardipino [INN-Spanish]; Nicardipine (stn);Antagonil
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0854 mL | 10.4269 mL | 20.8538 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4171 mL | 2.0854 mL | 4.1708 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2085 mL | 1.0427 mL | 2.0854 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。